Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Labangon Elementary School Diagnostic Test in Science-6
Uploaded by
JulianFlorenzFalcone0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views2 pagesThis document appears to be a diagnostic test in science for 6th grade students at Labangon Elementary School for the 2020-2021 school year. It consists of 40 multiple choice questions testing students' knowledge of various science topics including mixtures and solutions, physical and chemical changes, the human body systems, forces and motion, earth science concepts like earthquakes, and weather and climate with a focus on the Philippines. The test covers a wide range of middle school science curriculum.
Original Description:
PUPILSCIENCE-DIAGNOSTIC-TEST-
Original Title
PUPILSCIENCE-DIAGNOSTIC-TEST-
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document appears to be a diagnostic test in science for 6th grade students at Labangon Elementary School for the 2020-2021 school year. It consists of 40 multiple choice questions testing students' knowledge of various science topics including mixtures and solutions, physical and chemical changes, the human body systems, forces and motion, earth science concepts like earthquakes, and weather and climate with a focus on the Philippines. The test covers a wide range of middle school science curriculum.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views2 pagesLabangon Elementary School Diagnostic Test in Science-6
Uploaded by
JulianFlorenzFalconeThis document appears to be a diagnostic test in science for 6th grade students at Labangon Elementary School for the 2020-2021 school year. It consists of 40 multiple choice questions testing students' knowledge of various science topics including mixtures and solutions, physical and chemical changes, the human body systems, forces and motion, earth science concepts like earthquakes, and weather and climate with a focus on the Philippines. The test covers a wide range of middle school science curriculum.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Labangon Elementary School
Diagnostic Test in Science-6
S.Y. 2020-2021
Name__________________________________ Grade and Sec. _______________ Date __________
Direction: Read and understand each question. Write the letter of the correct answer.
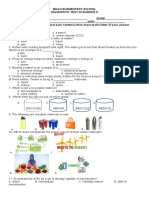
1. What do you call the scattering of light in colloid?
A. Brownian Movement B. Coagulation C. Electrolysis D. Tyndall effect
2. Which mixtures will require the use of the filtration method?
A. Juice C. calamansi juice with seed
B. Oil and water D. separating the good mongo seeds from the bad seeds
3. What type of colloid is Margarine?
A. Sol B. foam C. aerosol D. emulsion
4. Which of the following environmental problems can be separated by physical manipulations?
A. Smog B. oil spill C. flood water D. garbage in the landfill
5. You want to prepare a lemonade. Which amount of sugar dissolves fastest in a glass of hot water?
A. ½ teaspoon B. 1 teaspoon C. ¼ teaspoon D. ¾ teaspoon
6. What benefits can we get from segregation of garbage?
A. More garbage will be accumulated.
B. The surroundings will be free from pollutants.
C. Garbage collected become breeding places of pests.
D. It causes the overgrowth of algae in the bodies of water.
7. Your sister is catching a cold, but your other is not around. You don’t know what medicine is the best
for cough. You see a Kalabo in your garden you know it is good medicine for the cough. What is the
best way to extract its juice?
A. Heat the leaves with water C. Perform the physical manipulation
B. Filter the leaves of Kalabo D. Use a magnet to separate the juice
8. Which of the following is an example of a sol?
A. Milk B. froth C. paint D. whipped cream
9. How could you differentiate a colloid mixture from solution? Colloid particles are _________.
A. Larger B. smaller C. the same D. scattered
10. How does temperature affect the ability of solute? Solubility ________.
A. is not affected by temperature
B. decrease with an increase temperature
C. increase with an increase in temperature
D. decrease with a decrease of temperature
11. What happens to the muscles when they are not often used? They become ________.
A. big C. toned
B. strong D. weak
12. How do muscles work?
A. If one muscle contracts, the opposite relaxes
B. Smooth muscles move when you walk.
C. The biceps pull the bones of your chest
D. Cardiac muscles make your arm muscles move.
13. Which muscle moves rhythmically, contract and relax alternately?
A. Cardiac muscle C. Skeletal muscle
B. Smooth muscle D. Muscular dystrophy
14. Why do bones move in different ways?
A. Cartilage is present in the bones.
B. The bones are connected by joints.
C. The backbone is able to twist and bend.
D. The ligaments pull the bones in various directions.
15. Which of the following is the function of the Skeletal System?
A. It protects the internal organs.
B. It controls all bodily activities.
C. It eliminates undigested foods.
D. It pumps blood to the different parts of the body.
16. Which part of the muscular system enables movement of your arm through the contraction and relaxation
of muscles?
A. biceps and triceps B. facial muscles C. plexus D. tibialis
17. Why is nervous system important? It helps _________.
A. protect our bones C. nourish our excretory system
B. keep us away from diseases D. gather information about the things around us
18. If there were no bones, the muscles around drop to the ground. Which function of the bone is shown here?
A. Protect heart and lungs. C. Form a strong care for delicate organ.
B. Provide framework of the body D. Hold the weight of the body
19. Which is the outermost layer of the skin?
A. dermis B. epidermis C. glands D. subcutaneous layer
20. Which is a major function of the integumentary system?
A. distribution of nutrients C. inhalation and exhalation
B. digestion of food taken D. protection of the internal body system
21. Which of the following statement is TRUE about friction? Friction ________.
A. does not affect objects in motion
B. slows down or stops objects in motion
C. primarily affects objects that contain iron
D. pulls objects toward the center of the Earth
22. The following are the examples of fiction as a helpful force, except one. Using a _______.
A. scrub brush to wash dishes
B. cloth to clean a pair of glasses
C. marker to draw a picture on paper
D. your hand to wave hello to a friend
23. What type of friction is making it hard for the boy to move a box?
A. Fluid friction B. Rolling friction C. Sliding friction D. Static friction
24. A type of friction where a swimmer has to work really hard to overcome this. _____ friction.
A. Fluid B. Rolling C. Static D. Sliding
25. This type of friction works against gravity to keep the parachute floating through the air. ____ friction
A. Fluid B. Rolling C. Static D. Sliding
26. What is the force acting between any two objects in the known universe all the time?
A. Normal force C. Gravitational force
B. Formal force D. Electromagnetic force
27. If a feather and a human are dropped at the same time on the room, where there is no atmosphere,
which one will hit the ground first?
A. Neither, there is no gravity on the room.
B. The feather because it has less mass.
C. Human because it has more mass.
D. Both all hit at the same time.
28. Why is the heavier object harder to accelerate? Because it has _______.
A. more mass C. both the same time
B. less mass D. negative and positive mass
29. Why would a cart start moving faster as you gave it a hard push than if you gave it a light push?
Because you __________ .
A. put more force on it C. put even force till the end
B. less force at the first D. everything in the world start with force
30. Johnny loves to swim on the swimming pool. How do Johnny moves forward in the water as he swim?
A. Swimmer will float because it has a lighter weight.
B. Hands of swimmer push against water, while water pushes against hand.
C. Johnny uses flippers to make it move faster.
D. Everything that float will move fast on top of the water.
31. How does earthquake occur? Earthquake occurs due to _________
A. loose rocks falling from mountainside.
B. movements of rocks along the fault.
C. crustal plates float over asthenosphere
D. earth crust has changeable temperature
32. What are changes caused by an earthquake?
A. Change in landforms
B. Occurrence of seasons
C. Movements of the mantle
D. Warm weather throughout the year
33. What precautionary measures should be done before an earthquake?
A. Stay under hard table
B. Avoid rushing to the exit
C. Perform an earthquake drill
D. Avoid touching live electrical wires
34. What should you do during an earthquake?
A. keep calm C. listen to the radio
B. store food and water D. store flammable materials in safe place
35. What precautionary measures should be done after an earthquake?
A. listen to the latest broadcast C. go back immediately to your home
B. prepare an evacuation plan and foods D. seek shelter near the doorway
36. What seasonal wind brings dry cooler air to the Philippines?
A. Trade winds C. Polar easterlies
B. Northeast monsoon D. Southwest monsoon
37. What are the two seasons in the Philippines?
A. Wet and Dry C. Wet and winter
B. Summer and Winter D. Dry and Cold
38. The children are playing in an open field. The sun always shines during this season and it brings much
heat. Flowers bloom and fiestas in the country are celebrated. What season is described?
A. Dry B. Fall C. Wet D. Winter
39. Which activities can you do during the wet season?
A. planting B. swimming C. drying crops D. going to a picnic
40. What activities can you do during dry seasons?
A. going to picnic C. sliding on the muddy field
B. planting rice D. playing indoor games
You might also like
- Best Trivia Book: A Lot of Random Questions From all Domains, One of The Best Trivia Quiz BookFrom EverandBest Trivia Book: A Lot of Random Questions From all Domains, One of The Best Trivia Quiz BookNo ratings yet
- Pre Test - Science 6Document6 pagesPre Test - Science 6JEFFREY VALLENTE0% (1)
- Diagnostic Science Test ReviewDocument7 pagesDiagnostic Science Test ReviewCzarina PedroNo ratings yet
- Science G 6 DappDocument6 pagesScience G 6 DappChester Austin Reese Maslog Jr.No ratings yet
- Elementary Science Department Pre - Test in Science ViDocument5 pagesElementary Science Department Pre - Test in Science ViHarold ArradazaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test - Science 6Document5 pagesPre-Test - Science 6JANIÑA KHAY MILANo ratings yet
- I. Directions: Read Each Questions or Situations Carefully Encircle The Letter of The Best Answer. Each Erasure Corresponds To Minus 1Document7 pagesI. Directions: Read Each Questions or Situations Carefully Encircle The Letter of The Best Answer. Each Erasure Corresponds To Minus 1JeanRachoPaynandosNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test - Science 6Document7 pagesPre-Test - Science 6Sheryl AvilaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test - Science 6Document6 pagesPre-Test - Science 6Eugene GadeNo ratings yet
- Pre Test Science Grade 6Document3 pagesPre Test Science Grade 6Lorraine CalderonNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test - Science 6Document7 pagesPre-Test - Science 6John Cyrel MondejarNo ratings yet
- Philippines Education Dept Batangas School ExamDocument6 pagesPhilippines Education Dept Batangas School ExamLV BENDANANo ratings yet
- Pre-Test Science 6Document6 pagesPre-Test Science 6Anonymous yIlaBBQQNo ratings yet
- Science 4Document4 pagesScience 4JEFFREY VALLENTENo ratings yet
- Pre-test Science 6Document6 pagesPre-test Science 6Mary Joy De la BandaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in Science Covers Key ConceptsDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Test in Science Covers Key ConceptsDenver TamayoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic TEST SCIENCE 6Document6 pagesDiagnostic TEST SCIENCE 6Mary Ann MahomotNo ratings yet
- Local Media3696114243247248611Document6 pagesLocal Media3696114243247248611Cyrus GerozagaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test Science 6Document7 pagesPre-Test Science 6Joanne Lahip IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test - Science 6Document5 pagesDiagnostic Test - Science 6Sunshine Selosa0% (1)
- Pre-Test in Science 6 I. Directions: Read Each Questions or Situations Carefully. Then Select The Letter of The Best AnswerDocument6 pagesPre-Test in Science 6 I. Directions: Read Each Questions or Situations Carefully. Then Select The Letter of The Best AnswerNora Herrera0% (2)
- Pre-Test in Science 6: Schools Division of CapizDocument7 pagesPre-Test in Science 6: Schools Division of CapizKriselle May DeslateNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test - Science 6Document5 pagesPre-Test - Science 6jerwin remocalNo ratings yet
- Sample TestDocument10 pagesSample TestprecillaugartehalagoNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Diagnostic TestDocument5 pagesScience 6 Diagnostic TestRacquel NerosaNo ratings yet
- Science 5Document4 pagesScience 5JaneDandanNo ratings yet
- Ysabelle ScienceDocument3 pagesYsabelle Scienceysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- Science 4Document3 pagesScience 4Christian GumarangNo ratings yet
- Science Grade Six PretestDocument5 pagesScience Grade Six Pretestcatherine renanteNo ratings yet
- Unit Test in Science Iv 2021-2022 2Document5 pagesUnit Test in Science Iv 2021-2022 2FernandoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test - Science 7Document5 pagesPre-Test - Science 7KIM MARLON GANOBNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Diagnostic-Test SY2022-2023Document9 pagesScience 6 Diagnostic-Test SY2022-2023Joseph PederisoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test - Science 4Document4 pagesPre-Test - Science 4Jonalyn AntonioNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic - Science 4Document4 pagesDiagnostic - Science 4Loralyn Sadiasa CapagueNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test Science 6Document7 pagesPre-Test Science 6RANDY ALVARONo ratings yet
- Diagnostic-Test (Grade7)Document4 pagesDiagnostic-Test (Grade7)Avon Kaye GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- General Instructions and Science Test QuestionsDocument5 pagesGeneral Instructions and Science Test QuestionsMary Rose CalamayanNo ratings yet
- General Science and Biology Reviewer for College StudentsDocument3 pagesGeneral Science and Biology Reviewer for College StudentsRomelyn LaguraNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Gtest - ScienceDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Gtest - ScienceCathy APNo ratings yet
- Science Third Grading ExamDocument3 pagesScience Third Grading Exammaria cristine cabangcalaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test - Science 5Document5 pagesPre-Test - Science 5Eugene GadeNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test ScienceDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test ScienceJey VlackNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in Science Grade Iv School Year 2020-2021: Schools Division Office Quezon CityDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Test in Science Grade Iv School Year 2020-2021: Schools Division Office Quezon Citypido29100% (2)
- Science4 - q3 - Mod4 Properties and Characteristics of Light and Sound - PDFDocument5 pagesScience4 - q3 - Mod4 Properties and Characteristics of Light and Sound - PDFRhodoraCabangalBocalaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Diagnostic TestDocument3 pagesScience 7 Diagnostic TestPangkabuhayan DavaoNo ratings yet
- 4th QUARTER RBT EXAMDocument4 pages4th QUARTER RBT EXAMAZia Cañedo VillNo ratings yet
- LET Module 2 - GENERAL EDUCATION-2Document12 pagesLET Module 2 - GENERAL EDUCATION-2Dada AlconesNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument4 pagesFinal ExamAbegail FajardoNo ratings yet
- DepEd Zambales Grade 6 Science DAT ReviewDocument5 pagesDepEd Zambales Grade 6 Science DAT ReviewMARLYN GAY EPANNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Diagnostic TestDocument6 pagesScience 4 Diagnostic TestMary Ann Mahomot100% (1)
- Third Quarter Examination in Science 6Document4 pagesThird Quarter Examination in Science 6nimfa t. plazaNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Diagnostic TestDocument6 pagesScience 6 Diagnostic TestGuiteb ESNo ratings yet
- Pre Test - Science 5Document4 pagesPre Test - Science 5Queen Ve NusNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test - Science 5Document4 pagesPre-Test - Science 5Vivian FernandezNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in Science V Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer and Write It On Your Answer SheetDocument8 pagesDiagnostic Test in Science V Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer and Write It On Your Answer SheetKristanae ReginioNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic TestpaperDocument10 pagesDiagnostic TestpaperHANNA GALENo ratings yet
- Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer and Write It On Your Answer SheetDocument5 pagesChoose The Letter of The Correct Answer and Write It On Your Answer SheetBhzl Oliveros PacisNo ratings yet
- DS Science5 - 20 21Document6 pagesDS Science5 - 20 21Shiela Mae Talisic PalacioNo ratings yet
- Sheik Mustafa Elementary School Soil TestDocument3 pagesSheik Mustafa Elementary School Soil TestNurhidaya Jaji Bandahala100% (2)
- Earth and Life Science BrochureDocument2 pagesEarth and Life Science BrochureJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Math YyyDocument1 pageMath YyyJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument1 pageScriptJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Playing An Instrument Relieves Stress It Builds Your Confidence Playing Music Is Fun!Document1 pagePlaying An Instrument Relieves Stress It Builds Your Confidence Playing Music Is Fun!JulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- SUBJECTDocument1 pageSUBJECTJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Labangon Elementary School Diagbostic Test in Epp/Tle 6 Directions: Multiple Choice. Choose The Correct The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument4 pagesLabangon Elementary School Diagbostic Test in Epp/Tle 6 Directions: Multiple Choice. Choose The Correct The Letter of The Correct AnswerJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Coe Louiejay S. EspanolaDocument1 pageCoe Louiejay S. EspanolaJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Special Power of AttorneyDocument1 pageSpecial Power of AttorneyJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Facts About The UniverseDocument2 pagesEarth and Life Science: Facts About The UniverseJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Coe Jose Abalo JRDocument1 pageCoe Jose Abalo JRJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Practice ModuleDocument9 pagesLevel 3 Practice ModuleJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Level 4 Practice ModuleDocument8 pagesLevel 4 Practice ModuleJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test in Mathematics 10Document2 pagesMastery Test in Mathematics 10JulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Coe Benjie CanqueDocument1 pageCoe Benjie CanqueJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Coe Louiejay S. EspanolaDocument1 pageCoe Louiejay S. EspanolaJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Coe Louiejay S. EspanolaDocument1 pageCoe Louiejay S. EspanolaJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Coe Antonio U. CapablancaDocument1 pageCoe Antonio U. CapablancaJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Epicenter Lab HW1Document6 pagesEpicenter Lab HW1johnygaddar0% (1)
- Cover Letter For Covid CebuDocument1 pageCover Letter For Covid CebuJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Math 10Document4 pages8.2 Math 10JulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Coe Rolly LapitanDocument1 pageCoe Rolly LapitanJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- 1 Is CompleteDocument93 pages1 Is CompleteJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Logoloyaltycard 2Document1 pageLogoloyaltycard 2JulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument1 pageDownloadJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- How computer networks workDocument14 pagesHow computer networks workJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Grade 10Document1 pageGrade 10JulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Paper Sizes Do Not DeleteDocument1 pagePaper Sizes Do Not DeleteJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- 1 Is CompleteDocument93 pages1 Is CompleteJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Dressmaking G9 3RD Quarter Pre Post TestDocument3 pagesDressmaking G9 3RD Quarter Pre Post TestJulianFlorenzFalcone71% (17)
- Bio3 2Document11 pagesBio3 2HarmonyChuiNo ratings yet
- Runkeeper Fitness Class Training GuideDocument41 pagesRunkeeper Fitness Class Training GuideWooNo ratings yet
- Muscles and Movements: Types of Muscles Structure of Skeletal MusclesDocument16 pagesMuscles and Movements: Types of Muscles Structure of Skeletal MusclesMahin FatimaNo ratings yet
- Moxy HIT GuideDocument18 pagesMoxy HIT GuideLukasNo ratings yet
- Running NutritionDocument42 pagesRunning NutritionAlejandro JustoNo ratings yet
- Trap 3 RaiseDocument3 pagesTrap 3 RaiseQuốc HuyNo ratings yet
- Survey A&P Lab 1 GuideDocument7 pagesSurvey A&P Lab 1 Guidegabriella IrbyNo ratings yet
- Energetic Kinesiology22Document1 pageEnergetic Kinesiology22Marius Dan GiolgauNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY DOUBTS PART 1 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERSDocument22 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY DOUBTS PART 1 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERSDivyaNo ratings yet
- 1 A 1 and 2 Only (1) (1) : Topic 6: Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics Chapter 6C: Decomposition and ForensicsDocument3 pages1 A 1 and 2 Only (1) (1) : Topic 6: Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics Chapter 6C: Decomposition and ForensicssalmaNo ratings yet
- The Cthulhu Hack From Unformed Realms v1 ReadingDocument19 pagesThe Cthulhu Hack From Unformed Realms v1 Readingniklim360No ratings yet
- Marathon Training BrochureDocument16 pagesMarathon Training BrochurebrainiousNo ratings yet
- Marieb Human Anatomy Course Materials OutlineDocument1 pageMarieb Human Anatomy Course Materials OutlineArianne KimNo ratings yet
- Federal Bureau of Investigation: Physical Fitness Test (PFT) ProtocolDocument10 pagesFederal Bureau of Investigation: Physical Fitness Test (PFT) ProtocolKOLD News 13No ratings yet
- Par QDocument5 pagesPar QJomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 1 - Week 1-3Document2 pagesSummative Test 1 - Week 1-3Ginevieve GibertasNo ratings yet
- The LIONESS MACRO CALCULATORDocument60 pagesThe LIONESS MACRO CALCULATORAlicia BNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness and Wellness GuideDocument7 pagesPhysical Fitness and Wellness GuideALlan ABiangNo ratings yet
- Open-CSAM, A New Tool For Semi-Automated Analysis of Myofiber Cross - Sectional Area in Regenerating Adult Skeletal MuscleDocument12 pagesOpen-CSAM, A New Tool For Semi-Automated Analysis of Myofiber Cross - Sectional Area in Regenerating Adult Skeletal MuscleJessicaNo ratings yet
- The Collected Papers of Irvin M. Korr Vol. IDocument257 pagesThe Collected Papers of Irvin M. Korr Vol. IGaël Dans100% (9)
- Mennohenselmans Com Why Women Should Not Train Like MenDocument9 pagesMennohenselmans Com Why Women Should Not Train Like MenTheBulgarianWolfNo ratings yet
- Greater Electromyographic Responses Do Not Imply.31 PDFDocument4 pagesGreater Electromyographic Responses Do Not Imply.31 PDFAgustin LopezNo ratings yet
- Performance Matrix of Strength and ConditioningDocument8 pagesPerformance Matrix of Strength and ConditioningBen WatNo ratings yet
- Health Optimizing Physical Education 1: Quarters 1 and 2 - Module 1: The Healthiest and Fittest MEDocument30 pagesHealth Optimizing Physical Education 1: Quarters 1 and 2 - Module 1: The Healthiest and Fittest MEJanix Magbanua100% (3)
- Making Music - A Real Pain in The NeckDocument10 pagesMaking Music - A Real Pain in The NeckTony LeeNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 (Muscular) - ALSDocument5 pagesCase Study 1 (Muscular) - ALSSamantha AquinoNo ratings yet
- Plant & Animal TissueDocument39 pagesPlant & Animal TissuePrincess Erbie Austria100% (1)
- Comprehensive Strength and ConditioningDocument9 pagesComprehensive Strength and ConditioningJohnette Abreu LautiNo ratings yet
- Mapeh ReviewDocument2 pagesMapeh ReviewroseNo ratings yet
- Muscle Media June15Document40 pagesMuscle Media June15Noel Antonio Tremaria Iniesta100% (1)
- Aging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayFrom EverandAging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayNo ratings yet
- Chair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouFrom EverandChair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- Power of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionFrom EverandPower of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (11)
- Chakras and Yoga: Finding Inner Harmony Through Practice, Awaken the Energy Centers for Optimal Physical and Spiritual Health.From EverandChakras and Yoga: Finding Inner Harmony Through Practice, Awaken the Energy Centers for Optimal Physical and Spiritual Health.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Boundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingFrom EverandBoundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (66)
- Strong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerFrom EverandStrong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Peak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsFrom EverandPeak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (95)
- Relentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableFrom EverandRelentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (781)
- Weight Lifting Is a Waste of Time: So Is Cardio, and There’s a Better Way to Have the Body You WantFrom EverandWeight Lifting Is a Waste of Time: So Is Cardio, and There’s a Better Way to Have the Body You WantRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (38)
- Functional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindFrom EverandFunctional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1)
- Whole Body Barefoot: Transitioning Well to Minimal FootwearFrom EverandWhole Body Barefoot: Transitioning Well to Minimal FootwearRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- Endure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human PerformanceFrom EverandEndure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human PerformanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (237)
- Muscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!From EverandMuscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- Body by Science: A Research Based Program for Strength Training, Body building, and Complete Fitness in 12 Minutes a WeekFrom EverandBody by Science: A Research Based Program for Strength Training, Body building, and Complete Fitness in 12 Minutes a WeekRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (84)
- Music For Healing: With Nature Sounds For Natural Healing Powers: Sounds Of Nature, Deep Sleep Music, Meditation, Relaxation, Healing MusicFrom EverandMusic For Healing: With Nature Sounds For Natural Healing Powers: Sounds Of Nature, Deep Sleep Music, Meditation, Relaxation, Healing MusicRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessFrom EverandThe Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (104)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Applied Polyvagal Theory in Yoga: Therapeutic Practices for Emotional HealthFrom EverandApplied Polyvagal Theory in Yoga: Therapeutic Practices for Emotional HealthNo ratings yet
- The Calisthenics Codex: Fifty Exercises for Functional FitnessFrom EverandThe Calisthenics Codex: Fifty Exercises for Functional FitnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Deezify's Epic Workout Handbook: An Illustrated Guide to Getting SwoleFrom EverandDeezify's Epic Workout Handbook: An Illustrated Guide to Getting SwoleRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Body by Science: A Research Based Program to Get the Results You Want in 12 Minutes a WeekFrom EverandBody by Science: A Research Based Program to Get the Results You Want in 12 Minutes a WeekRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (38)
- The Seven Spiritual Laws of Yoga: A Practical Guide to Healing Body, Mind, and SpiritFrom EverandThe Seven Spiritual Laws of Yoga: A Practical Guide to Healing Body, Mind, and SpiritRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (73)
- Yamas & Niyamas: Exploring Yoga's Ethical PracticeFrom EverandYamas & Niyamas: Exploring Yoga's Ethical PracticeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- 7 Weeks to 10 Pounds of Muscle: The Complete Day-by-Day Program to Pack on Lean, Healthy Muscle MassFrom Everand7 Weeks to 10 Pounds of Muscle: The Complete Day-by-Day Program to Pack on Lean, Healthy Muscle MassRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (132)
- Hero Maker: 12 Weeks to Superhero Fit: A Hollywood Trainer's REAL Guide to Getting the Body You've Always WantedFrom EverandHero Maker: 12 Weeks to Superhero Fit: A Hollywood Trainer's REAL Guide to Getting the Body You've Always WantedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)