Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 6
Uploaded by
Ishaan IslamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 6
Uploaded by
Ishaan IslamCopyright:
Available Formats
Explain the difference between extrusion amd drawing?
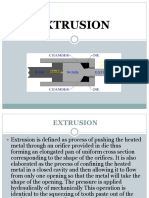
Extrusion: It is a process where a billet is forced through a die.
Drawing: It is a process where a cross-section of solid rod, wire, or tubing is reduced
or changed in shape by pulling it through a die.
What types of defects may occur in (a) extrusion and (b) drawing?
(a) Surface Cracking, Pipe, and Internal Cracking.
(b) Center Cracking and Seams.
How are tubes extruded? can they also be drawn? explain.
There are two ways of extruding tube: the porthole method and the seamless or
mandrel method.
Porthole extrusion is the most widely used process for making tube. A billet of
material is pushed over a former that creates the internal cross-section. This former
is held in place by ribs, so the material has to flow around them too. As it flows it
separates, so to make a tube the individual pieces are forced back together. Heat
and pressure work together to create a kind of weld or seam that’s practically
imperceptible to the human eye.
The alternative is to create an extrusion without seams along the length. This is done
by pushing a mandrel into the billet from the back. (The opposite end to the die.)
The tip of the mandrel goes almost all the way through the billet, stopping a short
distance from the extrusion die. This leaves a small gap between mandrel and die for
the metal to flow through.
After extrusion the hot tube is cooled and often subjected to stretching to improve
straightness. When a higher quality tube, a thinner wall or more consistent size are
needed extrusion is followed by a drawing process.
What is the difference between cold, warm and hot forging ?
The difference between cold, warm, and hot forging is the temperature for which
the forging is carried out at.
For example, cold forging is done at room temperature and warm and hot forging
are at elevated temperatures.
Explain the difference between fullering, edging, and blocking.
Fullering: Material is distributed away from an area.
Edging: Material is gathered into a localized area.
Blocking: The part is formed into the rough shape.
What is flash? What is its function?
Flash, also known as flashing, is excess material attached to a molded, forged, or cast
product, which must usually be removed. This is typically caused by leakage of the
material between the two surfaces of a mold or between the base material and the
mold in the case of overmolding.
Molding flash is seen when the optimized parameter on cull height is not calibrated.[citation
needed] Proper design of mold parting surfaces can reduce or eliminate flash.
How can you tell whether a certain part is forged or cast? Describe the features that you
would investigate.
Forged parts are often tougher than cast parts. This can be determined by
performing tensile tests on various areas on the parts. Additionally, the
microstructures of forged and cast parts can be used to determine if a part was
forged or cast. The microstructure of a cast part will have a more uniform grain
structure.
What is the difference between a plate and a sheet?
The distinction between sheet and plate is as equally ambiguous as a number of
other terms used to describe steel product forms. Generally speaking, a sheet is a
thinner item of metal that has been cut from a continuously rolled coil. As such, it
can be less than 1mm, or up to 25mm, in thickness. A plate is a thicker item of metal
that has been produced (rolled) as a single item. Thickness can be up to 150mm or
more, but also as low as 2mm from certain producers.
Therefore, it’s quite possible that certain thickness items could be produced via either
process and described differently, although both are in the hot rolled condition.
Plate metal is typically used in machines, structural sections and larger fabrications,whereas
sheet metal is used in producing appliances and enclosure
Explain the difference between punching and blanking.
In a punching operation, they typically remove the smallest amount of material
necessary from the original workpiece to minimize material waste. In contrast,
Blanking operations are most efficient when the maximum amount of material is
removed from the workpiece.
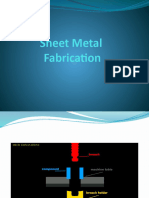
What is the difference between deep drawing and redrawing?
Deep drawing is a sheet metal forming process in which a sheet metal blank is
radially drawn into a forming die by the mechanical action of a punch.[1] It is
thus a shape transformation process with material retention. The process is
considered "deep" drawing when the depth of the drawn part exceeds its
diameter. This is achieved by redrawing the part through a series of dies. The
flange region (sheet metal in the die shoulder area) experiences a radial drawing
stress and a tangential compressive stress due to the material retention
property.
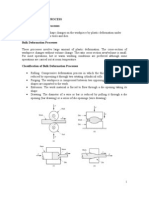
What is the difference between a bloom,a slab, and a billet?
A bloom is a rolled steel workpiece with a square cross section of about 150 mm by
150 mm. ... A slab is rolled from an ingot or a bloom and has a rectangular cross
section of about 250 mm by 40 mm. A billet is rolled from a bloom and has a square
cross section of about 40 mm by 40 mm.
You might also like
- Sheet Metal Design - GuideDocument7 pagesSheet Metal Design - GuidechoonhooiNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming ProcessesDocument40 pagesMetal Forming ProcessesRyat AtmadjaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Sheet Metal Operations Are:: 1. Shearing OperationDocument10 pagesDifferent Types of Sheet Metal Operations Are:: 1. Shearing OperationSai Asrith KonagallaNo ratings yet
- Sheetmetal IntroDocument48 pagesSheetmetal IntroBharat M GajeraNo ratings yet
- DieDocument6 pagesDieAditya GoelNo ratings yet
- WELDING-Root Cause For DefectsDocument10 pagesWELDING-Root Cause For DefectsSiddhardha Msv50% (4)
- Home Instruction for Sheet Metal Workers - Based on a Series of Articles Originally Published in 'Metal Worker, Plumber and Steam Fitter'From EverandHome Instruction for Sheet Metal Workers - Based on a Series of Articles Originally Published in 'Metal Worker, Plumber and Steam Fitter'No ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Design Guide by MSMTCDocument33 pagesSheet Metal Design Guide by MSMTCNanda Sagar100% (3)
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)Document34 pagesSubmerged Arc Welding (SAW)Gaballah Aman0% (1)
- An Introduction to Metal-Working (Illustrated)From EverandAn Introduction to Metal-Working (Illustrated)Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Unit IV 180208091907Document153 pagesUnit IV 180208091907tamilselvan nNo ratings yet
- Forging and Extrusion Defects Causes and TypesDocument8 pagesForging and Extrusion Defects Causes and TypesVenkat KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Classic Handplanes and Joinery: Essential Tips and Techniques for WoodworkersFrom EverandClassic Handplanes and Joinery: Essential Tips and Techniques for WoodworkersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Sheet Metal BasicsDocument69 pagesSheet Metal Basicskiran_wakchaure50% (2)
- Week 8 Sheet Metal FormingDocument69 pagesWeek 8 Sheet Metal FormingashkansoheylNo ratings yet
- Automatic Bending Machine Report-1Document70 pagesAutomatic Bending Machine Report-1ganeshNo ratings yet
- Design of Sheet Metal Working ToolsDocument38 pagesDesign of Sheet Metal Working ToolsAsef ShahriarNo ratings yet
- A Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesFrom EverandA Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesNo ratings yet
- Module 5 PDFDocument93 pagesModule 5 PDFVishal Shanmuga SundramNo ratings yet
- Roll Forging.Document36 pagesRoll Forging.jaydee420No ratings yet
- Dies1 2Document23 pagesDies1 2Ajay BabuNo ratings yet
- Wire Drawing Shearing Processes FinalDocument19 pagesWire Drawing Shearing Processes FinalJairam AtluriNo ratings yet
- Rolling (Bulk Deformation Process)Document27 pagesRolling (Bulk Deformation Process)Kazal ArefinNo ratings yet
- Design Guide For Surface Coating 05 v18 72dpiDocument54 pagesDesign Guide For Surface Coating 05 v18 72dpifunluaslan100% (2)
- Lecture-14 Sheet Metal Forming ProcessesDocument34 pagesLecture-14 Sheet Metal Forming ProcessesDida KhalingNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal OperationDocument17 pagesSheet Metal Operationsekar_scribd60% (5)
- Dimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyFrom EverandDimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Rolling Machine With SplinesDocument41 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Rolling Machine With SplinestadiwosNo ratings yet
- Cold FormingDocument7 pagesCold FormingglaxionNo ratings yet
- Extrusion FundamentalsDocument5 pagesExtrusion FundamentalsJoNo ratings yet
- Unit IV OrigionalDocument25 pagesUnit IV OrigionalPrakash SinghNo ratings yet
- Multi-operation die types and their functionsDocument3 pagesMulti-operation die types and their functionsCleng LaynesNo ratings yet
- Forging of MetalsDocument31 pagesForging of MetalsSaiful IslamNo ratings yet
- GR GNT 00166580000000717Document25 pagesGR GNT 00166580000000717ashoku24007No ratings yet
- Drawing (Manufacturing)Document3 pagesDrawing (Manufacturing)Carlos BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Cairo University Metallurgy Lecture on Metal Forming ProcessesDocument20 pagesCairo University Metallurgy Lecture on Metal Forming Processesيوسف عادل حسانينNo ratings yet
- Extrusion process guide: how it works and its benefits/TITLEDocument22 pagesExtrusion process guide: how it works and its benefits/TITLESantoshNo ratings yet
- MT 2nd AssignmentDocument72 pagesMT 2nd AssignmentDixitNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming ProcessDocument5 pagesMetal Forming Processrk_kamatchi3483No ratings yet
- Unit - IV Drawing of Rods, Wires and TubesDocument13 pagesUnit - IV Drawing of Rods, Wires and TubesMaddipudi RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Bulk Deformation Processes: Forging & ExtrusionDocument24 pagesBulk Deformation Processes: Forging & ExtrusionDân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming Processes Guide: Forging, Rolling & MoreDocument46 pagesMetal Forming Processes Guide: Forging, Rolling & MorearhlboyNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming and Casting Processes GuideDocument31 pagesMetal Forming and Casting Processes GuideSHAIK BAJI50% (2)
- ExtrusionDocument5 pagesExtrusionklawsis100% (1)
- Cold Working MethodsDocument34 pagesCold Working MethodsSarojKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PDF Forging Sheet MetalDocument75 pagesUnit 3 PDF Forging Sheet MetalYash KalraNo ratings yet
- Metal ExtrusionDocument41 pagesMetal ExtrusionRashiqah RazlanNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument4 pagesAbstractneptunaNo ratings yet
- College of Education Akwanga, Nasarawa StateDocument14 pagesCollege of Education Akwanga, Nasarawa StatePilgrim KaterNo ratings yet
- BTI1133 Ch16Document82 pagesBTI1133 Ch16ACC SHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Sheet Metal Fabrication) With VideoDocument71 pagesChapter 4 (Sheet Metal Fabrication) With VideoSamrat BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Classification and Forming Methods of Sheet Metal PartsDocument39 pagesClassification and Forming Methods of Sheet Metal PartssasikumarNo ratings yet
- Extrusion ProcessesDocument6 pagesExtrusion ProcessesSreejith VaneryNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Working of Metals MaterialDocument40 pagesMechanical Working of Metals MaterialRoyalmechNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming LabDocument57 pagesMetal Forming LabRohitGuptaNo ratings yet
- College of Education Akwanga, Nasarawa State: Number 1Document10 pagesCollege of Education Akwanga, Nasarawa State: Number 1Pilgrim KaterNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering II (ch3)Document93 pagesManufacturing Engineering II (ch3)beila.amu.22No ratings yet
- Metal Forming Processes ExplainedDocument42 pagesMetal Forming Processes ExplainedSatyajeet SahooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document17 pagesChapter 15Lhekha RaviendranNo ratings yet
- Universal Grinding - Machine - Report-FinalDocument48 pagesUniversal Grinding - Machine - Report-FinalGopuNo ratings yet
- Rock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesFrom EverandRock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesNo ratings yet
- Major types of sand molds and their characteristicsDocument7 pagesMajor types of sand molds and their characteristicsIshaan IslamNo ratings yet
- 316 Stainless Steel Price, Composition, Testing & Heat TreatmentDocument6 pages316 Stainless Steel Price, Composition, Testing & Heat TreatmentIshaan IslamNo ratings yet
- What Materials Are Used To Make Cell Phones?: GlassDocument2 pagesWhat Materials Are Used To Make Cell Phones?: GlassIshaan IslamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1Ishaan IslamNo ratings yet
- AdmixturesDocument7 pagesAdmixturesCass Ysabel Guanco AtencioNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Flame Straightening410 113398Document32 pagesFundamentals of Flame Straightening410 113398Waldo AtNo ratings yet
- Casting: Aim of The ExperimentDocument7 pagesCasting: Aim of The Experimentsanskar mittalNo ratings yet
- B.tech Welding LAb QuestionsDocument2 pagesB.tech Welding LAb QuestionsArg SreekarNo ratings yet
- Brosur Guard Rail (Pagar Pengaman Jalan)Document1 pageBrosur Guard Rail (Pagar Pengaman Jalan)hervandyNo ratings yet
- PipeworkDocument5 pagesPipeworkTAPIZ ACMVNo ratings yet
- TDS Byk-094 enDocument2 pagesTDS Byk-094 enHiroshi PhanNo ratings yet
- Fabric Wrapped Panel SystemDocument5 pagesFabric Wrapped Panel SystemMohammed SayeeduddinNo ratings yet
- Production Technology - GATE 2020Document54 pagesProduction Technology - GATE 2020Saravana Mahe-ShanNo ratings yet
- Petrochemicals Processing For Detergents Production:-Linear Paraffins For Biodegradable Detergents. Petroleum DerivativesDocument2 pagesPetrochemicals Processing For Detergents Production:-Linear Paraffins For Biodegradable Detergents. Petroleum DerivativesSubbaReddy PuliNo ratings yet
- AMP NOTES on Non-Traditional Machining ProcessesDocument44 pagesAMP NOTES on Non-Traditional Machining ProcessesDJNo ratings yet
- Handmade Paper From Waste Banana Fibre, This Study Aimed To CreateDocument3 pagesHandmade Paper From Waste Banana Fibre, This Study Aimed To CreateK maNo ratings yet
- C01 C117Document117 pagesC01 C117HENRY DAVID PURUNCAJAS PAUCARNo ratings yet
- NHB 700 - The Practice of Heat TreatmentDocument75 pagesNHB 700 - The Practice of Heat TreatmentConrad Hendrik De KockNo ratings yet
- Perfect Charging Solar EnergyDocument8 pagesPerfect Charging Solar Energyseham qafesheh100% (1)
- KFUPM Lathe Machines GuideDocument5 pagesKFUPM Lathe Machines Guidegunawan refiadiNo ratings yet
- Painting of The Parts Used in Manufacturing by Piaggio NormaDocument12 pagesPainting of The Parts Used in Manufacturing by Piaggio NormaSuresh ShindeNo ratings yet
- Waterproofing Retaining WallDocument2 pagesWaterproofing Retaining WallHimagiri Rao KunaNo ratings yet
- Martempering and Austempering Final SlideDocument25 pagesMartempering and Austempering Final SlidekeirthNo ratings yet
- 202004032240236827nksingh Polymer ProcessingDocument9 pages202004032240236827nksingh Polymer ProcessingMuhammad Umair Akbar GujjarNo ratings yet
- Welding Shop Manual 27112020Document12 pagesWelding Shop Manual 27112020Jeevan MandalaNo ratings yet
- Rolling Defects in Metal SheetsDocument14 pagesRolling Defects in Metal SheetsMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Conference Paper 3d PrintingDocument8 pagesConference Paper 3d PrintingAbdelmajid AittalebNo ratings yet
- Wps 22Document2 pagesWps 22Avishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Catalagram 99 - 2006Document32 pagesCatalagram 99 - 2006saleh4060No ratings yet
- Copper SlagDocument6 pagesCopper SlagpushkarNo ratings yet