Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Artificial Ground Tuner PDF
Artificial Ground Tuner PDF
Uploaded by
Marckos FrancoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Artificial Ground Tuner PDF
Artificial Ground Tuner PDF
Uploaded by
Marckos FrancoCopyright:
Available Formats
Hans
Remeeus PA0Q
ex PA1HR
donderdag 28
nov
Tekst grootte
HOME AMATEUR RADIO HAM RADIO DIEREN SCHEVENINGENRADIO CONTACT SITEMAP
Arti icial Ground Tuner
Home mode Artificial Ground
This Artificial Ground has been designed by Colyn Baillie-Searle GD4EIRP
(Practival Wireless, October 1990)
Inside view of the homemade Artificial Ground
Frontside of the Artificial Ground device
Schematics of the Artificial Ground
L1 primary = 2 turns on Amidon T50-2, you may use the same wire as for L2
L1 secondary = 12 turns, 0,5 mm wire
L2 = 12 turns, 2 mm wire, with a coil diameter of 37 mm
Isolated (!) variable capacitor = between 390 and 500 pF
In QST March 2004 I did read an interesting article about grounding and the "artificial ground" device.
David asks:
I recently moved my ham shack from the basement of my house to the second floor. My question has
to do with the grounding of my station equipment. I've been told that I should ground my equipment.
Other than a good ground at the electrical plug (I checked it and it is good). I can run a ground line to a
stake (copper clad) driven into the ground. I was also told that the line running to the ground rod
should not be resonant at any frequency that I plan to use. With my current rig, I operate from 70 cm
to 80 meters and may add 160 meters, too. What would be the easiest way to calculate a safe length
for my ground line or what would you suggest?
Answer from QST Workbench:
I assume that when you say that you checked the ground at the electrical plug and that it was good,
you're refering to the dc ground. Unfortunately, this has nothing to do with a good RF ground, except at
very low frequencies. That plug ground will probably be useless as an RF ground on the HF bands. At
the very least, however, it could be effective as an ac ground for the station and can be used for that
purpose. It will not be a good lightning ground, however, and it shouldn't be relied upon for that
purpose. For lightning (if that's a problem at your location), the shortest direct path to ground, outside
the house, using an 8 to 10 foot ground rod with at least 10 gauge wire from either the coax shield or
an arc arrester is to be preferred. This can also serve as an effective dc ground for the station. Keep the
wire gauge large and the run short.
A good RF ground would require the lead to be short relative to a wavelength - generally less that 1/4
wavelength at the highest frequency of interest. As a rule, it is best to keep ground leads as short as
possible with a minimum of bends in the wire. It's also advisable to use a wide, flat braid for a ground
wire, as the RF tends to travel on the outside of the conductor (the "skin effect").
As a practical matter, accomplishing a good RF ground is difficult at best, especially on the second floor.
The good news, however, is that most installations do not necessarily require one. If you have a well
balanced antenna/feed line system, you're probably okay.
If you use a wire antenna and you do have a relatively poor RF counterpoise or ground system, you
might look into at "artificial ground". This can successfully resonate a random length ground wire and
make the station "see" an effective counterpoise. These can work well, although every situation is
unique, and it would have to be evaluated for your particular RF environment.
The bottom line: I suggest running the shortest ground lead that is pratical for your station and keeping
bends to a minimum. Make sure the station is at least at dc ground potential (ground all the equipment
chassis to a common point and then to a good dc ground) and keep the lightning ground outside the
house. If you're using a wire antenna and you're plagued with a poor RF counterpoise, try using the
"artificial ground" device.
(Thanks QST/ARRL "The Doctor", www.arrl.org/tis/, doctor@arrl.org)
With thanks to the designer
Colyn Baillie-Searle GD4EIP!
HOME AMATEUR RADIO HAM RADIO DIEREN SCHEVENINGENRADIO CONTACT SITEMAP
Copyright © 2019 Hans Remeeus PA0Q. Alle rechten voorbehouden. Designed by JoomlArt.com.
You might also like
- Emp Generator Circuit Diagram: GrandcaretDocument7 pagesEmp Generator Circuit Diagram: GrandcaretMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- Practical AntennasDocument59 pagesPractical AntennasCarlos A. Gallardo100% (6)
- 1 4963228644928389236 PDFDocument196 pages1 4963228644928389236 PDFAlexandre Barbieri Folatre100% (3)
- DIY 3-Wheeled Electric Skateboard With A Hub-Motor: InstructablesDocument28 pagesDIY 3-Wheeled Electric Skateboard With A Hub-Motor: InstructablesMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- Crossbow Trigger Mechanism Simple But Sturdy PDFDocument3 pagesCrossbow Trigger Mechanism Simple But Sturdy PDFMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- Low Band Receiving Antennas-1Document37 pagesLow Band Receiving Antennas-1David Bohorquez RamosNo ratings yet
- Pink Noise Generator For Audio TestingDocument3 pagesPink Noise Generator For Audio Testingmmd3No ratings yet
- Simple, Low Cost Wire Antennas For Radio Amateurs by WilliamDocument191 pagesSimple, Low Cost Wire Antennas For Radio Amateurs by Williamtriplojota100% (1)
- 2 M - Pre Amplifier - VHFDocument15 pages2 M - Pre Amplifier - VHFAnonymous Kti5jq5EJINo ratings yet
- Handheld EMP Device: Food Living Outside Play Technology WorkshopDocument14 pagesHandheld EMP Device: Food Living Outside Play Technology WorkshopMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- What Is Difference Between Resonant and NonDocument20 pagesWhat Is Difference Between Resonant and NonAditya Agarwal0% (1)
- Small Transmitting Loop Antennas Aa5tbDocument14 pagesSmall Transmitting Loop Antennas Aa5tbDiego García MedinaNo ratings yet
- Antenna MythsDocument85 pagesAntenna MythsStephen Kinford100% (4)
- Walkman Wonder MW LoopDocument3 pagesWalkman Wonder MW Loopmax_orwellNo ratings yet
- 9 To 1 Balun For End Fed AntennaDocument24 pages9 To 1 Balun For End Fed AntennaKlaudio Kosta100% (1)
- Half Length 80m Loaded DipoleDocument2 pagesHalf Length 80m Loaded DipoleBenjamin Dover0% (1)
- A Truly Broadband, Efficient Low-Band Dipole - W7ZZ and N6RYDocument25 pagesA Truly Broadband, Efficient Low-Band Dipole - W7ZZ and N6RYNoorman NoorNo ratings yet
- Cheap Antennas For LEO SatellitesDocument5 pagesCheap Antennas For LEO Satellitesdiglemar100% (1)
- Ground Plane AntennaDocument7 pagesGround Plane AntennaarijeetdguyNo ratings yet
- All Band Large LoopDocument4 pagesAll Band Large Loopbearbullride10No ratings yet
- Circuit Schematic and Technical Details For Receiving 7.83hz Schumann FrequenciesDocument5 pagesCircuit Schematic and Technical Details For Receiving 7.83hz Schumann Frequenciesstimoceiver83% (6)
- Emf DetectorDocument99 pagesEmf Detectorvilvaram100% (1)
- Devops With Kubernetes and Helm: Jessica Deen Cloud Developer AdvocateDocument40 pagesDevops With Kubernetes and Helm: Jessica Deen Cloud Developer Advocatestalemate97100% (1)
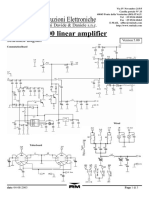
- Mod. KLV 400 Linear Amplifier Costruzioni Elettroniche: Di Marchioni Davide & Daniele S.N.C. Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMod. KLV 400 Linear Amplifier Costruzioni Elettroniche: Di Marchioni Davide & Daniele S.N.C. Schematic DiagramPisu Miau Pisu MiauNo ratings yet
- Final ThesisDocument43 pagesFinal ThesisArthur Zhou100% (1)
- Astm D1287Document4 pagesAstm D1287Eduardo CarlovichNo ratings yet
- 160half Slooper AntennaDocument4 pages160half Slooper Antenna1c1b964d100% (1)
- Budget Radio Telescope For DIYDocument14 pagesBudget Radio Telescope For DIYtawfekmNo ratings yet
- Ham Mag EngDocument32 pagesHam Mag EngKenbur100% (1)
- Low Voltage - Two Tube Regen ReceiverDocument8 pagesLow Voltage - Two Tube Regen Receiverest_nuNo ratings yet
- HVA-BBHCC HVA Excel ToolDocument8 pagesHVA-BBHCC HVA Excel ToolWahjuda SaputraNo ratings yet
- BECKMAN J6-Mi USER MANUAL PDFDocument58 pagesBECKMAN J6-Mi USER MANUAL PDFEngineer Awais50% (2)
- Artifical Ground For HAM'sDocument4 pagesArtifical Ground For HAM'sPetrika JanekuNo ratings yet
- Station GroundingDocument4 pagesStation GroundingFABIANO FREIRE DA SILVANo ratings yet
- article-STL Magnetic LoopDocument7 pagesarticle-STL Magnetic Loopemulador05No ratings yet
- P Ake You Whole House Wiring A Huge TV Antennap or So Say The Ads For This Scam DeviceDocument3 pagesP Ake You Whole House Wiring A Huge TV Antennap or So Say The Ads For This Scam DeviceAlvin M AlcaynoNo ratings yet
- HF Active Loop AntennaDocument10 pagesHF Active Loop Antennalu1agpNo ratings yet
- Endfed Halfwave DipolesDocument12 pagesEndfed Halfwave DipolesJean-Marie FrancoisNo ratings yet
- What Is A "Good Ground?": Joe Carr's Radio Tech-NotesDocument7 pagesWhat Is A "Good Ground?": Joe Carr's Radio Tech-NotesSatish RajuNo ratings yet
- Aterramento Da EstaçãoDocument185 pagesAterramento Da EstaçãoAnízio Luiz Freitas de MesquitaNo ratings yet
- SWR Meters Make You StupidDocument16 pagesSWR Meters Make You StupidJose MesquitaNo ratings yet
- The Dark Side of The Conjugate Match (Archive) - QRZ ForumsDocument101 pagesThe Dark Side of The Conjugate Match (Archive) - QRZ ForumsKate Ebneter100% (1)
- Types of AntennasDocument10 pagesTypes of AntennasKevinAngeloMaNo ratings yet
- 2.4-GHz Patch AntennasDocument3 pages2.4-GHz Patch AntennasHam Radio HSMMNo ratings yet
- Saturn 1Document8 pagesSaturn 1Adytya MahawardhanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Radio2Document4 pagesChapter 4 - Radio2pythagorus_banNo ratings yet
- Antennas For Low Power Wireless ApplicationsDocument19 pagesAntennas For Low Power Wireless ApplicationsRafi MohammadNo ratings yet
- ArialDocument13 pagesArialhackinsteinNo ratings yet
- Antennas For Low Power Applications: AN36 AN36A-070898Document16 pagesAntennas For Low Power Applications: AN36 AN36A-070898api-26731722No ratings yet
- Features, Electrical Design, and Efficiency of The Rubber Duck AntennaDocument11 pagesFeatures, Electrical Design, and Efficiency of The Rubber Duck AntennajackNo ratings yet
- Antenna UnUn Article 2Document12 pagesAntenna UnUn Article 2Demetrius CioncaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Operating On 160mDocument9 pagesAn Introduction To Operating On 160mTaufiq Fahlifi YfzerobrrNo ratings yet
- Radio Am y AmplificadorDocument16 pagesRadio Am y AmplificadorLuis HaugNo ratings yet
- 160-20m LOG Loop-On-Ground Page 01 RadioReference - Com ForumsDocument11 pages160-20m LOG Loop-On-Ground Page 01 RadioReference - Com ForumstlebrykNo ratings yet
- BBTD Antenna Presentation PDFDocument11 pagesBBTD Antenna Presentation PDFgolf1rvdNo ratings yet
- DSB 75Document4 pagesDSB 75Cibi CristianNo ratings yet
- pd8 ModifikacijaDocument5 pagespd8 ModifikacijaprezimeNo ratings yet
- 300 Ohm Twin-Lead J-Pole Portable AntennaDocument3 pages300 Ohm Twin-Lead J-Pole Portable Antennakc0fzzNo ratings yet
- Ground Loops On ElectronicsDocument17 pagesGround Loops On Electronicsshadowling2013No ratings yet
- Antenna Tip1Document3 pagesAntenna Tip1mustafa.karacaNo ratings yet
- Horisontal Loop Antenna For Shortwave Listening and Amateur Radio UseDocument7 pagesHorisontal Loop Antenna For Shortwave Listening and Amateur Radio UseBig DaveNo ratings yet
- Endfed6 40Document8 pagesEndfed6 40Leopoldo AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Loop AntennaDocument4 pagesLoop AntennaGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Endfedz Ef-Swl: HF End Fed Receive AntennaDocument4 pagesEndfedz Ef-Swl: HF End Fed Receive AntennaKane Wilson GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Multi Band EFHWDocument9 pagesMulti Band EFHWCosmyn Zaharia100% (1)
- Using The Small Loop Antenna: Joe Carr's Radio Tech-NotesDocument8 pagesUsing The Small Loop Antenna: Joe Carr's Radio Tech-Notesbahriun syahriNo ratings yet
- My Mag LoopDocument4 pagesMy Mag LoopmorristhecatNo ratings yet
- Passive Solar Water HeaterDocument5 pagesPassive Solar Water HeaterMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- Kenwood KDC-316S Service ManualDocument18 pagesKenwood KDC-316S Service ManualMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- AA5TB - Homebrew CW PaddlesDocument1 pageAA5TB - Homebrew CW PaddlesMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- K4ICY's Home-Brew CW PaddleDocument1 pageK4ICY's Home-Brew CW PaddleMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- FS-T4A - Manual (HK - T4A) - Rádio PDFDocument15 pagesFS-T4A - Manual (HK - T4A) - Rádio PDFMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
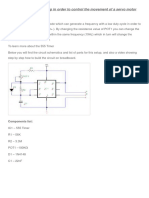
- Using A 555 Timer Chip in Order To Control The Movement of A Servo MotorDocument1 pageUsing A 555 Timer Chip in Order To Control The Movement of A Servo MotorMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- Simple Electronic KeyerDocument1 pageSimple Electronic KeyerMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- A $20 HF Mobile Antenna: A Few Hours of Fun With PVC and Wire and You've Got Yourself A Respectable Road Radiator!Document4 pagesA $20 HF Mobile Antenna: A Few Hours of Fun With PVC and Wire and You've Got Yourself A Respectable Road Radiator!Marckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- The G4Zu.... Spider Beam...... SkypperDocument1 pageThe G4Zu.... Spider Beam...... SkypperMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- 176 Gazette 2014-12 1 2014Document274 pages176 Gazette 2014-12 1 2014Rajesh Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Filing of ReturnsDocument10 pagesFiling of ReturnsSayudh SarkarNo ratings yet
- "Michael, Waiting" - Mikey Havoc, Metro, Jan-Feb 2012Document5 pages"Michael, Waiting" - Mikey Havoc, Metro, Jan-Feb 2012Metro magazine0% (1)
- Naskah - Jamita 2 Kronika 9 1-8, Erlast Laban Ponjot, S.THDocument8 pagesNaskah - Jamita 2 Kronika 9 1-8, Erlast Laban Ponjot, S.THmarisonNo ratings yet
- Rexroth Lubrication GuideDocument28 pagesRexroth Lubrication Guidefurkan100% (1)
- Technical Report On Student S IndustrialDocument41 pagesTechnical Report On Student S IndustrialChinwuba Samuel EbukaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Measures: CEQUAKE430-E41 Group 3Document25 pagesEarthquake Measures: CEQUAKE430-E41 Group 3Eulecris MartinNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Essentials of Athletic Injury Management 10th Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Essentials of Athletic Injury Management 10th Edition PDF Scribdjune.thompson131100% (48)
- Ncma Tek: Concrete Masonry Basement Wall Construction TEK 3-11Document6 pagesNcma Tek: Concrete Masonry Basement Wall Construction TEK 3-11SugarPOP666No ratings yet
- Banking Skills ResumeDocument5 pagesBanking Skills Resumec2zgddnx100% (1)
- Weak Regulatory FrameworksDocument9 pagesWeak Regulatory FrameworksDanil GheatauNo ratings yet
- Safety Seal DatabaseDocument46 pagesSafety Seal DatabaseLOUIE ADUCALNo ratings yet
- Terminal KasugaDocument16 pagesTerminal Kasugameida suryani100% (1)
- 2007 COST Workshop Meeting The Needs of Gifted Children and Adolescents - Towards A European RoadmapDocument43 pages2007 COST Workshop Meeting The Needs of Gifted Children and Adolescents - Towards A European RoadmapMustafa YAVUZNo ratings yet
- Un High Seas TreatyDocument8 pagesUn High Seas Treatyapi-662605390No ratings yet
- Ayuba Grace Manga Phone Number: 08164655929Document4 pagesAyuba Grace Manga Phone Number: 08164655929Martins MatthewNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Strong Password: "L Kout" InitiativeDocument17 pagesChoosing A Strong Password: "L Kout" InitiativeSaladin KamarudinNo ratings yet
- GradingDocument59 pagesGradingsudiptouniv100% (2)
- China Water Purifier Production: 4.2.2 by SegmentDocument3 pagesChina Water Purifier Production: 4.2.2 by SegmentWendell MerrillNo ratings yet
- Chromium VI Azo Report enDocument14 pagesChromium VI Azo Report enBeshoy RedaNo ratings yet
- Roman Catalogs ROMAN Interior 2015 PDFDocument89 pagesRoman Catalogs ROMAN Interior 2015 PDFVidia Deasinta Kusuma ChandraNo ratings yet
- Brave New World - Penguin Readers - Aldous Huxley - PDFDocument280 pagesBrave New World - Penguin Readers - Aldous Huxley - PDFmuddasirNo ratings yet
- School of Graduate StudiesDocument184 pagesSchool of Graduate StudiesAbraham OmomhenleNo ratings yet
- XIAMETER™ PMX-0245 Cyclopentasiloxane: Features & BenefitsDocument5 pagesXIAMETER™ PMX-0245 Cyclopentasiloxane: Features & Benefitsrafaeldelperu1982No ratings yet