Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maximum Price or Price Ceiling
Uploaded by
HidayahJohariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maximum Price or Price Ceiling
Uploaded by
HidayahJohariCopyright:
Available Formats
1) Maximum Price or price ceiling
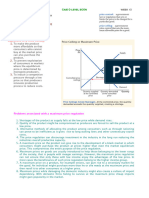
Maximum price refers to the limit on the price charged for a product. Maximum price, also known as
price ceiling, is set by government below the market price, as illustrated. When government imposes
a maximum price, or price ceiling at Rm 2, which is below the market equilibrium price of RM 5, the
quantity demanded is 110 units of good Y while the quantity supplied is only 50 units.
The government imposes a price ceiling to protect customers from circumstances that could
make the necessary goods uttainnable. The objective of a maximum price is to protect consumer’s
interests. This kind of policy, in most cases is used to curb of the cost of essential goods and
commodities such as food medicines and so on.
The equilibrium price is Pe. A maximum price leads to demand of QD, but a fall in supply to QS.
Advantages
1. Help prevent suppliers from engaging in price gouging, or charging outrageously high prices
for limited goods
2. Keeping the cost of living affordable during periods of high inflation
Consequences
1.Shortage-Suppliers are no longer eligible to charge as they did before so some suppliers will frop
out of the market. Consumers find they can nnow buy the product at a lower price, so quantity
demanded will increase.
2.Black market.
-If consumers are unable to obtain the needed goods because a price ceiling reduces the quantity
they may turn to the black market. The black market price is hiher than the free market because the
quantity is less than in afree market transaction, where more sellers could afford to sell the product.
3.Reduce the quantity produce.
-The imposition of maximum price will reduce the quantity produced of an already scarce
commodity.
2) Minimum Price or price floor
Minimum price refers to the limit set on the price charged for a product. Minimum price is also
known as price floor, which is set by government above the market price, as illustrated.The
government imposes a price floor to protect producers. It ensures taht prices stay high so taht
production can be continued.
The equilibrium price is Pe. A minimum price leads to increase in supply to QS, but fall in demand to
QD.
Consequences
1. Surplus
-COnsumers find they mst pay a higher price for the same product. As a result, they reduce their
purchases or drop out of the market. The suppliers have a higher price than they weere charging
before. They will increase production. This situation will result in supply exceeding demand, which
causes a surplus.
2. To protect producers income
-Imposition of a minimum price protects the producers incomes, for example, agriculture producers
usually or always face an uncertain climate for the production of agriculture goods. Minimum price
would ensure taht producers incomes wil be protected.
3. Consumers need to pay more to get a product
-Consequently, it is nit fair to consumers because they need to pay more for the same products.
You might also like
- Lecture 2 Price TheoryDocument6 pagesLecture 2 Price Theorykizito thomasmoreNo ratings yet
- Gov Int in Markets 2Document2 pagesGov Int in Markets 2Tanshit SarmadiNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - The Market System: Market Economy - Interaction Between Supply and Demand Determines What IsDocument21 pagesCH 3 - The Market System: Market Economy - Interaction Between Supply and Demand Determines What Isamer328No ratings yet
- Difference Between Stock and Supply:-: Is WillingDocument13 pagesDifference Between Stock and Supply:-: Is WillingMustafa ShaikhNo ratings yet
- ECO162 - Market Equilibrium and Government InterventionDocument41 pagesECO162 - Market Equilibrium and Government InterventionPixie Hollow100% (1)
- Price Stability Definition:: ImportanceDocument3 pagesPrice Stability Definition:: ImportanceMadhu khanNo ratings yet
- Government InterventionDocument8 pagesGovernment Interventionjamilhasan8No ratings yet
- Economics1 Micro and Macro Theory and ApplicationDocument12 pagesEconomics1 Micro and Macro Theory and ApplicationEi Hnin ChoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument62 pagesUntitledKAJJUBI VINCENTNo ratings yet
- Wk10 11 - Basic MicroeconomicsDocument10 pagesWk10 11 - Basic MicroeconomicsWhats PoppinNo ratings yet
- Market EquilibriumDocument7 pagesMarket Equilibriumunicornsarecoolasice100% (2)
- Answer-Assignment - DMBA105 - MBA1 2 - Set-1 and 2 - Sep - 2023Document11 pagesAnswer-Assignment - DMBA105 - MBA1 2 - Set-1 and 2 - Sep - 2023Sabari NathanNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Objectives (Of The Lesson)Document4 pagesActivity 1: Objectives (Of The Lesson)Grim Creeper900No ratings yet
- SUPPLYDocument5 pagesSUPPLYNeha RoyNo ratings yet
- Economics Price Theory s5Document104 pagesEconomics Price Theory s5Creative MindNo ratings yet
- Sample Policy AnswerDocument2 pagesSample Policy Answermeena malikNo ratings yet
- Economic Report Price Celing Price FloorDocument15 pagesEconomic Report Price Celing Price Floor2023-25 SOURABH PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Economic Report (Price Celing & Price Floor)Document15 pagesEconomic Report (Price Celing & Price Floor)Amit BeheraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13 - Econ 2 (Abegail Blanco Mm2-I)Document14 pagesLesson 13 - Econ 2 (Abegail Blanco Mm2-I)Abegail BlancoNo ratings yet
- Main Features of Perfect CompetitionDocument6 pagesMain Features of Perfect CompetitionStorm BreakerNo ratings yet
- SwebeDocument3 pagesSwebeJuma SimbanoNo ratings yet
- Economics Lesson 14-Measuring InflationDocument26 pagesEconomics Lesson 14-Measuring InflationBecky GalanoNo ratings yet
- Importance of PEDDocument6 pagesImportance of PEDDylan ChiparaNo ratings yet
- Economics Project (Applications)Document12 pagesEconomics Project (Applications)sweetieNo ratings yet
- Pricing TheoryDocument12 pagesPricing TheoryZubair Hussain AdeshinaNo ratings yet
- Market Structure and PricingDocument5 pagesMarket Structure and PricingAbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Examples of Maximum PricesDocument3 pagesExamples of Maximum Pricesdoudou liuNo ratings yet
- How Is The Government Going To Control PricesDocument4 pagesHow Is The Government Going To Control PricesFakhrulrazi IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Question 22Document3 pagesQuestion 22Bali AngyanNo ratings yet
- Pricing MethodsDocument4 pagesPricing Methodssatya narayanaNo ratings yet
- SUPPLY Bba NotesDocument9 pagesSUPPLY Bba NotesAbhiNo ratings yet
- Price and IncomeDocument7 pagesPrice and IncomeNishant JainNo ratings yet
- Price FloorDocument6 pagesPrice FloorUgly DucklingNo ratings yet
- Indirect Taxes: (Diagram On Page 73-74)Document5 pagesIndirect Taxes: (Diagram On Page 73-74)suryanshranaNo ratings yet
- Auctioning/bidding. Your Parents/guardians Could Have Bought An Item ThroughDocument18 pagesAuctioning/bidding. Your Parents/guardians Could Have Bought An Item ThroughobilakolmuzamilNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic Competition, Oligopoly, and Pure MonopolyDocument5 pagesMonopolistic Competition, Oligopoly, and Pure MonopolyImran SiddNo ratings yet
- Soci PTDocument8 pagesSoci PTquentutraNo ratings yet
- Inflation Hand-OutDocument4 pagesInflation Hand-OutTashaneNo ratings yet
- Economics Summary Sheet Part 2Document6 pagesEconomics Summary Sheet Part 2SidNo ratings yet
- Pricing Decisions Policies & PracticesDocument7 pagesPricing Decisions Policies & PracticesHarty Robert0% (1)
- S.5 Price Theory EconomicsnotesDocument100 pagesS.5 Price Theory EconomicsnotesJohnson NjasotehNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Saq 3 LatestDocument3 pagesJawapan Saq 3 LatestAre HidayuNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document15 pagesModule 3vaseem aktharcpNo ratings yet
- Ba-Eco101 Basic MicroeconomicsDocument4 pagesBa-Eco101 Basic MicroeconomicsJohn Lloyd GregorioNo ratings yet
- S - T Chronicle IAS (Shashidthakur23.Wordpress - Com)Document66 pagesS - T Chronicle IAS (Shashidthakur23.Wordpress - Com)krishanNo ratings yet
- Price ControlsDocument2 pagesPrice ControlsapeapesajeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Key TermsDocument3 pagesChapter 6 Key TermsEvan CrewsNo ratings yet
- Dmba105 - Managerial EconomicsDocument12 pagesDmba105 - Managerial EconomicsMuhammed AdnanNo ratings yet
- Mba 0042Document4 pagesMba 0042Ashish YadavNo ratings yet
- Task 10+11Document5 pagesTask 10+11bendermacherrickNo ratings yet
- Price Ceiling and FloorDocument2 pagesPrice Ceiling and Floorraquel mNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Economics RevisionDocument51 pagesIGCSE Economics Revisionkiritnarain67% (9)
- MB0042 Managerial Economics Assig Set-1Document8 pagesMB0042 Managerial Economics Assig Set-1Sushanth PerambraNo ratings yet
- Key Points:: Case Study: Rent Control in The Short Run and The Long RunDocument2 pagesKey Points:: Case Study: Rent Control in The Short Run and The Long Runnasper34No ratings yet
- ACC08/FMS01 Lectures: Economic Foundation of Financial ManagementDocument15 pagesACC08/FMS01 Lectures: Economic Foundation of Financial ManagementmiolataNo ratings yet
- Module 3 The Law of Demand and Supply and Market EquilibriumDocument68 pagesModule 3 The Law of Demand and Supply and Market EquilibriumAlvin OroscoNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document2 pagesModule 2MGNo ratings yet
- Importance of Ed in Managerial Decision MakingDocument10 pagesImportance of Ed in Managerial Decision MakingVijay Singh Kumar Vijay100% (1)
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Negatives Impact of Migrant Remittance Towards Economy in MalaysiaDocument7 pagesNegatives Impact of Migrant Remittance Towards Economy in MalaysiaHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in LedgerDocument2 pagesWorksheet in LedgerHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Sta AssignmentDocument6 pagesSta AssignmentHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Data Validation in Excel Name Employee No. Salary Salary Bonus Date of Entry DepartmentDocument2 pagesData Validation in Excel Name Employee No. Salary Salary Bonus Date of Entry DepartmentHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Synopsis JapanDocument1 pageSynopsis JapanHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2Document4 pagesCase Study 2HidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Provides The Sense of TogethernessDocument2 pagesProvides The Sense of TogethernessHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- 4251 11271 1 SMDocument12 pages4251 11271 1 SMHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Budget + ProgramDocument4 pagesBudget + ProgramHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Property Tax Management Model of Local Authorities in MalaysiaDocument12 pagesProperty Tax Management Model of Local Authorities in MalaysiaHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Economy Slide LatestDocument2 pagesEconomy Slide LatestHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- References: Crossroads, Given EU Resolution To Ban Palm Oil in Biofuels by 2020? Retrieved From GlobalDocument1 pageReferences: Crossroads, Given EU Resolution To Ban Palm Oil in Biofuels by 2020? Retrieved From GlobalHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument1 pageExecutive SummaryHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Appendices (Ent530)Document6 pagesAppendices (Ent530)HidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in LedgerDocument2 pagesWorksheet in LedgerHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PPDocument1 pageTutorial PPHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Method and ConclusionDocument2 pagesMethod and ConclusionHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- ELC550Document1 pageELC550HidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- The Phenomenon of International Conflict in International RelationsDocument15 pagesThe Phenomenon of International Conflict in International RelationsHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Background of Nokia CompanyDocument2 pagesBackground of Nokia CompanyHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Property Tax Management Model of Local Authorities in MalaysiaDocument12 pagesProperty Tax Management Model of Local Authorities in MalaysiaHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Question 1: Describe What Management Can Do To Create A Safe Work EnvironmentDocument2 pagesQuestion 1: Describe What Management Can Do To Create A Safe Work EnvironmentHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Tuto Exercise (KM)Document1 pageTuto Exercise (KM)HidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Tutorial HR (ADM551)Document4 pagesTutorial HR (ADM551)HidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Explain Types and Segment of Actors in International Relations?Document1 pageExplain Types and Segment of Actors in International Relations?HidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- List Problems of Traditional File Environment and Explain TWO of ThemDocument4 pagesList Problems of Traditional File Environment and Explain TWO of ThemHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Explain Types and Segment of Actors in International Relations?Document1 pageExplain Types and Segment of Actors in International Relations?HidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise Applications Activity: Self Learning TemplateDocument5 pagesChapter 9 - Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise Applications Activity: Self Learning TemplateHidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Noor Amirah Binti Kamaruddin AM1104F 2016559275Document2 pagesNoor Amirah Binti Kamaruddin AM1104F 2016559275HidayahJohariNo ratings yet
- Original For Recipient: Order Number: RDF15750659Document2 pagesOriginal For Recipient: Order Number: RDF15750659Rajat DawraNo ratings yet
- James Rafferty.2024.Q1.L6.How Long Will You Judge UnjustlyDocument7 pagesJames Rafferty.2024.Q1.L6.How Long Will You Judge UnjustlyLaurent DecouvrirDieuNo ratings yet
- System of Particles and Rotational MotionDocument53 pagesSystem of Particles and Rotational MotionANshul Sharma50% (16)
- Sale Deed 1Document4 pagesSale Deed 1Tanvir AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Book 1 DOTDocument9 pagesBook 1 DOTMark RanggasNo ratings yet
- PD 1144Document7 pagesPD 1144Dinnah Mae AlconeraNo ratings yet
- CHENG V GENATODocument2 pagesCHENG V GENATOLaurena ReblandoNo ratings yet
- Injunction Example Essay ResponseDocument9 pagesInjunction Example Essay ResponseRonald AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Henry SingletonDocument11 pagesHenry Singletonapi-260143426No ratings yet
- Tax Invoice: Warranty Expired:NDocument3 pagesTax Invoice: Warranty Expired:NSanjay PatelNo ratings yet
- FIP501 Foundational Financial Planning and Financial Management Course Addendum - September 2020Document8 pagesFIP501 Foundational Financial Planning and Financial Management Course Addendum - September 2020rimi2215_382182883No ratings yet
- Schedule of Social Security Benefit Payments 2019: Socialsecurity - GovDocument1 pageSchedule of Social Security Benefit Payments 2019: Socialsecurity - GovBejan OvidiuNo ratings yet
- Drafting Project SynopsisDocument5 pagesDrafting Project SynopsisbhanwatiNo ratings yet
- Binary Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument4 pagesBinary Vapor Liquid EquilibriumFarid DarwishNo ratings yet
- AB-518b Quality Manual and Audit ChecklistDocument24 pagesAB-518b Quality Manual and Audit ChecklistStan Lee PaulsonNo ratings yet
- 4.2 F6 Cap AllowsDocument21 pages4.2 F6 Cap AllowsAnas KhalilNo ratings yet
- Arguments For The Ban LajjaDocument3 pagesArguments For The Ban Lajjapizzabythebay kNo ratings yet
- Noli Me Tangere & El FilibusterismoDocument3 pagesNoli Me Tangere & El FilibusterismoMaria Alyana VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Abubakar - Islam in The PhilippinesDocument19 pagesAbubakar - Islam in The PhilippinesJennica A.No ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Reading OrganizerDocument3 pagesChapter 18 Reading OrganizerAnna SongNo ratings yet
- Cailles vs. BonifacioDocument2 pagesCailles vs. BonifacioLAIZA TRISHA M MONTALLANo ratings yet
- Direct LaborDocument8 pagesDirect LaborAreli DuyoNo ratings yet
- SCL Delay and Disruption Protocol - Rider 1 - FINALDocument18 pagesSCL Delay and Disruption Protocol - Rider 1 - FINALTanveerAhmed NiaziNo ratings yet
- Nse4 Infraestructura 351-387Document37 pagesNse4 Infraestructura 351-387leydis GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Modern Prince: A Review of The Prince and On Machiavellianism of TodayDocument7 pagesThe Modern Prince: A Review of The Prince and On Machiavellianism of TodayRafael Kieran MondayNo ratings yet
- Education - Justice and DemocracyDocument37 pagesEducation - Justice and DemocracyRicardo Torres RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Motion To Dismiss Petition For ReviewDocument5 pagesMotion To Dismiss Petition For ReviewOzkar KalashnikovNo ratings yet
- Rules of Court - New Rule On AdoptionDocument11 pagesRules of Court - New Rule On AdoptionChristian Marko CabahugNo ratings yet
- Prof DR Ismail Omar Uthm: Rentice For TNBDocument16 pagesProf DR Ismail Omar Uthm: Rentice For TNBmadzrulNo ratings yet
- Decide Which Answer (A, B, C or D) Best Fits Each Space.: Inspector Crumbs InvestigatesDocument2 pagesDecide Which Answer (A, B, C or D) Best Fits Each Space.: Inspector Crumbs InvestigatesХристина КоникNo ratings yet