Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tarlac State University Graduate Studies
Uploaded by
L.J. SantosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tarlac State University Graduate Studies
Uploaded by
L.J. SantosCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
TARLAC STATE UNIVERSITY
College of Education
GRADUATE STUDIES
Lucinda Campus, Tarlac City
A.Y. 2020-2021
Second Semester
Definion of
Terms
Chickenpox - an acute contagious disease especially of children marked by low-grade fever and formation of vesicles and caused by a herpesvirus (species Human
herpesvirus 3 of the genus Varicellovirus) - Merriam
Chickenpox - An infectious disease causing a mild fever and a rash of itchy inflamed pimples which turn to blisters and then loose scabs. It is caused by the herpes
zoster virus and mainly affects children. - Oxford
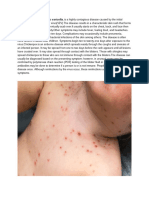
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a
characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the chest, back, and face. It then spreads to the rest of the
body. Other symptoms may include fever, tiredness, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to seven days. Complications may occasionally
include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, and bacterial skin infections. The disease is often more severe in adults than in children. Symptoms begin 10 to 21
days after exposure to the virus.
Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily from one person to the next through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from
one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread
chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. (source: Wikipedia)
Measles - an acute contagious disease that is caused by a morbillivirus (species Measles virus) and is marked especially by an eruption of distinct red circular spots
- Merriam
Measles - An infectious viral disease causing fever and a red rash, typically occurring in childhood. - Oxford
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–
10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than 40 °C (104 °F), cough, runny nose, and inflamed eyes. Small white spots known as Koplik's
spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of
the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms. Common complications include diarrhea (in 8% of cases), middle ear infection (7%),
and pneumonia (6%). These occur in part due to measles-induced immunosuppression. Less commonly seizures, blindness, or inflammation of the brain may
occur. Other names include morbilli, rubeola, red measles, and English measles. Both rubella, also known as German measles, and roseola are different diseases
caused by unrelated viruses.
Measles is an airborne disease which spreads easily from one person to the next through the coughs and sneezes of infected people. It may also be spread
through direct contact with mouth or nasal secretions. It is extremely contagious–nine out of ten people who are not immune and share living space with an
infected person will be infected. People are infectious to others from four days before to four days after the start of the rash.[5] While often regarded as a
childhood illness, it can affect people of any age. Most people do not get the disease more than once. (source: Wikipedia)
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to Childhood Infectious DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Childhood Infectious DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- UnidentifiedDocument2 pagesUnidentifiedNiño Franco Azur CatanguiNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: Chickenpox Is A HighlyDocument4 pagesSigns and Symptoms: Chickenpox Is A HighlysaaaraelleNo ratings yet
- RubellaDocument2 pagesRubellaRenelia BarbosaNo ratings yet
- MeaslesDocument2 pagesMeaslesmark rosarioNo ratings yet
- MeasDocument22 pagesMeasSriLestariFajerinNo ratings yet
- Measles Rash and Incubation PeriodDocument14 pagesMeasles Rash and Incubation PeriodAyen PaloNo ratings yet
- Measles Overview for NCM 102-RLE IMCI RotationDocument9 pagesMeasles Overview for NCM 102-RLE IMCI RotationChrisel Joy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Chikungunya, Meningococcemia, Measles, Rubella and Dengue VirusesDocument8 pagesChikungunya, Meningococcemia, Measles, Rubella and Dengue VirusesMary Christine IlangaNo ratings yet
- Humen Herpesvirus and Chicken PoxDocument62 pagesHumen Herpesvirus and Chicken Poxprabad dunusingheNo ratings yet
- Measles and Mumps RubellaDocument13 pagesMeasles and Mumps RubellaDayana PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:: Prof. DR/ Samia Mahmoud Dr/Hanan Gad. Community Health Nursing Mansoura UniversityDocument16 pagesPrepared By:: Prof. DR/ Samia Mahmoud Dr/Hanan Gad. Community Health Nursing Mansoura UniversityAya RefaatNo ratings yet
- Diseases ClinicalDocument57 pagesDiseases Clinicalsomayya wali100% (1)
- W9 Measles German Measles Influenza Chicken Pox Covid19Document16 pagesW9 Measles German Measles Influenza Chicken Pox Covid19Jamie De LunaNo ratings yet
- M13 v2 Dermatology & STI - LO5Document6 pagesM13 v2 Dermatology & STI - LO5medipro clinicNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox: 2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection Health and MedicineDocument5 pagesChickenpox: 2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection Health and MedicinenvijaykanthNo ratings yet
- MeaslesDocument4 pagesMeaslesSweetyfe GabatanNo ratings yet
- MeasleDocument9 pagesMeasleNajmussaqibNo ratings yet
- Measles Virus InfectionDocument20 pagesMeasles Virus Infectionsuryanto_malvinNo ratings yet
- Contagious Infection Varicella Zoster Virus Vesicular Rash PockmarksDocument34 pagesContagious Infection Varicella Zoster Virus Vesicular Rash PockmarksbbhoeeNo ratings yet
- Fwd. Epi 8Document40 pagesFwd. Epi 8Sumayya ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- Common Cold: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesCommon Cold: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaazetteaNo ratings yet
- Malaria, Measles, DHF Quiz#2Document8 pagesMalaria, Measles, DHF Quiz#2Cherub ChuaNo ratings yet
- Module 05 Homework AssignmentDocument4 pagesModule 05 Homework Assignmentstephanie4dubielNo ratings yet
- Diseases With The Rash Syndrome11.Document33 pagesDiseases With The Rash Syndrome11.ManishNo ratings yet
- SMALLPOXDocument3 pagesSMALLPOXJyoti SidhuNo ratings yet
- Health Care DiseasesDocument18 pagesHealth Care DiseasesShelley CarreonNo ratings yet
- Signs and SymptomsDocument6 pagesSigns and SymptomsKajim SharibiNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox and Shingles GuideDocument32 pagesChickenpox and Shingles GuideCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- VaricellachickenpoxDocument6 pagesVaricellachickenpoxDedi SofyanNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis 1. Background of The Problem Chickenpox Is A Highly Contagious Disease Caused by Primary Infection With VaricellaDocument6 pagesTuberculosis 1. Background of The Problem Chickenpox Is A Highly Contagious Disease Caused by Primary Infection With VaricellaFkrygeustobat Tikamarimunteupercaya TanyakeunkajalminaNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox and SmallpoxDocument28 pagesChickenpox and SmallpoxFourth YearNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument13 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionsJavaid Mustuffa100% (1)
- What is rubella? Causes, symptoms, and prevention of German measlesDocument9 pagesWhat is rubella? Causes, symptoms, and prevention of German measlesMd A RAZZAKNo ratings yet
- Overview of Measles DiseaseDocument3 pagesOverview of Measles DiseaseLighto RyusakiNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox 160531062051 PDFDocument16 pagesChickenpox 160531062051 PDFJu Lie AnnNo ratings yet
- Measles: A Highly Contagious Viral DiseaseDocument2 pagesMeasles: A Highly Contagious Viral DiseaseKAREEM WAHEEDNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument84 pagesChickenpoxraymondabaduNo ratings yet
- Common ColdDocument24 pagesCommon Coldxiang_xiang56No ratings yet
- Table of Communicable Diseases: Disease Signs & Symptoms Incubation Prevention Chicken PoxDocument10 pagesTable of Communicable Diseases: Disease Signs & Symptoms Incubation Prevention Chicken PoxKristel_Ramall_6985No ratings yet
- Lane Nichols Disease WebcastDocument3 pagesLane Nichols Disease WebcastKerry Ottesen NicholsNo ratings yet
- VirulenceDocument3 pagesVirulenceAna Ross Villarin GorospeNo ratings yet
- MeaslesDocument53 pagesMeaslestummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- Chickenpox Chickenpox Is A Highly Contagious Disease Caused by Primary Infection With Varicella ZosterDocument12 pagesChickenpox Chickenpox Is A Highly Contagious Disease Caused by Primary Infection With Varicella Zostersubbu2raj3372100% (2)
- MEASLESDocument28 pagesMEASLESAjitesh MahalingamNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox What Is Chickenpox?Document19 pagesChickenpox What Is Chickenpox?s.khan9211rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- Viral Exanthema: Dharmendra MandalDocument57 pagesViral Exanthema: Dharmendra MandalMaunank TandelNo ratings yet
- Measles: Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, Treatment, and PreventionDocument15 pagesMeasles: Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, Treatment, and PreventionWidya Ayu SetyaningrumNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox: Varicella-Virus InfectionsDocument5 pagesChickenpox: Varicella-Virus InfectionsAjay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Common Childhood DDocument23 pagesCommon Childhood DLiza JeonNo ratings yet
- Ebola Virus: Causes, Symptoms & FactsDocument5 pagesEbola Virus: Causes, Symptoms & FactsRomel Ricafort John DavidNo ratings yet
- Answers For MICI 1100 Final ReviewDocument16 pagesAnswers For MICI 1100 Final Reviewashley.danielngenegboNo ratings yet
- Fever and RashesDocument32 pagesFever and RashesYamuna SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: Prodromal MalaiseDocument3 pagesSigns and Symptoms: Prodromal Malaisegmanooj_484213209No ratings yet
- Hiv and AidsDocument5 pagesHiv and AidsMhie RecioNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Signs, Symptoms, and PreventionDocument9 pagesDengue Fever Signs, Symptoms, and PreventionKyla BalboaNo ratings yet
- Varicella by Siva MurugadossDocument34 pagesVaricella by Siva MurugadossPrakask BalanNo ratings yet
- Vaccinated Persons: Other Typical Symptoms That May Begin To Appear 1-2 Days Before Rash IncludeDocument5 pagesVaccinated Persons: Other Typical Symptoms That May Begin To Appear 1-2 Days Before Rash IncludePrimita Ayu DamayantiNo ratings yet
- List of ContentsDocument7 pagesList of ContentsAhsan MoinNo ratings yet
- Measles: EtiologyDocument14 pagesMeasles: EtiologyHan SANo ratings yet
- PAMINTUAN, JOHN ERIC L. - WEEKLY-HOME-LEARNING-PLAN-IN - SCIENCE 8 - Q1 W4 Temp SoundDocument2 pagesPAMINTUAN, JOHN ERIC L. - WEEKLY-HOME-LEARNING-PLAN-IN - SCIENCE 8 - Q1 W4 Temp SoundL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Individual-Workweek-Plan-Accomplishment-June 15-19Document3 pagesIndividual-Workweek-Plan-Accomplishment-June 15-19L.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Individual-Workweek-Plan-Accomplishment-June 22-26Document3 pagesIndividual-Workweek-Plan-Accomplishment-June 22-26L.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Individual-Workweek-Plan-Accomplishment-June 29 July 3Document3 pagesIndividual-Workweek-Plan-Accomplishment-June 29 July 3L.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- PAMINTUAN, JOHN ERIC L. - WEEKLY-HOME-LEARNING-PLAN-IN - SCIENCE 8 - Q1 M1 ForceDocument2 pagesPAMINTUAN, JOHN ERIC L. - WEEKLY-HOME-LEARNING-PLAN-IN - SCIENCE 8 - Q1 M1 ForceL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- PAMINTUAN, JOHN ERIC L. - WEEKLY-HOME-LEARNING-PLAN-IN - SCIENCE 8 - Q1 M1 ForceDocument2 pagesPAMINTUAN, JOHN ERIC L. - WEEKLY-HOME-LEARNING-PLAN-IN - SCIENCE 8 - Q1 M1 ForceL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Final ExaminationDocument2 pagesFinal ExaminationL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- G8 Le 01Document3 pagesG8 Le 01L.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Teacher workweek planDocument3 pagesTeacher workweek planL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- PAMINTUAN, JOHN ERIC L. - WEEKLY-HOME-LEARNING-PLAN-IN - SCIENCE 8 - Q1 M1 ForceDocument2 pagesPAMINTUAN, JOHN ERIC L. - WEEKLY-HOME-LEARNING-PLAN-IN - SCIENCE 8 - Q1 M1 ForceL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox and Measles: A Virtual Information Dissemination of Communicable DiseasesDocument5 pagesChickenpox and Measles: A Virtual Information Dissemination of Communicable DiseasesL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Republic of the Philippines Weekly Home Learning PlanDocument2 pagesRepublic of the Philippines Weekly Home Learning PlanL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Population DensityDocument24 pagesBiodiversity and Population DensityL.J. Santos100% (1)
- Tarlac State University Graduate StudiesDocument4 pagesTarlac State University Graduate StudiesL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Implementation Management in The School &: Alternative of Waste Science Subject, Student's HomeDocument11 pagesImplementation Management in The School &: Alternative of Waste Science Subject, Student's HomeL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Intro PDFDocument1 pageIntro PDFL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Delirium 2Document1 pageDelirium 2L.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Maed - Psci 507 Topic Guide PresentationDocument8 pagesMaed - Psci 507 Topic Guide PresentationL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- 9 Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument1 page9 Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Heat and ElectricityDocument11 pagesHeat and ElectricityL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Science - G9 - Week 7 (Lessons 19-20)Document19 pagesScience - G9 - Week 7 (Lessons 19-20)L.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Delirium 1Document1 pageDelirium 1L.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Delirium 4Document1 pageDelirium 4L.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Delirium 3Document1 pageDelirium 3L.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- Big DeeDocument1 pageBig DeeL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- SickleDocument1 pageSickleL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- DeliriumDocument1 pageDeliriumL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- PukepieDocument1 pagePukepieL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- KuzuDocument1 pageKuzuL.J. SantosNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Practice Questions 7 14Document8 pagesTOEFL Practice Questions 7 14Syarifah Fauziah Arnia TunisaNo ratings yet
- Jessica Evans Epi PaperDocument12 pagesJessica Evans Epi Paperapi-439893609No ratings yet
- AIIMS CAPSULE AtfDocument70 pagesAIIMS CAPSULE Atfsimrankaur2003studNo ratings yet
- Viral MeningitisDocument4 pagesViral MeningitisLucky PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Master Tung's Four Horses Combination - Master Tung's Magic PointsDocument12 pagesMaster Tung's Four Horses Combination - Master Tung's Magic PointsAWEDIOHEAD93% (14)
- Ophthalmology: by Dr. Laraib Jameel RPHDocument75 pagesOphthalmology: by Dr. Laraib Jameel RPHDhivya SekarNo ratings yet
- 144 DAFTAR DIAGNOSA NON-SPESIALISTIK (Dr. M. GENTA)Document8 pages144 DAFTAR DIAGNOSA NON-SPESIALISTIK (Dr. M. GENTA)lucianaayu febrina67% (3)
- Agesta Sacred Codes ListDocument10 pagesAgesta Sacred Codes ListEnigma Vita100% (2)
- Summary of DermaDocument29 pagesSummary of DermaAbdelrahman ElsaadawiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pearls Herpes Eye InfectionDocument20 pagesClinical Pearls Herpes Eye InfectionmudymaxNo ratings yet
- Oral Dermatology: Important Oral Questions & AnswersDocument29 pagesOral Dermatology: Important Oral Questions & AnswersMedo JTNo ratings yet
- Cranial NeuralgiasDocument14 pagesCranial NeuralgiasHabib G. Moutran BarrosoNo ratings yet
- OceanofPDF - Com DR Sebi Herpes Solution DR Sebis 3-Ste - Serena BrownDocument145 pagesOceanofPDF - Com DR Sebi Herpes Solution DR Sebis 3-Ste - Serena BrownKristine Gerbolingo100% (1)
- Communicablediseases 110227001506 Phpapp02 PDFDocument30 pagesCommunicablediseases 110227001506 Phpapp02 PDFCrystal Ann Monsale TadiamonNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument16 pagesIntegumentary Systemshenric16100% (8)
- PHAR 233 - Pathophysiology of Infectious DiseasesDocument89 pagesPHAR 233 - Pathophysiology of Infectious DiseasesLina RamojNo ratings yet
- List of DiseasesDocument7 pagesList of DiseasesLoveleen SinghNo ratings yet
- 253 Complexes For Biomedis Trinity - DescriptionDocument74 pages253 Complexes For Biomedis Trinity - Descriptionjanhendrik4444100% (1)
- Oral Lesions and HomoeopathyDocument27 pagesOral Lesions and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pathophysiology Study Guide Last Test (Test 5)Document53 pagesNursing Pathophysiology Study Guide Last Test (Test 5)rainbowunicorn25100% (1)
- ShinglesDocument8 pagesShinglesapi-3366481170% (1)
- The Cruel Hoax Called Herpes GenetalisDocument48 pagesThe Cruel Hoax Called Herpes GenetalisPeter M. Randall0% (1)
- Pertanyaan ReferatDocument2 pagesPertanyaan ReferatBuydh BfdsfsNo ratings yet
- 2023 Obstetrics1 Part5Document1 page2023 Obstetrics1 Part510 B: Bravo, OliveNo ratings yet
- Viral Meningitis: David R. ChadwickDocument14 pagesViral Meningitis: David R. ChadwickVina HardiantiNo ratings yet
- Uworld: Maria Elizabeth SharmaDocument87 pagesUworld: Maria Elizabeth SharmaElizabeth SharmaNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Dermatology NMT 10Document18 pagesMCQ in Dermatology NMT 10R Ratheesh100% (2)
- Leech Therapy ArticlesDocument27 pagesLeech Therapy ArticlesRapal Ahmad100% (1)
- Dermatological Diseases of The Nose and Ears - An Illustrated Guide - C. Baykal, K. Yazganoglu (Springer, 2010) WWDocument150 pagesDermatological Diseases of The Nose and Ears - An Illustrated Guide - C. Baykal, K. Yazganoglu (Springer, 2010) WWthanos bakourasNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument176 pagesCommunicable DiseasesKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet