Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antifungals PDF
Uploaded by
dhamee970 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesThere are several classes of antifungal drugs that work through different mechanisms:
1. Echinocandins block beta-glucan synthesis in fungal cell walls. Azoles like fluconazole inhibit ergosterol formation, reducing membrane permeability. Terbinafine inhibits microtubule formation in dermatophytes.
2. Polyenes like amphotericin B bind to ergosterol in fungal cell membranes, forming pores that allow leakage of ions and killing the cells. It has a broad spectrum but can cause kidney damage.
3. Flucytosine is an antimetabolite that blocks fungal DNA and RNA production. It is converted to
Original Description:
USMLE Antifungal Pharmacology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are several classes of antifungal drugs that work through different mechanisms:
1. Echinocandins block beta-glucan synthesis in fungal cell walls. Azoles like fluconazole inhibit ergosterol formation, reducing membrane permeability. Terbinafine inhibits microtubule formation in dermatophytes.
2. Polyenes like amphotericin B bind to ergosterol in fungal cell membranes, forming pores that allow leakage of ions and killing the cells. It has a broad spectrum but can cause kidney damage.
3. Flucytosine is an antimetabolite that blocks fungal DNA and RNA production. It is converted to
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesAntifungals PDF
Uploaded by
dhamee97There are several classes of antifungal drugs that work through different mechanisms:
1. Echinocandins block beta-glucan synthesis in fungal cell walls. Azoles like fluconazole inhibit ergosterol formation, reducing membrane permeability. Terbinafine inhibits microtubule formation in dermatophytes.
2. Polyenes like amphotericin B bind to ergosterol in fungal cell membranes, forming pores that allow leakage of ions and killing the cells. It has a broad spectrum but can cause kidney damage.
3. Flucytosine is an antimetabolite that blocks fungal DNA and RNA production. It is converted to
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
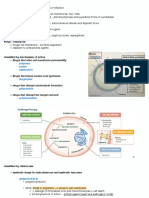
Antifungals
Beta-Glucan Synthesis Blockers
• Echinocandins
Membrane Permeability Agents
• Azoles
o Systemic infections
o Oral bioavailability, some IV
o Cytochrome inducers: Decrease bioavailability
o Toxicity
• Vomiting, diarrhea, rash, hepatoxicity
• Ketoconazole: bad for drug interactions and steroid blocking effects
(Gynecomastia)
o Mechanism
• Inhibit ergosterol formation
• Reduces membrane permeability
▪ Increased leak of cations and nutrients
o Resistance
• Resistance developing due to widespread use
• Reduction of susceptible enzymes to azoles
o Ketoconazole
• Narrow spectrum antifungal
• More adverse than others
• Against chronic candidiasis and derm fungal infections
• Strong inhibitor of Cyt 450 (increase level of other drugs)
• Gynecomastia
o Fluconazole
• Drug of choice in esophageal/oropharyngeal candidiasis
• Oral dose eliminate vaginal candidiasis
• Cryptococcal meningitis (drug of choice)
o Miconazole, Clotrimazole
• Topical
• Well with topical/vaginal, not much systematically
• Combined with steroid; to treat
▪ Tinea corporis
▪ Tinea cruris
▪ Tinea pedis
o Itraconazole
• Wide spectrum
▪ Drug of choice for Blastomyces and Sporothrix
▪ Choice for chromoblastomycosis
▪ Alternate: aspergillus, coccidiosis, Cryptococcus, histoplasma
o Variconazole
• Wider than Itraconazole
▪ Possibly better than amphotericin B
• 30% visual blurring or unknown cause
o Posaconazole
• Widest spectrum
▪ Most species of Candida and Aspergillus
• Only one with activity against Rhizopus
• Terbinafine
• Oral ingestion for skin infection
• Distributed to stratum corneum
• Not be used in patients with porphyria
o Mechanism
• Inhibits microtubule formation in dermatophytes
• Fungistatic: Absorbed into fungal cells through active transport
o Toxicity
• Headache, GI distress
• Fever, rash, flushing from histamine release
• Interference with warfarin levels
• Polyenes
o Superficial infections
o Topically to suppress candida infections
• "Swish and swallow"
o Mechanism
• Bind to ergosterol and cause artificial pores
▪ Leakage of H, K, Cl, Na thourgh pore
▪ Increases free radical in cell
o Amphotericin B
• Related to nystatin
▪ Usually IV (Nystatin: Oral)
• Elimination through slow hepatic metabolism
▪ 2 weeks
▪ Minimal renal excretion
• Systemic mycoses
• Widest antifungal spectrum
• Aspergillus, blastomyces, candida, cryptococcus, histoplasma, mucor
• IV or intrathecal (rarely)
• Mycotic corneal ulcers and keratitis
• Toxicity
▪ Infusion related chills, nauseas, muscle spasms, vomiting
▪ Shocking fall in B
• Premedicated with antihistamines/glucocorticoids
▪ Renal tubule acidosis, Mg and K wasting
▪ Anemia (Decreased EPO production)
▪ Nephrotoxic
▪ Liposomal version: reduce renal toxicity
▪ Intrathecal: associated with seizures and neurologic damage
Nucleic Acid Synthesis Blocker
• Flucytosine
• Antimetabolite, also in cancer chemotherapy
• Eliminated intact in urine (dosage adjustment necessary)
• Narrow spectrum: Used in cryptococcus neoformans infections
o Mechanism
• Accumulated in fungal cells by membrane permease
• Converted by cytosine deaminase (Flucocytosine->5FC
• 5-FC: Blocks production of thymidine through inhibiting thymidylate synthase
• Fungal cells stop producing DNA and RNA
• Synergy occurs when combined with Amphotericin B or itraconazole (strong
effect)
o Toxicity
• Reversible bone marrow depression
Microtubule Function Inhibitors
• Griseofulvin
You might also like
- Kuliah ANTIFUNGAL AGENTSDocument24 pagesKuliah ANTIFUNGAL AGENTSfitri dwiyantiNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents: Halia Wanadiatri, DR., M.SiDocument24 pagesAntifungal Agents: Halia Wanadiatri, DR., M.SiBaiqLinaAnggrianNo ratings yet
- Antifungal DrugsDocument45 pagesAntifungal DrugsAbdulai WakoNo ratings yet
- Anti Fungal: Dr. Dr. Nico L Lumbuun, SPFKDocument45 pagesAnti Fungal: Dr. Dr. Nico L Lumbuun, SPFKAudhrey BNo ratings yet
- ANTIFUNGALS Lecture Notes Colour - 2022Document35 pagesANTIFUNGALS Lecture Notes Colour - 2022Dr Jaco MaraisNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents: Dewi Selvina R & Instiaty Department of Pharmacology FmuiDocument37 pagesAntifungal Agents: Dewi Selvina R & Instiaty Department of Pharmacology Fmuisalsa2506No ratings yet
- 1.antifungal Drug Derma Presentation .DoneDocument38 pages1.antifungal Drug Derma Presentation .Donesahghanshyam9160No ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents: Laboratorium Farmakologi Dan Terapi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Jenderal SoedirmanDocument51 pagesAntifungal Agents: Laboratorium Farmakologi Dan Terapi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Jenderal SoedirmanprofNo ratings yet
- Antifungal - Anticancer 21Document83 pagesAntifungal - Anticancer 21DR AbidNo ratings yet
- Lec 11 - Antifungal DrugsDocument12 pagesLec 11 - Antifungal DrugsAiqa QaziNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics 2Document38 pagesAntibiotics 2Tommy ZeusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Antifungal DrugsDocument55 pagesChapter 5 Antifungal DrugsAssssssNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Antifungals Antithelminics Antimalarial DrugsDocument98 pagesPharmacology Antifungals Antithelminics Antimalarial DrugsAntonyNo ratings yet
- 1.antifungal Drug Derma Presentation .DoneDocument29 pages1.antifungal Drug Derma Presentation .Donesahghanshyam9160No ratings yet
- Antifungal DrugsDocument20 pagesAntifungal DrugsTommy ZeusNo ratings yet
- Antifungal AgentsDocument72 pagesAntifungal AgentsChristine OnyangoNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents - DMS - 130220Document41 pagesAntifungal Agents - DMS - 130220bunny booNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal and AntihelminticDocument36 pagesAntiprotozoal and AntihelminticDiriba feyisaNo ratings yet
- Ulcera CornealDocument43 pagesUlcera Corneal̶L̶u̶c̶i̶a̶ L̶a̶w̶l̶i̶e̶d F̶r̶i̶s̶m̶a̶No ratings yet
- Anti Fungal DrugsDocument18 pagesAnti Fungal DrugsAmrit paruaNo ratings yet
- 15 Antifungal Drugs-Notes-3Document43 pages15 Antifungal Drugs-Notes-3Sindhu BabuNo ratings yet
- @ Drug Antibiotics AntifungalDocument57 pages@ Drug Antibiotics AntifungalDr. Anil Virani SurgeonNo ratings yet
- Anti-Fungal Agents: Jagir R. Patel Asst Professor Dept. PharmacologyDocument62 pagesAnti-Fungal Agents: Jagir R. Patel Asst Professor Dept. PharmacologyJagirNo ratings yet
- 9 - Anti Fungal DrugsDocument73 pages9 - Anti Fungal DrugsIjaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Anti Fungal DrugsDocument6 pagesAnti Fungal Drugsdamion clarkeNo ratings yet
- Revized 5 - Antifungal Medications - 2021Document28 pagesRevized 5 - Antifungal Medications - 2021احمد علىNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs (Revised) Aug 2022Document62 pagesAntifungal Drugs (Revised) Aug 2022sankethNo ratings yet
- Anti Fungal & Anthelminthic DrugsDocument62 pagesAnti Fungal & Anthelminthic DrugsKasturiRangan SrivatsaNo ratings yet
- Antifungal AgentsDocument25 pagesAntifungal AgentsCham MontimanNo ratings yet
- Antifungal DrugsDocument20 pagesAntifungal DrugsboeykhNo ratings yet
- Antifungal: Department of Medical Microbiology University of Maiduguri Teaching Hospital 19TH JANUARY, 2021Document37 pagesAntifungal: Department of Medical Microbiology University of Maiduguri Teaching Hospital 19TH JANUARY, 2021Hafsat JimetaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Lecture Notes 2013 2Document140 pagesPharmacology Lecture Notes 2013 2muleyazegetNo ratings yet
- Anti-Fungal Drugs SushDocument31 pagesAnti-Fungal Drugs SushCheng XinvennNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents (Topic C-4) Amphotericin BDocument2 pagesAntifungal Agents (Topic C-4) Amphotericin Blillo24No ratings yet
- Quinolones: Presented by Asst. Prof Jagir Patel Dept. PharmacologyDocument37 pagesQuinolones: Presented by Asst. Prof Jagir Patel Dept. PharmacologyJagirNo ratings yet
- Antifungal AgentsDocument16 pagesAntifungal AgentstheintrovNo ratings yet
- 408 Antifungal Stu 1 07Document6 pages408 Antifungal Stu 1 07Hassan.shehriNo ratings yet
- Anti FungalsDocument20 pagesAnti FungalsJUNKY DOCTORNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 - AntibioticsDocument46 pagesLec 7 - AntibioticsAiqa QaziNo ratings yet
- Antifungal AgentsDocument42 pagesAntifungal AgentsVickrant SinghNo ratings yet
- 4-Antifungal Penh Sakkdo MSCDocument41 pages4-Antifungal Penh Sakkdo MSCphearunmd11No ratings yet
- EIGBEFOH Pharmacology of AntimicrobialsDocument59 pagesEIGBEFOH Pharmacology of AntimicrobialskbNo ratings yet
- Seminar On - Infective Keratitis: Presented by - Dr. Mamleshwari Patil Department of OphthalmologyDocument72 pagesSeminar On - Infective Keratitis: Presented by - Dr. Mamleshwari Patil Department of Ophthalmologygyogi1989No ratings yet
- Ii. Antifungal Antiviral and Antiparasitic DrugsDocument73 pagesIi. Antifungal Antiviral and Antiparasitic DrugsMiguel Luis NavarreteNo ratings yet
- StiDocument60 pagesStiAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Micro 5Document37 pagesMicro 5Ha LeemNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides: Pharmacology & TherapeuticsDocument24 pagesAminoglycosides: Pharmacology & TherapeuticsMarieNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Antituberculosis Drugs: DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFK Dept - Farmakologi & Terapeutik Fak - Kedokteran UhnDocument45 pagesPharmacology of Antituberculosis Drugs: DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFK Dept - Farmakologi & Terapeutik Fak - Kedokteran UhnPutri Rahmi MaharaniNo ratings yet
- General Outline For Antibiotics: Chemistry - MIP Effect On Microbes - MIPDocument43 pagesGeneral Outline For Antibiotics: Chemistry - MIP Effect On Microbes - MIPWilliam WongNo ratings yet
- Antifungal FDocument16 pagesAntifungal Fymeen9829No ratings yet
- Antibiotics in Surgery: Wednesday - 13 February 2019 - MuluDocument33 pagesAntibiotics in Surgery: Wednesday - 13 February 2019 - MuluMohamad Ridhwan Mohd Muhaimin100% (1)
- Antiparasit AntifungiDocument63 pagesAntiparasit AntifungiMagfirah AlamNo ratings yet
- A. Bacterial Cell Envelope: Contraindications (Antibiotics)Document28 pagesA. Bacterial Cell Envelope: Contraindications (Antibiotics)Mike GNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs: - Polyene Antibiotics: Amphotericin B, Nystatin - Antimetabolites: 5-Fluorocytosine - AzolesDocument18 pagesAntifungal Drugs: - Polyene Antibiotics: Amphotericin B, Nystatin - Antimetabolites: 5-Fluorocytosine - AzolesgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Anti TB Medicines MBCHB3 2015Document17 pagesAnti TB Medicines MBCHB3 2015KelvinTMaikanaNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Class 03Document80 pagesAntibacterial Class 03tsegaab yosephNo ratings yet
- Antifungal AgentsDocument37 pagesAntifungal AgentsChandrashekhar UnakalNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents MBCHBD III - July 2021Document36 pagesAntifungal Agents MBCHBD III - July 2021KudzaisheNo ratings yet
- Corneal Ulcer: DR May DsouzaDocument31 pagesCorneal Ulcer: DR May DsouzaRithesh DiasNo ratings yet
- Recent Update in The Management of Invasive Fungal InfectionDocument30 pagesRecent Update in The Management of Invasive Fungal Infectionanoop61100% (3)
- Drug For Systemic Mycoses: Systemic Mycoses Can Be Subdivided Into Two CategoriesDocument39 pagesDrug For Systemic Mycoses: Systemic Mycoses Can Be Subdivided Into Two CategoriesCurex QANo ratings yet
- Focus On Nursing Pharmacology 6th Edition Karch Test BankDocument38 pagesFocus On Nursing Pharmacology 6th Edition Karch Test Bankgenericparaxialb41vmq100% (17)
- Pharmacology Chapter 42 zp-1-3Document42 pagesPharmacology Chapter 42 zp-1-3sho bartNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz Antimicrobials Antifungals Antituberculosis AnticancerDocument5 pagesLong Quiz Antimicrobials Antifungals Antituberculosis AnticancerJen PanganibanNo ratings yet
- PICU Drug Handbook 2014 PDFDocument106 pagesPICU Drug Handbook 2014 PDFMelissa SantosoNo ratings yet
- Aspergillosis IDSA GuidelinesDocument34 pagesAspergillosis IDSA GuidelinesAndreas IoannouNo ratings yet
- PRESENTED TO: Sir Zafar Iqbal Presented By: Group-EDocument31 pagesPRESENTED TO: Sir Zafar Iqbal Presented By: Group-EAdia MasooraNo ratings yet
- Antifungal DrugsDocument12 pagesAntifungal Drugsshibsankar rakshitNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Drug ReferenceDocument86 pagesPediatric Drug Referenceromaine_as100% (1)
- Pharm Shelf Big Boss Review Aka Pharmacology Shelf Study GuideDocument13 pagesPharm Shelf Big Boss Review Aka Pharmacology Shelf Study Guideemceelee100% (2)
- Anti-Fungal Antibiotics: Medicinal Chemistry-IIIDocument38 pagesAnti-Fungal Antibiotics: Medicinal Chemistry-IIIRohan SinghNo ratings yet
- CyclosporineDocument2 pagesCyclosporineMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MidtermDocument27 pagesPharmacology Midtermnaomie manaliliNo ratings yet
- Azusa Pacific University School of Nursing GNRS 588: Advanced Nursing Care For Adults Comprehensive Care Plan #: - 1Document18 pagesAzusa Pacific University School of Nursing GNRS 588: Advanced Nursing Care For Adults Comprehensive Care Plan #: - 1api-325691098No ratings yet
- Amphotericin BDocument5 pagesAmphotericin BdyasdaysNo ratings yet
- SingHealth GLF Handbook 1st Edition Feb2011Document79 pagesSingHealth GLF Handbook 1st Edition Feb2011Indra PratamaNo ratings yet
- Gao, 2012 Application of Drug Nanocrystal Technologies On Oral DrugDocument18 pagesGao, 2012 Application of Drug Nanocrystal Technologies On Oral DrugGaluh Primadani100% (1)
- AntifungalDocument3 pagesAntifungalDarren WilliamNo ratings yet
- Mega BacteriaDocument8 pagesMega BacteriaCarolina Montoya100% (1)
- Drug Design IIDocument42 pagesDrug Design IISophia LiuNo ratings yet
- Antiviral and Anti-Fungal DrugsDocument8 pagesAntiviral and Anti-Fungal DrugsAhmed HadeerNo ratings yet
- Macrorhabdus (Megabacteria) 10 Nov 2013 (2.0)Document10 pagesMacrorhabdus (Megabacteria) 10 Nov 2013 (2.0)Cristina Maria CampeanNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Antibiotics - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument16 pagesAntifungal Antibiotics - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfsovalaxNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs: University of Nairobi Department of Public Health, Pharmacology & ToxicologyDocument32 pagesAntifungal Drugs: University of Nairobi Department of Public Health, Pharmacology & ToxicologyAnonymous RA6sVagiNo ratings yet
- Antifungal DrugsDocument66 pagesAntifungal DrugsMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Amphotericin B Nephrotoxicity - UpToDateDocument11 pagesAmphotericin B Nephrotoxicity - UpToDateJuan Diego Fernández MurielNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs 3Document54 pagesAntifungal Drugs 3Mikee MeladNo ratings yet
- Disease and DrugsDocument599 pagesDisease and DrugsDIPANJAN MAJUMDAR100% (3)