Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer History Timeline
Uploaded by
Eneyda Quintero0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views3 pagesComputer History Timeline
Uploaded by
Eneyda QuinteroCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
1.
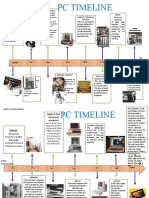
Computer History Timeline Computer Generations MHS-TH-28
2. *Table of Contents* Slide 5: Picture of first generation computer Slide 6: What
are first generation computers Slide 7: Picture of Cathode Ray Tube Slide 8: What is
a Cathode Ray Tube Slide 9: Picture of Selective Sequence Calculator Slide10: What
is a selective sequence calculator Slide11: picture of second generation technology
Slide12: What is second generation technology Slide13: Picture of AT&T’s data
phone Slide14: What is AT&T’s data phone Slide15:Picture of First industrial Robot
3. *Table of Contents* Slide 16: What is the First industrial Robot Slide 17: Picture
of Third Generation Technology Slide18: What are Third Generation Computer
Slide19: Picture of HP-2115 Slide 20: What is the HP-2115 Slide 21: Picture of The
Stanford Arm Slide 22:What is the Stanford Arm Slide 23:Picture of fourth
generation computers Slide 24: What are fourth generation computers
4. *Table of Contents* Slide25: The first e-mail Slide26: How the first e-mail
happened Slide27: Picture of Pixar Slide28: What is Pixar Slide29: Picture Of fifth
generation technology Slide30: What is fifth generation technology Slide31: Picture
of Voice Recognition Slide32:What is voice recognition Slide33: Picture of Future
Changes Slide34: What are the plans of the future
5. 1st generation 1946-1958 http://members.iinet.net.au/~dgreen/.com Table of
Contents
6. 1st Generation-Vacuum tubes • Used circuitry and magnetic drums for
memory. • Were enormous and very expensive. • Relied on machine language. •
Used the lowest-level programming language. • Solved one problem at a time. •
Generated a lot of heat causing malfunctions. Table of Contents
7. Cathode Ray Tube 1946-1958 Table of contents
8. 1947 • Introduced Williams tube, Cathode ray tube. • Painted dots and dashes
of phosphorescent. • Used as memory for vacuum tube machines. Table of
Contents
9. Selective Sequence Electronic Calculator 1946-1958
http://ei.cs.vt.edu/~history/50th/ABC.jpg Table of Contents
10. 1948 • IBM’S selective sequence electronic calculator • Produced 50
multiplications per second. Table of Contents
11. 2nd Generation 1959-1964 Table of Contents
12. 2nd Generation- Transistors • Transistors replaced vacuum tubes • Ushered in
the second generation of computers. • Computers became cheaper and more
energy-efficient. • Computers still generated a great amount of heat. Table of
Contents
13. AT&T’S Data Phone 1959-1964
http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/images/1960_data.jpg Table of Contents
14. 1960 • At&t designed its data phone. • Converts digital computer data to analog
signals. • Transmitted signals across its long distance network Table of Contents
15. First industrial robot at General Motors 1959-1964 http://robotics-
tamucc.com/images/GM.jpg Table of Contents
16. 1961 • First industrial robot works at general motors. • Obeying step-by-step
commands. • Commands stored on a magnetic drum. • It stacked hot pieces of die
cast metal Table of Contents
17. 3rd Generation 1965-1970 http://georgeboole.net/graphics/stuff/system
%20360.jpg Table of Contents
18. 3rd generation- integrated circuits • Integrated circuits brought fourth the
3rd generation. • Transistors were miniaturized and placed on chips. • Increased the
speed and efficiency of computers. • Different applications could be ran
simultaneously. Table of contents
19. HP-2115 1965-1970 Table of contents
20. 1966 • Hewlett Packard entered general purpose computer business. • Entered
with its HP-2115 for computation. • Power formerly founded in only larger
companies. Table of Contents
21. Stanford Arm 1965-1970
http://infolab.stanford.edu/pub/voy/museum/pictures/display/robots/StanfordArm.j
pg Table of Contents
22. 1969 • Invented by Victor Scheinman. • First successful electrical, computer
controlled robot arm. • Assembled ford model water pump by 1974. Table of
contents
23. 4TH Generation 1971 to Present http://nzedge.com/speeches/images/17.jpg
Table of Contents
24. 4th generation-Microprocessors • Microprocessors brought fourth the 4th
generation computers. • Integrated circuits were built on single chip. • Computers
now fit in your hand. • Computers can now be linked together. Table of Contents
25. The first e-mail Computer used to send first e-mail 1971-present
http://img.zdnet.com/techDirectory/_1EMAIL.JPG Table of Contents
26. 1971 • First E-mail was sent by Ray Tomlinson. • Sent while working on other
projects. • Ray also invented the use of “@”. Table of Contents
27. Pixar 1971-present http://www.jimhillmedia.com/mb/images/upload/Pixar-
Animation-Studios-A-w.jpg Table of Contents
28. 1986 • Pixar is founded • Pixar was, ”special effects Computer group”. • Steve
jobs paid10 million for Lucas films. • He later renamed Lucas films Pixar. Table of
Contents
29. 5th generation Present-beyond Table of Contents
30. 5th generation-Artificial Intelligence • Artificial intelligence is still in
development. • Intelligence that responds to natural language. • Capable of learning
and self-organization. Table of Contents
31. Voice recognition Present-beyond
http://www.technoride.com/images/img125371.jpg Table of Contents
32. 2007-2008 • Converts spoken words to machine readable inputs. • Used a lot in
health care. • Wanted to be used in Military weapons. Table of Contents
33. Changes Present-beyond
http://www.dailygalaxy.com/photos/uncategorized/2007/08/30/quantum_computin
g.jpg Table of Contents
34. Beyond • 2015-converse with the average computer. • Future systems will be
able to solve problems. • Computers will be easier to use • Will be more flexible and
easily customized. • Will access intelligence's from anywhere. Back to Beginning of
slide show Table of Contents
You might also like
- Practice: II. Part Choose 7 Sentences and Make Questions in Simple Past TenseDocument1 pagePractice: II. Part Choose 7 Sentences and Make Questions in Simple Past TenseEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- You Go To The Financial Audit: She Nova To Manage The Company The Other Year They Are Going To Make A SpreadsheetDocument1 pageYou Go To The Financial Audit: She Nova To Manage The Company The Other Year They Are Going To Make A SpreadsheetEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- With Regards, - Omayra Guerra 67368151Document1 pageWith Regards, - Omayra Guerra 67368151Eneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Office SituationsDocument8 pagesOffice SituationsEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Analysis I (Eng. 210 A) : Raquelguardia@up - Ac.paDocument2 pagesEnglish Grammar Analysis I (Eng. 210 A) : Raquelguardia@up - Ac.paEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Simple and Compound Subjects and Predicates: Task 3: Sentence Diagraming #1Document2 pagesSimple and Compound Subjects and Predicates: Task 3: Sentence Diagraming #1Eneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- English210 - Task#1 EnviadoDocument2 pagesEnglish210 - Task#1 EnviadoEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Espanol OracionDocument1 pageEspanol OracionEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Rubric ParticipationDocument1 page2.0 Rubric ParticipationEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Punched Cards-Data Storage Hollerith Tabulating Machine Eniac - Electronic ComputerDocument2 pagesPunched Cards-Data Storage Hollerith Tabulating Machine Eniac - Electronic ComputerEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- My Favorite AnimalDocument1 pageMy Favorite AnimalEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet: English 210-A Test 1Document2 pagesAnswer Sheet: English 210-A Test 1Eneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- A Tribe of Baboons - QuinteroEneydaDocument1 pageA Tribe of Baboons - QuinteroEneydaEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Democratic Origins of American LitDocument18 pagesDemocratic Origins of American LitEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- My Comments About ALIKE, A Short VideoDocument2 pagesMy Comments About ALIKE, A Short VideoEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- TranQuangHien-Intern Tester-Enlab SoftwareDocument5 pagesTranQuangHien-Intern Tester-Enlab SoftwareTrần Quang HiềnNo ratings yet
- Ivy League Essay ExamplesDocument7 pagesIvy League Essay Examplesxlgnhkaeg100% (2)
- Shoemaster Creative PDFDocument249 pagesShoemaster Creative PDFAshish Dixit75% (4)
- 2020 Data Center Roadmap Survey PDFDocument16 pages2020 Data Center Roadmap Survey PDFRitwik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Science Syllabus 2016 2017Document3 pagesScience Syllabus 2016 2017api-334773982No ratings yet
- Advanced CheckPoint Interview Questions and Answers 2018Document10 pagesAdvanced CheckPoint Interview Questions and Answers 2018shikhaxohebkhanNo ratings yet
- C-CAT BrochureDocument34 pagesC-CAT Brochurenikhil kaduNo ratings yet
- VPN Access Using Tunnel Mode User Manual PDFDocument6 pagesVPN Access Using Tunnel Mode User Manual PDFSreejith G SNo ratings yet
- Topic 14. Runge-Kutta MethodsDocument6 pagesTopic 14. Runge-Kutta Methodszzrot1No ratings yet
- Serial Data Plotting Programs - Arduino Stack ExchangeDocument10 pagesSerial Data Plotting Programs - Arduino Stack Exchange1113 ForçaBrutaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Cellar 283 2014-02Document84 pagesCircuit Cellar 283 2014-02Chaovalit JitsinthuNo ratings yet
- Autopilot Money Method (v3) Bitcoin Version!!!Document7 pagesAutopilot Money Method (v3) Bitcoin Version!!!That Kid MikeNo ratings yet
- What Process Involves Placing One PDU Inside of Another PDUDocument23 pagesWhat Process Involves Placing One PDU Inside of Another PDUMarema GetachewNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Course Handout Part A: Content Design: Work Integrated Learning ProgrammesDocument12 pagesBirla Institute of Course Handout Part A: Content Design: Work Integrated Learning ProgrammesSubrahmanyam GampalaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Message Flow in XI - SAP Blogs PDFDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Message Flow in XI - SAP Blogs PDFSujith KumarNo ratings yet
- Uday Tak: Data EngineerDocument2 pagesUday Tak: Data Engineeranthony talentitNo ratings yet
- Call PLSQL From BIP Through A Procedure Call: Solution DetailsDocument6 pagesCall PLSQL From BIP Through A Procedure Call: Solution DetailsmanikdarshanNo ratings yet
- Portfolio (Nafis Chitalwala)Document25 pagesPortfolio (Nafis Chitalwala)Anonymous m9adUyNo ratings yet
- 88-103 Agung Noviantoro, Amelia Belinda Silviana, Risma Rahmalia Fitriani, Hanum Putri PermatasariDocument16 pages88-103 Agung Noviantoro, Amelia Belinda Silviana, Risma Rahmalia Fitriani, Hanum Putri PermatasarinandaNo ratings yet
- CCN Lab 3Document10 pagesCCN Lab 3sameen khanNo ratings yet
- GD1B Block Diagram: Crestline Ati M64Document35 pagesGD1B Block Diagram: Crestline Ati M64Paulo chagas paulo ratoNo ratings yet
- The Complete List of Windows 7 ShortcutsDocument30 pagesThe Complete List of Windows 7 ShortcutsmsbeverlyNo ratings yet
- SHT4x: 4 Generation, High-Accuracy, Ultra-Low-Power, 16-Bit Relative Humidity and Temperature Sensor PlatformDocument16 pagesSHT4x: 4 Generation, High-Accuracy, Ultra-Low-Power, 16-Bit Relative Humidity and Temperature Sensor PlatformMOHAMED ALI OTHMANNo ratings yet
- Tidio Automations Ebook PDFDocument56 pagesTidio Automations Ebook PDFArilesere SodeeqNo ratings yet
- MS Paint ComputerDocument11 pagesMS Paint ComputerLiza JeonNo ratings yet
- BIT - Semester 6 - University of Colombo - DB Systems 2Document96 pagesBIT - Semester 6 - University of Colombo - DB Systems 2AmaliNo ratings yet
- Cs8791 Unit III Cloud Computing NotesDocument36 pagesCs8791 Unit III Cloud Computing NotesJUSTUS KEVIN T 2019-2023 CSENo ratings yet
- PostOffice (Repaired)Document76 pagesPostOffice (Repaired)091845331283% (6)
- The+Colour+Managed+Workflow Part2 MonitorDocument19 pagesThe+Colour+Managed+Workflow Part2 MonitorFlorin CMNo ratings yet
- Ricoh Pro C751 BrochureDocument8 pagesRicoh Pro C751 BrochureManager SupportNo ratings yet