Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M) IV Anticoagulation M) Arterial Thrombolytic (
Uploaded by
christine louise bernardo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageOriginal Title
Acute-arterial-ocllusion-map
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageM) IV Anticoagulation M) Arterial Thrombolytic (
Uploaded by
christine louise bernardoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
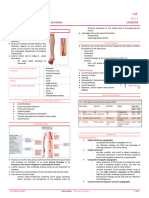
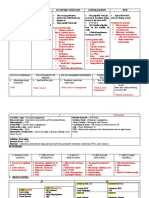
ETIOLOGY Risk Factors:
-atrial fibrillation -age
-myocardial infarction -smoking
-infective endocarditis Arterial emboli develop in -diabetes
-chronic heart failure the chambers of the heart -obesity
-atherosclerosis -sedentary
-Iatrogenic injury lifestyle
Thrombi become detached and are carried from the -family history of
-Rupture and thrombosis
left side of the heart into the arterial system vascular disease,
of an atherosclerotic
-high cholesterol
plaque
-Embolus from the heart Thrombi become lodged in and obstruct an Complications:
Platelet-rich thrombus formation artery that is smaller than the embolus. -Compartment
Medical Management: over a ruptured atherosclerotic syndrome
(M)IV anticoagulation plaque -Amputation
Blockage progresses distal and proximal to the site -Necrosis and
with heparin of the obstruction.
(M)Arterial thrombolytic Damaged arterial wall, generally gangrene
medications as a result of atherosclerosis The embolus can fragment or break apart, -Bleeding
(M)Fibrin specific resulting in occlusion of distal vessels. -Stroke
thrombolytic medications -Myocardial
Lab and Diagnostic Cessation of blood flow
Procedures:
*Physical exam Occlusion of distal
vessels PA: Upon inspection, distal extremities
*Ankle brachial
are pale in appearance.
indexABI poor collateral flow in the extremities PA: Upon palpation, the skin
*Ultrasound
Paresthesia integument is cold to touch
*Angiography paralysis Nd: Ineffective peripheral tissue
*Blood tests
Surgical Absent pulse
pallor perfusion related to impaired arterial
Management: pain coldness circulation
Endovascular N: Submit patient to diagnostic testing
Management: as indicated.
(S)Emergency N: Check for optimal fluid balance.
embolectomy Administer IV fluids as ordered.
N: Note urine output.
M: Administer nitroglycerin (NTG)
PROGNOSIS:
Prognosis is good. Acute arterial occlusion has high morbidity and mortality. The
outcomes for patients with an acutely ischemic limb due to arterial occlusion are
guarded. Even if the limb is salvaged, these patients have other comorbidities, which
can lead to a heart attack, renal failure, stroke, or wound infection. Unless an
interprofessional team is involved, the mortality for these individuals remains high.
You might also like
- 1 Acute Arterial OcclusionDocument3 pages1 Acute Arterial Occlusionchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Acute Ischemia of The Lower Limb (LL) : Sudden Occlusion of A Previously Patent Artery Supplying A LimbDocument4 pagesAcute Ischemia of The Lower Limb (LL) : Sudden Occlusion of A Previously Patent Artery Supplying A LimbOmar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Aortic Dissection (Schwartz's 11 Ed.) Pathology and Classification Causes and Clinical HX Clinical Manifestations Diagnostic Evaluation TreatmentDocument3 pagesAortic Dissection (Schwartz's 11 Ed.) Pathology and Classification Causes and Clinical HX Clinical Manifestations Diagnostic Evaluation TreatmentSean Dominique Cruz MaghinayNo ratings yet
- Aortic DissectionDocument2 pagesAortic DissectionTiffney NesakumarNo ratings yet
- MIND MAP Walking in PainDocument1 pageMIND MAP Walking in PainDRMAZLINANo ratings yet
- Cardio 3 Part 3Document40 pagesCardio 3 Part 3Lola WooNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischaemia:: Evaluation & Decision MakingDocument83 pagesAcute Limb Ischaemia:: Evaluation & Decision Makingjanicesusanto2000No ratings yet
- CVS Tables FranzDocument7 pagesCVS Tables FranzCole GoNo ratings yet
- Week 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, ArrhythmiaDocument14 pagesWeek 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, Arrhythmiashivani patel100% (1)
- TRP Surgery Study GuideDocument27 pagesTRP Surgery Study GuidekatNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Concept MappingDocument34 pagesMyocardial Concept MappingTHIRD YEARNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease CAD PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesCoronary Artery Disease CAD PathophysiologyKusum RoyNo ratings yet
- Qtsoi Concept MapDocument5 pagesQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischemia (Ali) : Tributed To: Ismoyo Sunu, MDDocument54 pagesAcute Limb Ischemia (Ali) : Tributed To: Ismoyo Sunu, MDMhd Ridho FahreziNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 Lec Prelim NotesDocument35 pagesNCM 114 Lec Prelim Notesmblanco.dchNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Darpen Subhashbhai Mori Group 2, MD 3BDocument13 pagesHemorrhagic Stroke: Darpen Subhashbhai Mori Group 2, MD 3BDarpen MoriNo ratings yet
- 04 SST Hemodynamic DerangementsDocument1 page04 SST Hemodynamic DerangementsFranz LibreNo ratings yet
- Vascular Trauma: Episode OverviewDocument11 pagesVascular Trauma: Episode OverviewwatimelawatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 - Pericardial Disease - 1Document10 pagesChapter 18 - Pericardial Disease - 1ganeabaicudragosNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischaemia (ALI) Refers To The Sudden: Interruption of Arterial Blood SupplyDocument36 pagesAcute Limb Ischaemia (ALI) Refers To The Sudden: Interruption of Arterial Blood SupplyAuliyah SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Where Problems With The Heart Mean There Isn't Enough Oxygen Present in The BloodDocument6 pagesWhere Problems With The Heart Mean There Isn't Enough Oxygen Present in The BloodRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Dr. Subagia - Neuro RadiologyDocument94 pagesLecture - Dr. Subagia - Neuro RadiologySyaimee Annisa AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischemia and VasculitisDocument6 pagesAcute Limb Ischemia and VasculitisnivraeNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischemia TransDocument2 pagesAcute Limb Ischemia TransnricojungaoNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3.1 Diathesis HemorragikDocument20 pages2.2.3.1 Diathesis HemorragikaiysahmirzaNo ratings yet
- Endocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Document8 pagesEndocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Eben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A. Narrative: Iv. PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesA. Narrative: Iv. Pathophysiologyr_cyrusNo ratings yet
- Journal StrokeDocument13 pagesJournal StrokeEufrasia VictaNo ratings yet
- Cvspa04 Ihd and MiDocument8 pagesCvspa04 Ihd and MiRobert So JrNo ratings yet
- CARDIAC TUMORS TransDocument12 pagesCARDIAC TUMORS TransjeccomNo ratings yet
- Overview of Stroke - Knowledge at AMBOSSDocument19 pagesOverview of Stroke - Knowledge at AMBOSSandimija16No ratings yet
- Ajith Kumar P MPT Cardiopulmonary SciencesDocument30 pagesAjith Kumar P MPT Cardiopulmonary SciencesSuhana JahangeerNo ratings yet
- Textbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroDocument12 pagesTextbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroJica Marie Bandiola GicaroNo ratings yet
- Post-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeDocument5 pagesPost-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Cardiovascular ProblemDocument52 pagesGroup 3 Cardiovascular ProblemWARREN WILLIAM PERAN100% (3)
- Week 13 Disorders of Secondary Hemostasis LecDocument8 pagesWeek 13 Disorders of Secondary Hemostasis LecCzarina Mae IlaganNo ratings yet
- Retinal Vein Occlusion Concept MapDocument2 pagesRetinal Vein Occlusion Concept MapJoe RealNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Disease TumoursDocument9 pagesCerebrovascular Disease TumoursCindy Van WykNo ratings yet
- IM Part 1Document48 pagesIM Part 1sasghfdgNo ratings yet
- IM Part 1 and 2 CombinedDocument100 pagesIM Part 1 and 2 CombinedsasghfdgNo ratings yet
- VALVULAR HEART DISEASES Transes PrelimsDocument3 pagesVALVULAR HEART DISEASES Transes PrelimsRichell CatianNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Peripheral Vascular Diseasept.mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Linician Pdate: Catheter Ablation of Ventricular TachycardiaDocument6 pagesLinician Pdate: Catheter Ablation of Ventricular TachycardiaSonia Rahma ANo ratings yet
- Acyanitic DefectsDocument9 pagesAcyanitic DefectsHalla BennaaNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis What and How?: Faris Basalamah, MD, FIHADocument24 pagesAtherosclerosis What and How?: Faris Basalamah, MD, FIHAfikriNo ratings yet
- NEURO2 1.02A Stroke Generalities and Mechanism - Dr. HiyadanDocument3 pagesNEURO2 1.02A Stroke Generalities and Mechanism - Dr. HiyadanAra DiocosNo ratings yet
- Medicine Revision - Neurology TableDocument10 pagesMedicine Revision - Neurology TableUnomoshNo ratings yet
- Notes 2Document87 pagesNotes 2steveNo ratings yet
- ISMT12 - Day 457 - Vito - Cerebellar DisorderDocument17 pagesISMT12 - Day 457 - Vito - Cerebellar DisorderVito MasagusNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart Disease: Epidemiology and Global TrendsDocument2 pagesIschemic Heart Disease: Epidemiology and Global TrendsRandom CommenterNo ratings yet
- MS Day 1 2Document9 pagesMS Day 1 2Geraldine MaeNo ratings yet
- 401 ReviewerDocument30 pages401 ReviewerSheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Cardio Day 3 TemplateDocument24 pagesCardio Day 3 TemplateMikeNo ratings yet
- Overview On Peripheral Artery Disease - FinalDocument78 pagesOverview On Peripheral Artery Disease - FinalMITHANo ratings yet
- CARDIAC TUMORS Approach To ManagementDocument12 pagesCARDIAC TUMORS Approach To ManagementAnkit GulatiNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER2Document6 pagesREVIEWER2Lorielyn Ashlee GaiteNo ratings yet
- Cardio I: Shock, CHF, HTN, ACS Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesCardio I: Shock, CHF, HTN, ACS Cheat Sheet: by ViaMariana NannettiNo ratings yet
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Aortic DissectionDocument3 pagesAortic Dissectionchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- ARDS Concept MapDocument1 pageARDS Concept Mapchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- M) IV Anticoagulation M) Arterial Thrombolytic (Document1 pageM) IV Anticoagulation M) Arterial Thrombolytic (christine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Ards Concept MapDocument1 pageArds Concept Mapchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Second Degree Av Block Type 1 (Mobitz I or Wenckebach)Document1 pageSecond Degree Av Block Type 1 (Mobitz I or Wenckebach)christine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- NCP Near DrowningDocument1 pageNCP Near Drowningchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Pharyngitis PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePharyngitis Pathophysiologychristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure: Left-Sided Heart Failure Right-Sided Heart FailureDocument1 pageCongestive Heart Failure: Left-Sided Heart Failure Right-Sided Heart Failurechristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure: Left-Sided Heart Failure Right-Sided Heart FailureDocument1 pageCongestive Heart Failure: Left-Sided Heart Failure Right-Sided Heart Failurechristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Aortic RegurgitationDocument1 pageAortic Regurgitationchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Aortic StenosisDocument1 pageAortic Stenosischristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Ards Concept MapDocument1 pageArds Concept Mapchristine louise bernardo100% (1)
- Aortic RegurgitationDocument1 pageAortic Regurgitationchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Aortic RegurgitationDocument1 pageAortic Regurgitationchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 Stomatology 2012Document22 pagesKrok 1 Stomatology 2012Saaha ParmarNo ratings yet
- Hypertension CaseDocument3 pagesHypertension CaseArnold Christian QuilonNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Ramadan Fasting On Tuberculin Skin Test and Leukocyte Count Dalam Bhasa InggrisDocument4 pagesThe Effect of Ramadan Fasting On Tuberculin Skin Test and Leukocyte Count Dalam Bhasa InggrisファラハンNo ratings yet
- 8-Ecg in CovidsDocument35 pages8-Ecg in CovidsyandraNo ratings yet
- Care Plan Prep May 13 Rheumatic FeverDocument16 pagesCare Plan Prep May 13 Rheumatic Feverapi-256360167No ratings yet
- Adult Jaundice: Symptoms and CausesDocument4 pagesAdult Jaundice: Symptoms and CausesDennis NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Infectios DiseasesDocument183 pagesInfectios DiseasesAnonymous eson90No ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Awareness - 13 October 2019Document4 pagesBreast Cancer Awareness - 13 October 2019Times MediaNo ratings yet
- MRCPass Notes For MRCP 1 - EnDOCRINOLOGYDocument12 pagesMRCPass Notes For MRCP 1 - EnDOCRINOLOGYsabdali100% (1)
- Tatalaksana Tekanan Tinggi Intrakranial Pada Anak-DikonversiDocument48 pagesTatalaksana Tekanan Tinggi Intrakranial Pada Anak-DikonversiAbdurrahman Arsyad As SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- PSYCH - 1st Sem Finals FeedbackDocument2 pagesPSYCH - 1st Sem Finals FeedbackEricNo ratings yet
- Pre Conception CareDocument58 pagesPre Conception CareMarkos MakishaNo ratings yet
- Vulvar Lesions: CAPT Mike Hughey, MC, USNRDocument31 pagesVulvar Lesions: CAPT Mike Hughey, MC, USNRlalalala50% (2)
- Nursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Postpartal Complications PDFDocument9 pagesNursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Postpartal Complications PDFTandingco, Olivia Mari H.No ratings yet
- Cureus 0013 00000017832Document8 pagesCureus 0013 00000017832raulNo ratings yet
- US Army Medical Course MD0008-100 - Introduction To Military Preventive MedicineDocument178 pagesUS Army Medical Course MD0008-100 - Introduction To Military Preventive MedicineGeorges100% (3)
- Abstract Apicon Category Section Title Author Name Author Name and Contact NumberDocument6 pagesAbstract Apicon Category Section Title Author Name Author Name and Contact NumberKriti KumariNo ratings yet
- The RH Blood Group System: Tudy ID NswersDocument2 pagesThe RH Blood Group System: Tudy ID NswersChatie PipitNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)Document15 pagesHereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)MarshallNo ratings yet
- Nasopharyngeal CarcinomaDocument25 pagesNasopharyngeal Carcinomananda surastyo100% (1)
- Menieres DiseaseDocument6 pagesMenieres Diseasecceng06No ratings yet
- Ocular Trauma Dr. As-Ali 2 OktoberDocument61 pagesOcular Trauma Dr. As-Ali 2 OktoberYama Piniel FrimantamaNo ratings yet
- Articol Medicina de TrimisDocument19 pagesArticol Medicina de TrimisMoldovan TiberiuNo ratings yet
- Maternal DistressDocument7 pagesMaternal DistressBharat Thapa83% (6)
- Recent Development of Travel Medicine: Current Issues Prof. Dr. Soesanto Tjokrosonto 2006Document28 pagesRecent Development of Travel Medicine: Current Issues Prof. Dr. Soesanto Tjokrosonto 2006Red DemonNo ratings yet
- 04 Taking A Case HistoryDocument38 pages04 Taking A Case HistoryMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health and Safety Including PadamsDocument27 pagesOccupational Health and Safety Including PadamsFerlyn SanorjoNo ratings yet
- Literature Feeding and Eating Quick GuideDocument17 pagesLiterature Feeding and Eating Quick GuideHana alassafNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPzharienabNo ratings yet
- PAINWeek Journal Vol 7, Q1Document78 pagesPAINWeek Journal Vol 7, Q1Apostolos T.No ratings yet