Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Febrile Seizures v19 Web
Uploaded by
Akira MasumiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Febrile Seizures v19 Web
Uploaded by
Akira MasumiCopyright:
Available Formats
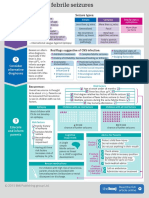
Managing febrile seizures
By Will Stahl-Timmins
Definition: Seizure types:
Childhood seizure Simple Complex Febrile status
1 After one month of age
Child has febrile illness Less than 15 mins More than 15 mins
epilepticus
More than
Is this a No CNS infection Generalised Focal
30 mins
No previous neonatal
febrile or unprovoked seizures No recurrence May have
seizure? within 24 hours repetitive seizures
Doesn’t meet criteria for other
acute symptomatic seizures No postictal Todd’s paresis
—International League Against Epilepsy pathology may be present
Beware an altern- Red flags suggestive of CNS infection: Any physical signs of
ative diagnosis, Antibiotic treatment Complex febrile seizures meningitis/encephalitis
especially if the • Bulging fontanelle
2 fever is less
than 38°C, or in
History of irritability, decreased feeding or lethargy
Incomplete Postictal symptoms
• Focal neurological signs
• Neck stiffness
infants younger immunisation: lasting more than 1 hour
Consider than 6 months.
• Photophobia
• Haemophilus • Limited social response
alternative Causes could influenzae B • Altered consciousness !
Symptoms and signs of
meningeal irritation may
diagnoses include CNS infec- • Streptococcus • Neurological deficit be absent in children
tions or other pneumoniae • Drowsiness under 2 years of age.
causes of fever.
Recurrence: Risk factors
Age at onset under 18 months
Overall recurrence is thought Fever less than 39°C
to be about 1 in 3. Parents can First degree relative has history of febrile seizure
be reassured that recurrence Shorter duration of fever before seizure (<1 hour)
is rare in children with no risk Multiple seizures during the same febrile illness
factors. Day nursery attendance
Epilepsy Children with no risk factors Children with all risk factors
Most children with
FS do not develop
an epilepsy.
3 Risk factors
Family history 4 in 100 80 in 100
Educate of epilepsy chance of further seizures chance of further seizures
and inform Complex febrile
parents seizure Cognitive Advice for Parents
Neurodevelop- impairment
mental Protect child from injury
impairment A single During Do not restrain child
simple seizure
Having all three Do not put anything in their mouth
febrile seizure
risk factors poses no threat Check airway
increases risk of to a child’s cognitive If seizure Place child in recovery position
epilepsy to 50%. development. ends
within 5 Explain that the child may
minutes be sleepy for up to an hour
Rescue medications Seek medical advice
If seizure
For children with high risk of recurrence, continues Call an ambulance
parents should be provided with longer than Administer rescue treatment
benzodiazepines (midazolam or rectal 5 minutes
diazepam) on discharge.
© 2015 BMJ Publishing group Ltd. Read the full
article online
You might also like
- DSM 5 Mood DisorderDocument9 pagesDSM 5 Mood DisorderErlin IrawatiNo ratings yet
- Nurses ChartingDocument2 pagesNurses ChartingdemethraNo ratings yet
- Obesity Weight Management With HomeopathyDocument6 pagesObesity Weight Management With HomeopathySiddharth MedicareNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Neurology - Pediatric Epilepsy SyndromeDocument6 pagesPediatric Neurology - Pediatric Epilepsy Syndromemkct111100% (1)
- Clinical Microbiology and Infection: Original ArticleDocument6 pagesClinical Microbiology and Infection: Original ArticleAkira Masumi100% (1)
- Josephine Morrow: Guided Reflection QuestionsDocument3 pagesJosephine Morrow: Guided Reflection QuestionsElliana Ramirez100% (1)
- Late SSSTDocument121 pagesLate SSSTSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizureDocument40 pagesFebrile SeizureMerry AngelineNo ratings yet
- Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome: HistoryDocument6 pagesMultiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome: HistoryJasmine BaduaNo ratings yet
- Meeting Special Needs: A practical guide to support children with EpilepsyFrom EverandMeeting Special Needs: A practical guide to support children with EpilepsyNo ratings yet
- Benign Epilepsies - Part 1Document35 pagesBenign Epilepsies - Part 1Azeem Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Bells Palsy Handbook Facial Nerve Palsy or Bells Palsy Facial Paralysis Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Face Exercises ... (Alan MC Donald DR Alexa Smith) (Z-Library)Document94 pagesBells Palsy Handbook Facial Nerve Palsy or Bells Palsy Facial Paralysis Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Face Exercises ... (Alan MC Donald DR Alexa Smith) (Z-Library)mayakhoNo ratings yet
- EPILEPSY-lesson-plan PUSHPDocument23 pagesEPILEPSY-lesson-plan PUSHPPushp LataNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizures Epilepsy OSCE Counselling PaediatricsDocument6 pagesFebrile Seizures Epilepsy OSCE Counselling PaediatricsJJ Lim100% (1)
- Febrile SeizureDocument16 pagesFebrile SeizureRashed Shatnawi100% (1)
- I. Acute Convulsions:: CNS Tonsillitis Otitis MediaDocument2 pagesI. Acute Convulsions:: CNS Tonsillitis Otitis MediaJinky MonteagudoNo ratings yet
- NCP Proper CholecystectomyDocument2 pagesNCP Proper CholecystectomyGail Lian SantosNo ratings yet
- Case 2: With Lawrence Richer and Angelo MikrogianakisDocument8 pagesCase 2: With Lawrence Richer and Angelo MikrogianakisSonam SonamNo ratings yet
- Counselling On Febrile SeizureDocument4 pagesCounselling On Febrile SeizureYasmin SadongNo ratings yet
- Clipp 19 PDFDocument9 pagesClipp 19 PDFPrashant MishraNo ratings yet
- 18.d SeizuresDocument6 pages18.d SeizuresSamantha LuiNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizuresDocument3 pagesFebrile SeizuresAbdalrahman AhmedNo ratings yet
- DAY 2 Febrile Seizure Kuliah MHSDocument45 pagesDAY 2 Febrile Seizure Kuliah MHSAdhi WiratmaNo ratings yet
- Febrile Convulsions Clinical Guideline V4.0 February 2020Document10 pagesFebrile Convulsions Clinical Guideline V4.0 February 2020AzmiNo ratings yet
- Febrile Convulsion - SeizuresDocument20 pagesFebrile Convulsion - Seizuressai saiNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizure: DefinitionDocument5 pagesFebrile Seizure: DefinitionRe-zha 'Putra'No ratings yet
- Terapi Kejang DemamDocument5 pagesTerapi Kejang DemamWulan MeilaniNo ratings yet
- Benign Febrile Seizure: PediatricsDocument2 pagesBenign Febrile Seizure: PediatricsKrista P. AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizure: Presented by Raksha DhakalDocument22 pagesFebrile Seizure: Presented by Raksha Dhakalsagar poudelNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy / Seizures: Roche'e Aguarin BSN - IiiDocument31 pagesEpilepsy / Seizures: Roche'e Aguarin BSN - IiiKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- Febrile Convulsion UHL Paediatric Emergency Department GuidelineDocument4 pagesFebrile Convulsion UHL Paediatric Emergency Department GuidelineAmila ShyamalNo ratings yet
- Seizures:epilepsyDocument8 pagesSeizures:epilepsysmitha lakkavallyNo ratings yet
- App To Child With SeizureDocument58 pagesApp To Child With Seizurear bindraNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics (Edition 20.) - Phialdelphia, PA: ElsevierDocument2 pagesPediatrics (Edition 20.) - Phialdelphia, PA: ElsevierJoherNo ratings yet
- Seizures PedsDocument1 pageSeizures PedsAisha Baniyas??No ratings yet
- Seizures in Childhood: John Bradford Ingram M.D. Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Division of Child NeurologyDocument50 pagesSeizures in Childhood: John Bradford Ingram M.D. Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Division of Child NeurologyTaylor ChristianNo ratings yet
- Convulsions, Not Elsewhere Classified: Lee Chun YengDocument28 pagesConvulsions, Not Elsewhere Classified: Lee Chun YengradverNo ratings yet
- Symposium On Seizure - CMEDocument42 pagesSymposium On Seizure - CMEHumaida Hasan SamiraNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizures: Janith ChandrakumaraDocument14 pagesFebrile Seizures: Janith ChandrakumaraJanith ChandrakumaraNo ratings yet
- Topics For Oral Exam FEBRILE ZEIZURE Necrotizing EnterocolitisDocument3 pagesTopics For Oral Exam FEBRILE ZEIZURE Necrotizing EnterocolitisPCRMNo ratings yet
- Patient Info/doctor/febrile-ConvulsionsDocument6 pagesPatient Info/doctor/febrile-Convulsionsholly theressaNo ratings yet
- Febrile Convulsion: Background To ConditionDocument4 pagesFebrile Convulsion: Background To ConditionAbdelrahmanEmbabiNo ratings yet
- What Is A Febrile ConvulsionDocument14 pagesWhat Is A Febrile ConvulsionJazendra TootNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Disorders in Children: Pediatric NeurologyDocument59 pagesNeurologic Disorders in Children: Pediatric NeurologyGelsey Gelsinator JianNo ratings yet
- Pediatric SeizuresDocument64 pagesPediatric SeizuresShobithaNo ratings yet
- Seizures Inpediatric Aand Epilepsy No VideoDocument42 pagesSeizures Inpediatric Aand Epilepsy No VideoAbdullah GadNo ratings yet
- 1 Febrile Seizures DDocument30 pages1 Febrile Seizures DDorjee SengeNo ratings yet
- Katie Doran, DO FAAP Division of Urgent Care Children's Mercy Hospital October 17, 2019Document36 pagesKatie Doran, DO FAAP Division of Urgent Care Children's Mercy Hospital October 17, 2019wisnusigitpratamaNo ratings yet
- Osce ped extern รวมเฉลยถึงรุ่นแปดโรสองDocument37 pagesOsce ped extern รวมเฉลยถึงรุ่นแปดโรสองNonthapat PaesarochNo ratings yet
- Referat Kejang Pada Anak - Silvi PrintDocument32 pagesReferat Kejang Pada Anak - Silvi PrintSilvi AprianiNo ratings yet
- BFS Case DiscxnDocument23 pagesBFS Case DiscxnLennon Ponta-oyNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Febrile SeizuresDocument4 pagesCase Report: Febrile SeizureswisnusigitpratamaNo ratings yet
- Seizures and The Epilepsies in Infants, Children, and AdolescentsDocument12 pagesSeizures and The Epilepsies in Infants, Children, and AdolescentsCecille Ann CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizures-FinalyrDocument41 pagesFebrile Seizures-Finalyrbilal aslamNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizuresDocument27 pagesFebrile SeizuresAman SamNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy and Seizure PresentationDocument21 pagesEpilepsy and Seizure PresentationPooja IyyarNo ratings yet
- Febrile ConvulsionDocument20 pagesFebrile ConvulsionnoblefxNo ratings yet
- 02 - IMCI Day 2Document6 pages02 - IMCI Day 2Sweet Zhel NarretoNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizure: Satanun Charoencholvanich, MDDocument10 pagesFebrile Seizure: Satanun Charoencholvanich, MDAPETT WichaiyoNo ratings yet
- Febrile Convulsions: Prepared By: Dr. Basem Abu-Rahmeh Directed By: Dr. Afaf Al-AriniDocument15 pagesFebrile Convulsions: Prepared By: Dr. Basem Abu-Rahmeh Directed By: Dr. Afaf Al-AriniAlfian Hari GunawanNo ratings yet
- Kejang Demam: Apakah Kejang Demam Itu? Apa Ciri-Ciri Kejang Demam?Document2 pagesKejang Demam: Apakah Kejang Demam Itu? Apa Ciri-Ciri Kejang Demam?Imam Adi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Neurologic DisorderDocument77 pagesNeurologic DisorderJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy SyndromesDocument6 pagesEpilepsy SyndromesHanin AlSiniNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizuresDocument24 pagesFebrile SeizuresShrikant Hemant JoshiNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizure and Epilepsy PDFDocument36 pagesFebrile Seizure and Epilepsy PDFMuhammad Amiro RasheeqNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizuresDocument4 pagesFebrile Seizuresmgonzalez_29No ratings yet
- Febrile Seizures 12 - 1 - 2019 3Document12 pagesFebrile Seizures 12 - 1 - 2019 3ninta karinaNo ratings yet
- Febrile Convulsions & Epilepsy (L)Document25 pagesFebrile Convulsions & Epilepsy (L)Touseef Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Black Neon Green Neon Pink Trendy Illustrative Creative PresentationDocument18 pagesBlack Neon Green Neon Pink Trendy Illustrative Creative PresentationLorren Frances Marie CalsarinNo ratings yet
- Simple Professional Virtual Meeting by SlidesgoDocument45 pagesSimple Professional Virtual Meeting by SlidesgoAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Lessons Learned About COVID-19 by SlidesgoDocument34 pagesLessons Learned About COVID-19 by SlidesgoAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccine Breakthrough - Case Investigation and Reporting by SlidesgoDocument53 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccine Breakthrough - Case Investigation and Reporting by SlidesgoAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Sports and Physical Activity During COVID-19 by SlidesgoDocument56 pagesSports and Physical Activity During COVID-19 by SlidesgoBeldia Cáceres CataldoNo ratings yet
- Art Subject For Elementary - 3rd Grade - Performing Arts by SlidesgoDocument56 pagesArt Subject For Elementary - 3rd Grade - Performing Arts by SlidesgoAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Simple Professional Virtual Meeting by SlidesgoDocument45 pagesSimple Professional Virtual Meeting by SlidesgoAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Sports and Physical Activity During COVID-19 by SlidesgoDocument56 pagesSports and Physical Activity During COVID-19 by SlidesgoBeldia Cáceres CataldoNo ratings yet
- Imaging in The Jaundiced Child PDFDocument14 pagesImaging in The Jaundiced Child PDFRahma Puji LestariNo ratings yet
- Art Subject For Elementary - 3rd Grade - Performing Arts by SlidesgoDocument56 pagesArt Subject For Elementary - 3rd Grade - Performing Arts by SlidesgoAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccine Breakthrough - Case Investigation and Reporting by SlidesgoDocument53 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccine Breakthrough - Case Investigation and Reporting by SlidesgoAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizures v19 WebDocument1 pageFebrile Seizures v19 WebAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin and Cipro Oxacin Inhibit Interleukin-Secretion Without Disrupting Human Sinonasal Epithelial Integrity in VitroDocument8 pagesAzithromycin and Cipro Oxacin Inhibit Interleukin-Secretion Without Disrupting Human Sinonasal Epithelial Integrity in VitroAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Lessons Learned About COVID-19 by SlidesgoDocument34 pagesLessons Learned About COVID-19 by SlidesgoAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Biomarkers During Bacterial Acute RhinosinusitisDocument6 pagesInflammatory Biomarkers During Bacterial Acute RhinosinusitisAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: Chronic Rhinosinusitis Without Nasal PolypsDocument16 pagesHHS Public Access: Chronic Rhinosinusitis Without Nasal PolypsAnnisa RahmadhaniaNo ratings yet
- Association Between Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and Later Risk of CardiomyopathyDocument8 pagesAssociation Between Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and Later Risk of CardiomyopathyPujiyono SuwadiNo ratings yet
- DS Boys HeadCirc 2-20yearsDocument1 pageDS Boys HeadCirc 2-20yearsInayahMaulaNo ratings yet
- Medicina: Inflammation and Endotyping in Chronic Rhinosinusitis-A Paradigm ShiftDocument13 pagesMedicina: Inflammation and Endotyping in Chronic Rhinosinusitis-A Paradigm ShiftAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- DS Boys HeadCirc Birthto36moDocument1 pageDS Boys HeadCirc Birthto36moPeregrine Albertus Ricco AzaliNo ratings yet
- Traumatologi 2015Document5 pagesTraumatologi 2015Jhun EjuNo ratings yet
- The Association of Leptospermum Honey With Cytokine Expression in The Sinonasal Epithelium of Chronic Rhinosinusitis PatientsDocument7 pagesThe Association of Leptospermum Honey With Cytokine Expression in The Sinonasal Epithelium of Chronic Rhinosinusitis PatientsAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Sarcomas of Bone - Clinical GateDocument8 pagesPediatric Sarcomas of Bone - Clinical GateAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- DS Girls Height 2to20yearsDocument1 pageDS Girls Height 2to20yearsAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Ds Girls Length Birthto36moDocument1 pageDs Girls Length Birthto36moWahyu DinataNo ratings yet
- Departemen Biostatistika Dan Kependudukan, Fakultas Kesehatan Masyarakat Kampus C UNAIR Mulyorejo Alamat Korespondensi: Alvita Brilliana R.ADocument11 pagesDepartemen Biostatistika Dan Kependudukan, Fakultas Kesehatan Masyarakat Kampus C UNAIR Mulyorejo Alamat Korespondensi: Alvita Brilliana R.AHeiddy Ch SumampouwNo ratings yet
- Effect of High Add Power, Medium Add Power, or Single-VisionDocument10 pagesEffect of High Add Power, Medium Add Power, or Single-VisionAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Tumors and Masses - Clinical GateDocument9 pagesOrthopaedic Tumors and Masses - Clinical GateAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- The Association of Leptospermum Honey With Cytokine Expression in The Sinonasal Epithelium of Chronic Rhinosinusitis PatientsDocument7 pagesThe Association of Leptospermum Honey With Cytokine Expression in The Sinonasal Epithelium of Chronic Rhinosinusitis PatientsAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Meconium Aspiration SyndromeDocument13 pagesMeconium Aspiration SyndromeJhing Rodriguez Borjal100% (1)
- Health Certificate: Personal Details: Section ADocument3 pagesHealth Certificate: Personal Details: Section APrashob SugathanNo ratings yet
- Nitazoxanide, A New Thiazolide Antiparasitic AgentDocument8 pagesNitazoxanide, A New Thiazolide Antiparasitic AgentHenry CollazosNo ratings yet
- Microbiology CaseDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Caseclower112100% (2)
- HemothoraxDocument13 pagesHemothoraxسما كركوكليNo ratings yet
- Botany 4Document6 pagesBotany 4Upadhyay HarshitNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAkiraMamoNo ratings yet
- Campy Lo Bacterio SisDocument14 pagesCampy Lo Bacterio SisHarikrishnan NamNo ratings yet
- RANITIDINEDocument2 pagesRANITIDINEChoox PriiNo ratings yet
- Scheuermanns DiseaseDocument26 pagesScheuermanns DiseaseMihnea VulpeNo ratings yet
- Amit ReportDocument3 pagesAmit ReportXlramitNo ratings yet
- Use of The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) As A Screening Tool in Prisons: Results of A Preliminary StudyDocument5 pagesUse of The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) As A Screening Tool in Prisons: Results of A Preliminary StudyRafael MartinsNo ratings yet
- Gen Medicine - Finalized Scheme of ExaminationDocument30 pagesGen Medicine - Finalized Scheme of Examinationsp_rao2000No ratings yet
- Poly-Trauma: by Dr. Elias Ahmed October 2003Document14 pagesPoly-Trauma: by Dr. Elias Ahmed October 2003Sisay FentaNo ratings yet
- Acute Painful ScrotumDocument15 pagesAcute Painful ScrotumthinkercolNo ratings yet
- LyphomaDocument7 pagesLyphomaNambuye Midyero AhmedNo ratings yet
- SpermatoceleDocument2 pagesSpermatocelemrizkidm2301No ratings yet
- Spinal Tumors Intra-Extra (Turgut Tali)Document92 pagesSpinal Tumors Intra-Extra (Turgut Tali)Drbaddireddy RayuduNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN 2 - Written ReportDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN 2 - Written ReportAkira PinedaNo ratings yet
- Monitoring An IV Site and InfusionDocument4 pagesMonitoring An IV Site and InfusionAlex Cacayan CortinaNo ratings yet
- Parkinsons Disease FinalDocument2 pagesParkinsons Disease Finalapi-266655633No ratings yet
- Cataracts The Mayo ClinicDocument6 pagesCataracts The Mayo ClinicJandz MNNo ratings yet