0% found this document useful (0 votes)
507 views2 pagesForces Summary Sheet Updated
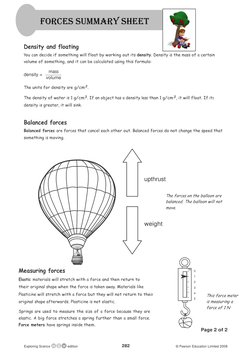
Forces can change the shape, speed, or direction of motion of objects. Forces can be contact forces like friction or non-contact forces like gravity and magnetism. Mass is the amount of substance in an object while weight is the force of gravity on the object. Friction can slow objects down or produce heat and can be reduced by lubrication. The density of an object determines if it will float, with objects less dense than water floating.
Uploaded by
Zantaye ThomasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
507 views2 pagesForces Summary Sheet Updated
Forces can change the shape, speed, or direction of motion of objects. Forces can be contact forces like friction or non-contact forces like gravity and magnetism. Mass is the amount of substance in an object while weight is the force of gravity on the object. Friction can slow objects down or produce heat and can be reduced by lubrication. The density of an object determines if it will float, with objects less dense than water floating.
Uploaded by
Zantaye ThomasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Weight and Mass: Discusses the concepts of weight and mass with a focus on gravitational force.
- Forces: Explains the nature and effects of forces, differentiating between contact and non-contact forces.
- Friction: Describes friction as a force that opposes motion, explaining its causes and effects.
- Measuring Forces: Details how forces can be measured using different materials and instruments.
- Density and Floating: Explores how density affects an object's ability to float and provides formulas to calculate density.
- Balanced Forces: Explains the concept of balanced forces using visual diagrams for better understanding.