Professional Documents
Culture Documents
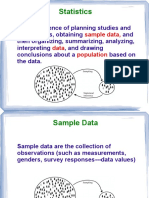
Calculating Median, Quartiles and Percentiles
Uploaded by
Zayed Ikbal Fahim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views7 pagesThe median is the middle value in a data set such that there are an equal number of values above and below the median. The median is not skewed by outliers like the mean and gives a better sense of typical values for data sets like income that vary greatly. Quartiles divide a data set into four equal parts with the first quartile being the middle number between the smallest value and median, and the third quartile being the middle between the median and highest value. Percentiles indicate the value below which a given percentage of observations fall, such as the 90th percentile being the score which 90% of observations are at or below.
Original Description:
Original Title
Median
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe median is the middle value in a data set such that there are an equal number of values above and below the median. The median is not skewed by outliers like the mean and gives a better sense of typical values for data sets like income that vary greatly. Quartiles divide a data set into four equal parts with the first quartile being the middle number between the smallest value and median, and the third quartile being the middle between the median and highest value. Percentiles indicate the value below which a given percentage of observations fall, such as the 90th percentile being the score which 90% of observations are at or below.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views7 pagesCalculating Median, Quartiles and Percentiles
Uploaded by
Zayed Ikbal FahimThe median is the middle value in a data set such that there are an equal number of values above and below the median. The median is not skewed by outliers like the mean and gives a better sense of typical values for data sets like income that vary greatly. Quartiles divide a data set into four equal parts with the first quartile being the middle number between the smallest value and median, and the third quartile being the middle between the median and highest value. Percentiles indicate the value below which a given percentage of observations fall, such as the 90th percentile being the score which 90% of observations are at or below.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Median
What is Median: In statistics and probability theory, a median
is a value separating the higher half from the lower half of a
data sample, a population or a probability distribution.
Explain: For a data set,it may be thought of as "the middle"
value. The basic advantage of the median in describing data
compared to the mean (often simply described as the
"average") is that it is not skewed so much by a small
proportion of extremely large or small values, and so it may
give a better idea of a "typical" value. For example, in
understanding statistics like household income or assets, which
vary greatly, the mean may be skewed by a small number of
extremely high or low values. Median income, for example,
may be a better way to suggest what a "typical" income is.
Because of this, the median is of central importance in robust
statistics, as it is the most resistant statistic, having a
breakdown point of 50%: so long as no more than half the data
are contaminated, the median will not give an arbitrarily large
or small result.
Example: The median is the middle value in a data set.
To calculate it, place all of your numbers in increasing
order. If you have an odd number of integers, the next
step is to find the middle number on your list. In this
example, the middle or median number is 15:
3, 9, 15, 17, 44
If you have an even number of data points, calculating the
median requires another step or two. First, find the two
middle integers in your list. Add them together, then
divide by two. The result is the median number. In this
example, the two middle numbers are 8 and 12:
3, 6, 8, 12, 17, 44
Written out, the calculation would look like this:
(8 + 12) / 2 = 20 / 2 = 10
In this instance, the median is 10 .
Quartile
What is quartile; Quartiles are values that divide a (part of a)
data table into four groups containing an approximately equal
number of observations. The total of 100% is split into four
equal parts: 25%, 50%, 75% and 100%.
The first quartile (or lower quartile), Q1, is defined as the value
that has an f-value equal to 0.25. This is the same thing as the
twenty-fifth percentile. The third quartile (or upper quartile),
Q3, has an f-value equal to 0.75. The interquartile range, IQR, is
defined as Q3-Q1.
Explain of Quartile ; A quartile is a type of quantile which
divides the number of data points into four more or less equal
parts, or quarters. The first quartile (Q1) is defined as the middle
number between the smallest number and the median of the data
set. It is also known as the lower quartile or the 25th empirical
quartile and it marks where 25% of the data is below or to the
left of it (if data is ordered on a timeline from smallest to
largest). The second quartile (Q2) is the median of a data set and
50% of the data lies below this point. The third quartile (Q3) is
the middle value between the median and the highest value of
the data set. It is also known as the upper quartile or the 75th
empirical quartile and 75% of the data lies below this point. [1]
Due to the fact that the data needs to be ordered from smallest to
largest to compute quartiles, quartiles are a form of Order
statistic.
Example of Quartile:
1st quartile or lower quartile basically separate the
lowest 25% of data from the highest 75%.
2nd quartile or middle quartile also same as median it
divides numbers into 2 equal parts.
3rd quartile or the upper quartile separate the highest
25% of data from the lowest 75%.
Formula For Quartile:
Let’s say that we have a data set with N data points:
X – {X1, X2, X3……….. XN}
What it basically means is that in a data set with N data
points:
((N+1) * 1 / 4)th term is the lower quartile
((N+1) * 2 / 4)th term is the middle quartile
((N+1) * 3 / 4)th term is the upper quartile
Percentiles
What is Percentile : A percentile is a measure at which that
percentage of the total values are the same as or below that
measure. For example, 90% of the data values lie below the 90th
percentile, whereas 10% of the data values lie below the 10th
percentile.
Explain of percentile : A percentile (or a centile) is a measure
used in statistics indicating the value below which a given
percentage of observations in a group of observations falls.
For example, the 20th percentile is the value (or score)
below which 20% of the observations may be found.
Equivalently, 80% of the observations are found above the
20th percentile.
The term percentile and the related term percentile rank are
often used in the reporting of scores from norm-referenced
tests. For example, if a score is at the 86th percentile, where
86 is the percentile rank, it is equal to the value below which
86% of the observations may be found (carefully contrast
with in the 86th percentile, which means the score is at or
below the value below which 86% of the observations may
be found—every score is in the 100th percentile).[dubious –
discuss][citation needed] The 25th percentile is also known
as the first quartile (Q1), the 50th percentile as the median
or second quartile (Q2), and the 75th percentile as the third
quartile (Q3). In general, percentiles and quartiles are
specific types of quantiles.
Example of Percentile :
Find the 90th percentile following the steps above.
(.9 x 8)=7.2 (round to 7)
K=72 (greater than), k=68 (greater than or equal
to)
Average (72 + 68) / 2 = 70
You might also like
- QuartileDocument3 pagesQuartileMJ BotorNo ratings yet
- What Is Measures of Central TendencyDocument4 pagesWhat Is Measures of Central TendencyMEL ABANo ratings yet
- Quartile: What Is A Quartile?Document3 pagesQuartile: What Is A Quartile?Bless TamayoNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument5 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyMEL ABANo ratings yet
- QuartilesDocument5 pagesQuartilessaqib khanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 MidtermDocument5 pagesAssignment 1 MidtermPatricia Jane CabangNo ratings yet
- Business StatisticsDocument7 pagesBusiness StatisticsFresher DatascienceNo ratings yet
- BBA Business Statics Course Outline SketchDocument7 pagesBBA Business Statics Course Outline SketchRabia BhattiNo ratings yet
- Data Science Essentials: Visualizing StatisticsDocument4 pagesData Science Essentials: Visualizing StatisticsThubtenDorjeNo ratings yet
- Box and Whisker PrimerDocument4 pagesBox and Whisker PrimerNenad MNo ratings yet
- Basic StatisticsDocument73 pagesBasic Statisticsartee_aggrawal4312100% (2)
- RESEARCHDocument15 pagesRESEARCHJerwin SanchezNo ratings yet
- What Can I Write in Mid TermDocument5 pagesWhat Can I Write in Mid TermAna ChikovaniNo ratings yet
- Statistical Machine LearningDocument12 pagesStatistical Machine LearningDeva Hema100% (1)
- Statistics Overview - Key Concepts and TerminologyDocument3 pagesStatistics Overview - Key Concepts and TerminologyVianelle BaroroNo ratings yet
- Statistics Quantiles ExplainedDocument2 pagesStatistics Quantiles Explainedrhianreign estudilloNo ratings yet
- Interpret Statistics & Graphs for Descriptive AnalysisDocument14 pagesInterpret Statistics & Graphs for Descriptive AnalysisMarkJasonPerezNo ratings yet
- YayDocument2 pagesYaymavioyuncu250No ratings yet
- DWDM Unit-2Document20 pagesDWDM Unit-2CS BCANo ratings yet
- Quartiles and PercentilesDocument7 pagesQuartiles and PercentilesApple_777No ratings yet
- Understand Key Statistics ConceptsDocument16 pagesUnderstand Key Statistics ConceptsSaadatNo ratings yet
- Edu 533 OutlineDocument10 pagesEdu 533 OutlineTeresa B. TimonNo ratings yet
- Measure of PositionsDocument5 pagesMeasure of PositionsDivyanshi DubeyNo ratings yet
- Statistics - Describing Data NumericalDocument56 pagesStatistics - Describing Data NumericalDr Rushen SinghNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument33 pagesStatisticsRado Mayson SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Introductory of Statistics - Chapter 3Document7 pagesIntroductory of Statistics - Chapter 3Riezel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Creating a normal probability plot of residualsDocument3 pagesCreating a normal probability plot of residualsTanjid HossainNo ratings yet
- Mining Data Dispersion CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesMining Data Dispersion Characteristics9696379353No ratings yet
- Interpretation of Data Topic: World Cup 2016 Subject: Business Analytics Assignment No 1Document3 pagesInterpretation of Data Topic: World Cup 2016 Subject: Business Analytics Assignment No 1daniyal shaikhNo ratings yet
- Introductory of Statistics - Chapter 3Document7 pagesIntroductory of Statistics - Chapter 3Riezel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Percentiles and Percentile Ranks PDFDocument17 pagesPercentiles and Percentile Ranks PDFKenneth RonoNo ratings yet
- # 4 Pemusatan & Penyebaran Data (TM)Document65 pages# 4 Pemusatan & Penyebaran Data (TM)yuza_maulana02No ratings yet
- Business Statistics: Qualitative or Categorical DataDocument14 pagesBusiness Statistics: Qualitative or Categorical DataSweety 12No ratings yet
- Assignment July-December 2014: Management ProgrammeDocument14 pagesAssignment July-December 2014: Management ProgrammeGopu PushpangadhanNo ratings yet
- STATISTIC (Methodology)Document10 pagesSTATISTIC (Methodology)Eliya AiyaniNo ratings yet
- Research Statistics DescriptiveDocument100 pagesResearch Statistics Descriptivejouie tabilinNo ratings yet
- Data Mining-5 - Getting Know Data 1Document27 pagesData Mining-5 - Getting Know Data 1يزيد زايدNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics NotesDocument6 pagesBiostatistics Notesdeepanjan sarkarNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument4 pagesDescriptive StatisticsRaghad Al QweeflNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistic - Session 5Document6 pagesDescriptive Statistic - Session 5rahuldengraNo ratings yet
- Business maths research project arithmetic meanDocument8 pagesBusiness maths research project arithmetic meanJoseph MasseyNo ratings yet
- Standard and Quartile DeviationDocument7 pagesStandard and Quartile DeviationGemine Ailna Panganiban NuevoNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document54 pagesLec 1Jayveer SinghNo ratings yet
- BBM AssignmentsDocument13 pagesBBM AssignmentsSky FallNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument48 pagesMeasures of Central TendencySheila Mae Guad100% (1)
- Range and QuartilesDocument4 pagesRange and Quartilesreasha0% (1)
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument4 pagesMeasures of Central TendencydeepikaajhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Count PropotionDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Count PropotionShreya YadavNo ratings yet
- First QuartileDocument5 pagesFirst Quartileapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Basic Statistical Description of DataDocument13 pagesBasic Statistical Description of DataTarika SaijNo ratings yet
- Percentile, Quartile and FractileDocument4 pagesPercentile, Quartile and FractileAl Joshua Ü PidlaoanNo ratings yet
- Probability TheoryDocument354 pagesProbability TheoryMohd SaudNo ratings yet
- SDA 3E Chapter 2Document40 pagesSDA 3E Chapter 2xinearpingerNo ratings yet
- Abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz: Alternative HypothesisDocument8 pagesAbcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz: Alternative Hypothesisabhinandabarman1168No ratings yet
- Calculating Quartiles and Interquartile RangeDocument4 pagesCalculating Quartiles and Interquartile RangeChandrabali SahaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Data Analysis Statistics LessonDocument4 pagesEngineering Data Analysis Statistics LessonRobert MacalanaoNo ratings yet
- Measure of Position and Location Statistics - Standard Scores, Percentiles, Quartiles, Deciles ExplainedDocument2 pagesMeasure of Position and Location Statistics - Standard Scores, Percentiles, Quartiles, Deciles ExplainedMelvin CabonegroNo ratings yet
- Measures of Position: MAT C301 Jose Rizal UniversityDocument16 pagesMeasures of Position: MAT C301 Jose Rizal UniversityRanier Factor AguilarNo ratings yet
- Name: John Carlo S. Mallabo Year&Course: Bs Cpe Topic 4: Measure of Relative PositionDocument3 pagesName: John Carlo S. Mallabo Year&Course: Bs Cpe Topic 4: Measure of Relative PositionMallabo John CarloNo ratings yet
- Statistics Question PaperDocument4 pagesStatistics Question PaperSufi KhanNo ratings yet
- Statistical Methods For Cross-Sectional Data AnalysisDocument1 pageStatistical Methods For Cross-Sectional Data AnalysisQueen ANo ratings yet
- Statasession3 Econ4136Document20 pagesStatasession3 Econ4136juchama4256No ratings yet
- Stucor Ma3251 EjDocument226 pagesStucor Ma3251 EjHarishNo ratings yet
- Test Bank: This Is Chapter 6, Problem 3Document6 pagesTest Bank: This Is Chapter 6, Problem 3miladNo ratings yet
- March April 2010 Quantitative AnalysisDocument3 pagesMarch April 2010 Quantitative AnalysisMonika ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Math 20-2 Unit Plan (Statistics)Document4 pagesMath 20-2 Unit Plan (Statistics)api-290174387No ratings yet
- CIGRE-367 - Reliability of TransformersDocument6 pagesCIGRE-367 - Reliability of TransformersDileepa Sachithra DaulagalaNo ratings yet
- Data Management Central TendencyDocument33 pagesData Management Central TendencyAnn Kristel EstebanNo ratings yet
- Excel Pronto PizzaDocument29 pagesExcel Pronto PizzaPattyNo ratings yet
- Basic Stat NarrativeDocument9 pagesBasic Stat NarrativeeL LeahNo ratings yet
- Edexcel s1 Revision NotesDocument5 pagesEdexcel s1 Revision Notesminamakin50% (2)
- First Course in Probability 10th Edition Ross Solutions ManualDocument23 pagesFirst Course in Probability 10th Edition Ross Solutions Manualveritymaximusjh8100% (20)
- Statistical Inferences PresentationDocument11 pagesStatistical Inferences PresentationDiwas RaiNo ratings yet
- CP and CPK SolutionDocument5 pagesCP and CPK SolutionlawtonNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution Theory: Population and SampleDocument8 pagesSampling Distribution Theory: Population and SampleSiddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Homework Problems Stat 490CDocument44 pagesHomework Problems Stat 490CleviNo ratings yet
- Representation and Summary of Data - Location (Questions)Document4 pagesRepresentation and Summary of Data - Location (Questions)Hassan HussainNo ratings yet
- Human Resources Competency and Internal Control Impact Financial Report QualityDocument13 pagesHuman Resources Competency and Internal Control Impact Financial Report QualityRekon BOS Disdik KaltengNo ratings yet
- Validacion Del Metodo Butirometrico de GerberDocument10 pagesValidacion Del Metodo Butirometrico de GerberAna Maria AcevedoNo ratings yet
- RDD Stata 1Document23 pagesRDD Stata 1Denis Lima E AlvesNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument8 pagesQuizosaliana budiartoNo ratings yet
- Imp - MEASURES OF DISPERSIONDocument5 pagesImp - MEASURES OF DISPERSIONSan PaulNo ratings yet
- Wentsworth Medical CenterDocument7 pagesWentsworth Medical CenterLeonardo Campos PoNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Student's Academic Performance in Ahuntegen General Secondary School, North Wollo Zone, EthiopiaDocument9 pagesFactors Affecting Student's Academic Performance in Ahuntegen General Secondary School, North Wollo Zone, EthiopiaJournal of Education and LearningNo ratings yet
- Engstat PS2Document2 pagesEngstat PS2Cha TingjuyNo ratings yet
- Logistics RegressionDocument30 pagesLogistics Regressioncat20091No ratings yet
- Process Capability Six Sigma Version 1 PDFDocument32 pagesProcess Capability Six Sigma Version 1 PDFshubhamNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Techniques Under 40 CharactersDocument55 pagesForecasting Techniques Under 40 CharactersDevanshu Sahay100% (1)
- A Coefficient of Variability: Manuel Martinez-PonsDocument3 pagesA Coefficient of Variability: Manuel Martinez-PonsRana UmarNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (79)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet