Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diagnostic Approach of Malignant Lesions in The Jaws PDF
Uploaded by
mahnoor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views1 pageOriginal Title
diagnostic-approach-of-malignant-lesions-in-the-jaws.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views1 pageDiagnostic Approach of Malignant Lesions in The Jaws PDF
Uploaded by
mahnoorCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
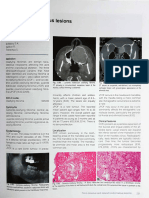
A Radiographic Features Of Oral Malignancy
B D F (1) F (3)
Histopathological Key Of Malignant Jaw Lisions C E F (2) F (4)
A, Ill-defined
01 Primary Malignant Tumors
invasive borders
01 Malignant Odontogenic Tumors followed by bone
destruction. C, Tumor invasion along E, Bone destruction
01 Malignant Vascular Tumors
the periodontal ligament around teeth,
02 Malignant Maxillofacial Bone and Cartilage Tumors space (PDLS) causing “floating teeth”
B, Destruction of the irregular thickening. in space. F, Four types of effects on cortical bone and periosteal reaction:
03 Malignant Neural Intraosseous Tumors
cortical boundary
(floor of maxillary (2) laminated "onion-skin“ (3) destruction of cortical
04 Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues D, Multifocal lesions located at root apices (1) cortical bone (4) a spiculated or sunray
bone with periosteal
antrum. and in the papilla of a developing tooth destruction without periosteal reaction with “hair-on-end” type of
reaction at the periphery
destroying the crypt cortex and displacing periosteal reaction. destruction of the cortical periosteal reaction.
07 Metastatic Carcinomas bone and the new forming Codman’s
the developing tooth in an occlusal direction. triangles.
periosteal bone.
Early Stage Late Stage
Solitary Multifocal Solitary Multifocal
Unilocular Unilocular Unilocular Unilocular Unilocular Multilocular Teeth Associated No Teeth Association
Teeth Associated No Teeth Association Multilocular No Teeth Association
Teeth Associated No Teeth Association
Radiolucent Mixed
Primary Intraosseous Primary Intraosseous Primary Intraosseous
Carcinoma, NOS Carcinoma, NOS Carcinoma, NOS Leukemia
Primary Odontogenic Sarcomas Chondrosarcoma
Intraosseous
Mucoepidermoid
Intraosseous
Mucoepidermoid
Multiple Myeloma Intraosseous Metastatic Carcinomas Primary Intraosseous Hepatosplenomegaly Multiple Myeloma
Carcinoma Carcinoma Carcinoma, NOS Osteosarcoma Carcinoma, NOS Lymphadenopathy
+ve CKs
Mesenchymal Any one or more of the
Metastatic Primary Intraosseous Chondrosarcoma
Ameloblastic Carcinoma Ameloblastic Carcinoma
Carcinomas Intraosseous Intraosseous following: CRAB,
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma, NOS
Osteolytic, Mixed or Mucoepidermoid Foci of leukemic Widening of the Clonal bone marrow
Solitary Carcinoma Carcinoma cells (chloromas) PDLS plasma cell ≥10-60%,
Intraosseous Plasmacytoma Osteoblastic: Intraosseous Ewing Sarcoma
Mucoepidermoid +ve CD38 Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Destruction of bone crypts of Abnormal serum free
Carcinoma
+ve CD138
• Breast • Lung Ameloblastic Charcterized by laminar periosteal
developing teeth. light chain ratio, >1 focal
Premature loss of deciduous
+ve Kappa • Prostate • Thyroid Carcinoma "onion-skin" new bone formation. widening of the
PDLS
“sunray” spicules
or “hair-on-end”
Unheald tooth Floating Teeth Ameloblastic Carcinoma teeth. lesions on MRI (at least
OR Lambda • Kidney Ameloblastic Carcinoma Burkitt’s Lymphoma socket
5mm in size).
+ve Alcian blue Soft tissue mass.
+ve Mucicarmine Low-Grade Osteosarcoma Ghost Cell Angiosarcoma Analysis
Chondrosarcoma Widening of the
of
Odontogenic Carcinoma PDLS +ve CD31
ALL AML
(Atypical blasts) (Anisopoikilocytosis)
Characterized by: +ve FLI 1 Cyto-
+ve CD99 +ve CD34
arcs and whorls of Chondrosarcoma osteoid matrix formation Chondroblastic osteosarcoma
+ve FLI-1
genetics
calcification Clear Cell Destruction of bone crypts
with radiolucent
Odontogenic Carcinoma of developing teeth.
+ve Factor VIII
CLL
centers
-ve HHV-8 CML
Ameloblastic Carcinoma
Premature loss of Chondrosarcoma -ve GLUT-1
(Smudge cells)
Leukemia deciduous teeth.
+ve S100 +ve CK14/CK19 Angiosarcoma Lymphoma
+ve S0X9
+ve EMA Soft tissue mass and Mesenchymal
Lymphoma +ve PAS
nodal involvement. Chondrosarcoma Widening of the PDLS +ve CD38
+ve CD138
Metastatic -ve S100 Kaposi Sarcoma Biphasic malignant tumour (small round +ve Kappa
Carcinomas blue cells and islands of differentiated Spindle Epithelioid OR Lambda
Metastatic hyaline cartilage) Soft tissue mass and nodal
Sclerosing Odontogenic Starry sky pattern
Carcinomas Soft tissue mass. involvement.
Carcinoma +ve LCA
The malignant cells Perineural +ve LCA B cell markers:
+ve CD20 Slit-like spaces +ve SOX9 +ve CD20
form single-file line invasion +ve c-MYC +ve CD31 T cell markers: Metastatic
+ve CD34 HEY1- NCOA2 +ve CD3
Carcinomas
+ve Factor VIII
+ve Podoplanin fusions +ve CD5
+ve HHV8
Malignant Peripheral
+ve CK19 Nerve Sheeth Tumor Epithelioid Metastatic Carcinomas
Presented by: +ve CK5/6
Hemangioendothelioma References:
Safaa Mohammed El-Baz Odontogenic
Carcinosarcoma
Spindle cells
+/-herring bone
Ghost Cell
Odontogenic Carcinoma 1-El-Naggar AK et al (2017) WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumours.
A s s is t a n t Le c tu re r, B UE pattern
+ve CD31
+ve CD34
+ve FLI1 2-Koenig, Lisa, Tamimi, Dania, Petriko, G. (2018) Diagnostic imaging oral and
P hD C an d i d at e , C airo Un ive r s it y -ve GLUT1 maxillofacial. second ed. Manitoba: Elsevier.
+ve P53 3-White, S. C. and Pharoah, M. J. (2014) Oral Radiology: Principles and Interpretation.
Under Subervision of:
+ve Ki-67
(Both markers are Epithelioid cells
7th ed. Mosby: Elsevier.
4-http://www.pathologyoutlines.com
Dr. Amal Hassan Abdelrahman
positive in both
epithelial and
connective tissue Odontogenic Sarcomas 5-https://librepathology.org
components)
Pro fe s s o r O f Oral Pat h o lo gy, C airo U niversity 6-https://www.medscape.com
You might also like
- 50 Famous Proverbs Meaning and ExamplesDocument7 pages50 Famous Proverbs Meaning and ExamplesAnonymous fjFtyLi100% (1)
- A0204 Vaginal HifuDocument14 pagesA0204 Vaginal HifuleanferoNo ratings yet
- Magic Items of The UnderdarkDocument4 pagesMagic Items of The UnderdarkAndré Rodrigues Mano0% (1)
- Mesenteric Venous Thrombosis NejmDocument6 pagesMesenteric Venous Thrombosis NejmJUAN LUIS PASAPERANo ratings yet
- Depressed Fracture: Modul Bedah, July 2021Document31 pagesDepressed Fracture: Modul Bedah, July 2021Muhammad MuhidNo ratings yet
- Clinical Significance of Dental Anatomy, Histology, Physiology, and OcclusionDocument1 pageClinical Significance of Dental Anatomy, Histology, Physiology, and OcclusionTayyuba AslamNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Intra-Osseous Transmigration and Ectopic Eruption of Mandibular Canines: Review of Literature and Report of Nine Additional CasesDocument6 pagesPatterns of Intra-Osseous Transmigration and Ectopic Eruption of Mandibular Canines: Review of Literature and Report of Nine Additional CasesfirmansyahddsNo ratings yet
- Dental Caries: Structure of TeethDocument11 pagesDental Caries: Structure of TeethArturo Trejo VeraNo ratings yet
- Missing Teeth After Maxillofacial Trauma A Case Report and Management ProtocolDocument6 pagesMissing Teeth After Maxillofacial Trauma A Case Report and Management ProtocolAngelia PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Oral Cavity, Salivary Glands and Jaws (K00-K14) : Search (Advanced Search)Document13 pagesDiseases of Oral Cavity, Salivary Glands and Jaws (K00-K14) : Search (Advanced Search)Ria MarthantiNo ratings yet
- Dens Invaginatus: Aetiology, Classification, Prevalence, Diagnosis and Treatment ConsiderationsDocument8 pagesDens Invaginatus: Aetiology, Classification, Prevalence, Diagnosis and Treatment ConsiderationsNur Hasnah HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Mcintyre Orthodontic Update Canine Part 1Document10 pagesMcintyre Orthodontic Update Canine Part 1Carlos MikaelNo ratings yet
- MC Intyre Orthodontic Update Canine Part 1Document9 pagesMC Intyre Orthodontic Update Canine Part 1dr.rhythm sharmaNo ratings yet
- Case Report: A Rare Case of Concrescence of Mandibular Third Molar and Supernumerary Fourth MolarDocument6 pagesCase Report: A Rare Case of Concrescence of Mandibular Third Molar and Supernumerary Fourth MolarClairy TNo ratings yet
- Excl.:: Diseases of The Digestive System (K00-K93)Document5 pagesExcl.:: Diseases of The Digestive System (K00-K93)hestiwidyawatiNo ratings yet
- Modern Endodontic Access and Dentin Conservation Part 1Document10 pagesModern Endodontic Access and Dentin Conservation Part 1Ram sharmaNo ratings yet
- Ramalingam 2019Document9 pagesRamalingam 2019sdadNo ratings yet
- MC Intyre Orthodontic Update Canine Part 1Document10 pagesMC Intyre Orthodontic Update Canine Part 1Jamal AfridiNo ratings yet
- RESORCIÓN CERVICAL EXTERNA Una Revisión. Shanon Patel, BDS, MSC, Shalini Kanagasingam, BDS, MFDSDocument10 pagesRESORCIÓN CERVICAL EXTERNA Una Revisión. Shanon Patel, BDS, MSC, Shalini Kanagasingam, BDS, MFDSIgnacio Glaría BengoecheaNo ratings yet
- Who 2017-244-253Document10 pagesWho 2017-244-253Seba OrtegaNo ratings yet
- RADIOLOGY 2.1e Skull FracturesDocument1 pageRADIOLOGY 2.1e Skull FracturesZazaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disorders Affecting Tooth StructureDocument59 pagesDevelopmental Disorders Affecting Tooth StructureJerry TurtleNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Imaging in Oral IntechDocument27 pagesDiagnostic Imaging in Oral Intechjamal100% (1)
- A 60-Year-Old Male With Gradual Loss of Tooth Surface: Presentation of Case Differential DiagnosisDocument4 pagesA 60-Year-Old Male With Gradual Loss of Tooth Surface: Presentation of Case Differential DiagnosisAlan MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Overdenture Abutments Support Fixed Partial DentureDocument4 pagesOverdenture Abutments Support Fixed Partial DentureDeasireeNo ratings yet
- DS125-2019 Root Caries 2019-10-29sDocument12 pagesDS125-2019 Root Caries 2019-10-29sZNo ratings yet
- The Cracked Tooth. Histopathologic and Histobacteriologic AspectsDocument11 pagesThe Cracked Tooth. Histopathologic and Histobacteriologic AspectsArturo Trejo VeraNo ratings yet
- The Epidemic of Cracked and Fractured TeethDocument4 pagesThe Epidemic of Cracked and Fractured TeethThe Bioclear ClinicNo ratings yet
- Anomalias Goaz SextaDocument30 pagesAnomalias Goaz SextaPablo GalindoNo ratings yet
- Qi 49 10 Kern p789Document10 pagesQi 49 10 Kern p789NonoNo ratings yet
- A Bilocular Radicular Cyst in The Mandible With Tooth Structure Components InsideDocument5 pagesA Bilocular Radicular Cyst in The Mandible With Tooth Structure Components InsideRoza LindaNo ratings yet
- Sgarancini,+11 Gie Lavagnoli+GuglielmiDocument8 pagesSgarancini,+11 Gie Lavagnoli+Guglielmiammar slimanNo ratings yet
- Quistes y Tumores Odontogénicos 1Document9 pagesQuistes y Tumores Odontogénicos 1Rocio CacñahuarayNo ratings yet
- Up-to-Date Approach in The Treatment of Impacted Mandibular Molars: A Literature ReviewDocument9 pagesUp-to-Date Approach in The Treatment of Impacted Mandibular Molars: A Literature Reviewmaria jose peña rojasNo ratings yet
- Dental CariesDocument13 pagesDental CariesDiana Gita MentariNo ratings yet
- Modern Endodontic Access and Directly Conserving DentinDocument5 pagesModern Endodontic Access and Directly Conserving Dentinizeldien5870No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Non-Carious Cervical Lesions - An Ex Vivo Study Using Micro Computed TomographyDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of Non-Carious Cervical Lesions - An Ex Vivo Study Using Micro Computed TomographyRicardo Rodrigues AmaralNo ratings yet
- Non CariousDocument4 pagesNon CariousUpasana BhandariNo ratings yet
- Complex OdontomasDocument1 pageComplex OdontomasAnkita AroraNo ratings yet
- Trauma in EndodonticsDocument49 pagesTrauma in EndodonticseedmdnndNo ratings yet
- Compound Odontoma Associated With Impacted Maxillary Anterior Teeth A Case ReportDocument4 pagesCompound Odontoma Associated With Impacted Maxillary Anterior Teeth A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cavity Configurations For IndirectDocument14 pagesCavity Configurations For IndirectLuciana EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Sara Pavlović Marko PongracDocument34 pagesSara Pavlović Marko Pongraclenami_91No ratings yet
- Endo PerioDocument2 pagesEndo PerioMohammed OmoshNo ratings yet
- CBCT Findings of Periapical Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesCBCT Findings of Periapical Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia: A Case ReportRestaWigunaNo ratings yet
- Pedo 4-DikonversiDocument7 pagesPedo 4-DikonversiFeby ElisabethNo ratings yet
- Sclerotic Lesions of The JawDocument9 pagesSclerotic Lesions of The JawGalgalo GarbichaNo ratings yet
- BCR 2017 220736.fullDocument2 pagesBCR 2017 220736.fullJessica Cuamatzi BaezNo ratings yet
- Oral Biology 1 Lab Manual: Faculty of DentistryDocument41 pagesOral Biology 1 Lab Manual: Faculty of DentistryMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Case Report on Rare Gardner's Syndrome Presenting with Odontogenic MyxomaDocument6 pagesCase Report on Rare Gardner's Syndrome Presenting with Odontogenic MyxomaAnne LydellNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Grafting Employing The Tunnel Technique: A Case Report of Complete Root Coverage in The Anterior MaxillaDocument8 pagesConnective Tissue Grafting Employing The Tunnel Technique: A Case Report of Complete Root Coverage in The Anterior MaxillaMonica MartínezNo ratings yet
- Solitary Intra-Osseous Myofibroma of The Jaw - A Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument8 pagesSolitary Intra-Osseous Myofibroma of The Jaw - A Case Report and Review of LiteratureJean Carlos Barbosa FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Peri: Around Odont: Tooth Logous: Study Itis: Inflammation Principle FibersDocument6 pagesPeri: Around Odont: Tooth Logous: Study Itis: Inflammation Principle FibersBea YmsnNo ratings yet
- Ijed 2022 03 s0340CracksGerdolleBrowetDocument16 pagesIjed 2022 03 s0340CracksGerdolleBrowetJavi Maldonado100% (2)
- Abilityofcone beamcomputerizedtomographytodetectVRFcasereport2011Document5 pagesAbilityofcone beamcomputerizedtomographytodetectVRFcasereport2011Jing XueNo ratings yet
- Cirugia Plastica Periodontal PDFDocument36 pagesCirugia Plastica Periodontal PDFJohnny CHNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Impaksi Caninus Rahang Atas Pada Pemeriksaan Radiograf Panoramik Dan CBCT Sebagai Penunjang OdontomyDocument8 pagesKlasifikasi Impaksi Caninus Rahang Atas Pada Pemeriksaan Radiograf Panoramik Dan CBCT Sebagai Penunjang OdontomyRahmi WastriNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Impaksi Caninus Rahang Atas Pada Pemeriksaan Radiograf Panoramik Dan CBCT Sebagai Penunjang OdontomyDocument8 pagesKlasifikasi Impaksi Caninus Rahang Atas Pada Pemeriksaan Radiograf Panoramik Dan CBCT Sebagai Penunjang OdontomyAlsya Yulia RosidiNo ratings yet
- Orth Update 2023 16 85-90Document6 pagesOrth Update 2023 16 85-90jlkdsjfljsdlfNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Oral CavityDocument13 pagesDiseases of Oral CavityBasway AdhiNo ratings yet
- 1) Fichera 2006 Cavity Configurations For in DirectDocument14 pages1) Fichera 2006 Cavity Configurations For in DirectMarinaNo ratings yet
- ClavusDocument4 pagesClavusargie3333No ratings yet
- Medicinal plants guide with uses and preparationsDocument6 pagesMedicinal plants guide with uses and preparationsCaroline Kim100% (1)
- Acute Paracetamol Poisoning Case Studies ReviewDocument5 pagesAcute Paracetamol Poisoning Case Studies Reviewbiya ao0No ratings yet
- St. Paul University PhilippinesDocument4 pagesSt. Paul University PhilippinesAshley DayagNo ratings yet
- AsbestosDocument4 pagesAsbestoskoketsoNo ratings yet
- 101 Ways To Reduce StressDocument11 pages101 Ways To Reduce StressStephen Comee100% (1)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/21Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/21jamalNo ratings yet
- Manual Breast Manual ExpressionDocument9 pagesManual Breast Manual ExpressionhoneykrizelNo ratings yet
- RFID Chip will Poison Me and Kill me if I Disobey. Microchip Implants - RFID Brain Chip : Crime, Malpratice, Mindcontrol, Sexual Abuse, Brain Abuse, Torture Abuse, Medical Abuse, and The Silent Killers via RFID Brain ChipDocument3 pagesRFID Chip will Poison Me and Kill me if I Disobey. Microchip Implants - RFID Brain Chip : Crime, Malpratice, Mindcontrol, Sexual Abuse, Brain Abuse, Torture Abuse, Medical Abuse, and The Silent Killers via RFID Brain ChipJohanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Medical Parasitology A Self Instructional Text 6th Edition Chapters 2 8 LeventhalDocument18 pagesTest Bank For Medical Parasitology A Self Instructional Text 6th Edition Chapters 2 8 LeventhalSabina Moskowitz100% (36)
- Single Patch Test PDFDocument17 pagesSingle Patch Test PDFmimienamNo ratings yet
- Blood SamplingDocument11 pagesBlood Samplingwiodi nazhofatunnisa umami swNo ratings yet
- Malignant Myopericytoma: Report of A New Case and Review of The LiteratureDocument6 pagesMalignant Myopericytoma: Report of A New Case and Review of The LiteratureRachel AutranNo ratings yet
- Fallopian Tube Infection Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument10 pagesFallopian Tube Infection Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentmustikaweniNo ratings yet
- Pathology and Hematology Exam QuestionsDocument40 pagesPathology and Hematology Exam QuestionsPONNUSAMY P50% (2)
- AlprazolamDocument3 pagesAlprazolamapi-3797941100% (1)
- Electro PDFDocument14 pagesElectro PDFFulg de NeaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics in Interventional RadiologyDocument7 pagesThesis Topics in Interventional Radiologygjfcp5jb100% (2)
- Pharmacy Guidelines and Instructions For DAIDS Clinical Trials Networks March 2016Document41 pagesPharmacy Guidelines and Instructions For DAIDS Clinical Trials Networks March 2016GerifalteNo ratings yet
- S2 Session 1Document3 pagesS2 Session 1s9419No ratings yet
- 23011214560126@70 - Pichay, Loren Sta - Teresa - L230000355933 - 2300013461Document2 pages23011214560126@70 - Pichay, Loren Sta - Teresa - L230000355933 - 2300013461maxor4242No ratings yet
- Description of The StrategyDocument6 pagesDescription of The Strategyiulia9gavrisNo ratings yet
- Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and PolicyDocument4 pagesPsychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and PolicyPerla MontellanoNo ratings yet
- Macadamia Felted Coccid: Eriococcus IronsideiDocument2 pagesMacadamia Felted Coccid: Eriococcus IronsideiAUDIR audirNo ratings yet
- Gua ShaDocument41 pagesGua ShaFerencne Hanis100% (2)
- Why Do We Dream Thesis StatementDocument8 pagesWhy Do We Dream Thesis Statementgbx272pg100% (2)