Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IC 38 Short Notes (2) 77
Uploaded by
Anil Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThe document discusses the evolution of health insurance in India. It describes the Employees' State Insurance Scheme introduced in 1948 which provides health insurance for workers earning under Rs. 15,000 per month funded through contributions from employees, employers, and state governments. It also describes the Central Government Health Scheme introduced in 1954 which provides nominal health insurance for central government employees and their families. The document outlines the key levels and providers of healthcare in India including primary, secondary, and tertiary care.
Original Description:
Original Title
IC-38-Short-notes(2)-77
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the evolution of health insurance in India. It describes the Employees' State Insurance Scheme introduced in 1948 which provides health insurance for workers earning under Rs. 15,000 per month funded through contributions from employees, employers, and state governments. It also describes the Central Government Health Scheme introduced in 1954 which provides nominal health insurance for central government employees and their families. The document outlines the key levels and providers of healthcare in India including primary, secondary, and tertiary care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageIC 38 Short Notes (2) 77
Uploaded by
Anil KumarThe document discusses the evolution of health insurance in India. It describes the Employees' State Insurance Scheme introduced in 1948 which provides health insurance for workers earning under Rs. 15,000 per month funded through contributions from employees, employers, and state governments. It also describes the Central Government Health Scheme introduced in 1954 which provides nominal health insurance for central government employees and their families. The document outlines the key levels and providers of healthcare in India including primary, secondary, and tertiary care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
P a g e | 77
Most of the times, the patients are referred to the secondary care by primary
health care providers / primary physician.
C.Tertiary healthcare :
Tertiary Health care is specialized consultative healthcare, usually for inpatients
and on referralfrom primary/secondary care providers.
e.g. Oncology (cancer treatment), Organ Transplant facilities, High risk
pregnancy specialists etc.
Factors affecting the health systems in India:
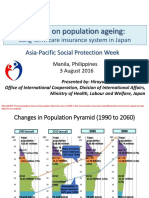
Demographic or Population related trends
Social trends
Life expectancy
Evolution of Health Insurance in India
a) Employees‟ State Insurance Scheme :
Introduced by ESI Act,1948.
All workersearning wages up to Rs. 15,000 are covered under the
contributory scheme wherein employee and employer contribute 1.75%
and 4.75% of pay roll respectively; state governments contribute 12.5% of
the medical expenses.
The benefits covered include:
a)Free comprehensive healthcare at ESIS facilities
b)Maternity benefit
c)Disability benefit
d)Cash compensation for loss of wages due to sickness and survivorship
e)Funeral expenses in case of death of worker
b) Central Government Health Scheme :
Introduced in the year 1954.
This scheme is for central governmentemployees including pensioners and their
family membersworking in civilian job.
The contribution from employees is quite nominal though progressively linked to
salary scale –Rs.15 per month to Rs.150 per month
Sterling Insurance ATI Services
You might also like
- Emerging Health Insurance in India-An Overview - J AnithaDocument17 pagesEmerging Health Insurance in India-An Overview - J AnithaSwayam Suraj NayakNo ratings yet
- Healthcare System in JapanDocument4 pagesHealthcare System in JapanBayuAkbarSyarifNo ratings yet
- Health Insurance in IndiaDocument16 pagesHealth Insurance in IndiaRuchir Sharda100% (1)
- Presentation On Health Care System ModelsDocument37 pagesPresentation On Health Care System ModelsTashi Makpen100% (1)
- Healthcare Insurance Evolution in India An Opportunity To Expand AccessDocument7 pagesHealthcare Insurance Evolution in India An Opportunity To Expand AccessCherylAlishaD'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Report On Health Insurance 2Document23 pagesReport On Health Insurance 2DrJaideep KumarNo ratings yet
- Nursing AssistantDocument58 pagesNursing AssistantswarnaNo ratings yet
- AYushman Bharat AnalysisDocument12 pagesAYushman Bharat Analysisravi767457507No ratings yet
- Health Care Delivery System in India and AbroadDocument46 pagesHealth Care Delivery System in India and AbroadANITTA S100% (6)
- Health SchemesDocument21 pagesHealth SchemesPankaj Khatri100% (1)
- Health Care ReformDocument8 pagesHealth Care ReformAnjliNo ratings yet
- Financial Products AssignmentDocument14 pagesFinancial Products AssignmentHimanshuNo ratings yet
- Health Law ProjectDocument22 pagesHealth Law ProjectVarun MittalNo ratings yet
- Health InsuranceDocument10 pagesHealth InsuranceDevendra SawantNo ratings yet
- AO 2017-0012 Guidelines On The Adoption of Baseline Primary Health Care Guarantees For All FilipinosDocument49 pagesAO 2017-0012 Guidelines On The Adoption of Baseline Primary Health Care Guarantees For All FilipinosCarlen Mae Laudencia Yacapin100% (1)
- Dr. Padma Bhatia: Assistant Professor Department of Community Medicine G.M.C., Bhopal. M.P. IndiaDocument30 pagesDr. Padma Bhatia: Assistant Professor Department of Community Medicine G.M.C., Bhopal. M.P. IndiaSakshi SuriNo ratings yet
- Ao2017 0012Document49 pagesAo2017 0012disasternursinNo ratings yet
- IRDA IC 38 (17 21) Refresher 2Document12 pagesIRDA IC 38 (17 21) Refresher 2Anant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Health Insurance: DR - Bharat PaulDocument74 pagesHealth Insurance: DR - Bharat PaulAnonymous So5qPSnNo ratings yet
- Health InsuranceDocument46 pagesHealth InsuranceVaishali UzzielNo ratings yet
- What Is Healthcare ?: Introduction To Health Insurance)Document5 pagesWhat Is Healthcare ?: Introduction To Health Insurance)Maulik PanchmatiaNo ratings yet
- CH - III ContinuedDocument7 pagesCH - III ContinuedAmrina RasadhaNo ratings yet
- Employees State Insurance SchemeDocument8 pagesEmployees State Insurance SchemeKrishnaveni MurugeshNo ratings yet
- Australia - International Health Care System ProfilesDocument10 pagesAustralia - International Health Care System ProfilesAboubacar SompareNo ratings yet
- Health Care DeliveryDocument29 pagesHealth Care DeliveryAloysius RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Ealth Nsurance: Chapter ReviewDocument222 pagesEalth Nsurance: Chapter ReviewYi QingNo ratings yet
- 1 DR.N.S.R Chandraprasad, Chairman & MD, National Insurance Company - Healthcare Insurance Past, Present & FutureDocument46 pages1 DR.N.S.R Chandraprasad, Chairman & MD, National Insurance Company - Healthcare Insurance Past, Present & FutureAkshayNo ratings yet
- Healthcare in IndiaDocument40 pagesHealthcare in Indiamanisha paikaray100% (1)
- Health Insurance: Awareness, Utilization, and Its Determinants Among The Urban Poor in Delhi, IndiaDocument8 pagesHealth Insurance: Awareness, Utilization, and Its Determinants Among The Urban Poor in Delhi, IndiaY S KusumaNo ratings yet
- The Feasibility of A Community Based Health Insurance (CBHI) at Wayanad, KeralaDocument43 pagesThe Feasibility of A Community Based Health Insurance (CBHI) at Wayanad, Keralatapz07No ratings yet
- Nhis Operational GuidelinesDocument38 pagesNhis Operational GuidelinestitooluwaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Health CareDocument8 pagesPhilippine Health CareCarl Mark Vincent BabasoroNo ratings yet
- Health InsuranceDocument23 pagesHealth InsuranceNicks DemonNo ratings yet
- Handbook Nhis PDFDocument9 pagesHandbook Nhis PDFagelonijoaNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Development of Health InsuranceDocument23 pagesA Study On The Development of Health InsuranceDilpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- 19571Document30 pages19571Prasanjeet BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- National Health Insurance Act (Philhealth)Document44 pagesNational Health Insurance Act (Philhealth)ruby cubionaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer in POLGOVDocument16 pagesMidterm Reviewer in POLGOVJam AlindadaNo ratings yet
- Leadership & ManagementDocument44 pagesLeadership & ManagementShaheed HayangNo ratings yet
- DATA ANALYSIS ManiDocument17 pagesDATA ANALYSIS ManiSyed AquibNo ratings yet
- Ealth Nsurance IN Ndia: R M - 05PH2010Document6 pagesEalth Nsurance IN Ndia: R M - 05PH2010api-26832469No ratings yet
- Pages From IJPHRD February - 2020-3Document5 pagesPages From IJPHRD February - 2020-3Tengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Health Care Deliver System AjayDocument41 pagesHealth Care Deliver System AjayAjay DNo ratings yet
- Essay-3 HealthcareDocument21 pagesEssay-3 HealthcareShretima AgrawalNo ratings yet
- HealthInsurance Ashortcasestudy RASDocument4 pagesHealthInsurance Ashortcasestudy RASRitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- BHIM 024 Healthcare Financing PDFDocument28 pagesBHIM 024 Healthcare Financing PDFpalak maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Health Care Financing: Preethi PradhanDocument21 pagesHealth Care Financing: Preethi PradhanRoHIT ShowNo ratings yet
- Medical Health Insurance Systems in Europe, USA, Canada, and AustraliaDocument13 pagesMedical Health Insurance Systems in Europe, USA, Canada, and Australiaeko abiNo ratings yet
- Thailand: Health Financing Models in Various CountriesDocument42 pagesThailand: Health Financing Models in Various CountriesChampaka Prasad RanaNo ratings yet
- Mba ProjectDocument46 pagesMba ProjectPayal DattaNo ratings yet
- APSP - Session 9A - Hiroyuki Yamaya - MHLWDocument8 pagesAPSP - Session 9A - Hiroyuki Yamaya - MHLWKristine PresbiteroNo ratings yet
- Health Insurance1Document3 pagesHealth Insurance1jincygeevarghese7132No ratings yet
- Health Insurance SchemeDocument10 pagesHealth Insurance SchemeKailash NagarNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument8 pagesThis Study Resource WasMae Ann BusicoNo ratings yet
- PHC Week1day1 Group2 - PPT-GHDocument21 pagesPHC Week1day1 Group2 - PPT-GHReichelle Reine LisingNo ratings yet
- HIS NotesDocument20 pagesHIS NotesGiane MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Ess 5Document12 pagesEss 5api-582020074No ratings yet
- Achieving the Human Right to a Caring Society in an Aging AmericaFrom EverandAchieving the Human Right to a Caring Society in an Aging AmericaNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-76 PDFDocument1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-76 PDFAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-72Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-72Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP - File Upload: What's The PHP Going To Do?Document1 pagePHP - File Upload: What's The PHP Going To Do?Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP - File Upload: Move - Uploaded - File FunctionDocument1 pagePHP - File Upload: Move - Uploaded - File FunctionAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-73Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-73Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP - String Capitalization FunctionsDocument1 pagePHP - String Capitalization FunctionsAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-77 PDFDocument1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-77 PDFAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Capitalizing The First Letter - Ucwords: PHP CodeDocument1 pageCapitalizing The First Letter - Ucwords: PHP CodeAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP - File Upload: Move - Uploaded - File FunctionDocument1 pagePHP - File Upload: Move - Uploaded - File FunctionAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-65Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-65Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-67Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-67Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-62Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-62Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP - File Upload: HTML CodeDocument1 pagePHP - File Upload: HTML CodeAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-66 PDFDocument1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-66 PDFAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-61 PDFDocument1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-61 PDFAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-64Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-64Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-59Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-59Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP - File Open: Read: 'R'Document1 pagePHP - File Open: Read: 'R'Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-54Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-54Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-61 PDFDocument1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-61 PDFAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP - File Read: Gets FunctionDocument1 pagePHP - File Read: Gets FunctionAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP - File Open: AdvancedDocument1 pagePHP - File Open: AdvancedAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-60Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-60Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Raw HTML Code:: When Would You Use Htmlentities?Document1 pageDangerous Raw HTML Code:: When Would You Use Htmlentities?Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-50Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-50Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-52Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-52Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-55Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-55Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-56 PDFDocument1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-56 PDFAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-49Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-49Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PHP Tizag Tutorial-51Document1 pagePHP Tizag Tutorial-51Anil KumarNo ratings yet