Professional Documents
Culture Documents
O o R O: Final Difficult
Uploaded by
Yan Mg MgOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
O o R O: Final Difficult
Uploaded by
Yan Mg MgCopyright:
Available Formats
lntroduction to Mechatronics, Measurement Systems and Control Systems 29
r:< :' \lechatronics
Limitations/Disadvantages :
1. Output powers are considerably less (than those of hydraulic systems).
::---: :: :OllOWS :
2. Accuracy of pneumatic actuators is poor at low velocities.
3. Slow response of final control elements, and transmission lag.
4. Operation difficult under freezing conditions.
5. Lubrication of the mating parts is difficult.
Uses :
o The pneumatic systems are employed for majority of the plant and process control
actions in petroleum, petrochemical, chemical, paper, textile and food industries.
;,i:. -: electricity o They are also sometimes used in the aircraft systems and guided missiles.
:,3-::l-.: aCCOfding
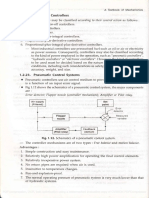
u4! *-: .- : --';!rollers" , 1.2,24. Hydraulic Control System
er:i: -::.-,ntrOllerS r Compressed air has seldom been used (except for low-pressure controllers) for the
t!.i.:: :: ; .rperating continuous control of the motion of devices having significant mass under external
"-l'.:: .. :eliability, load forces. For such a case, hydraulic controllers are generally preferred.
o The widespread use of hydraulic circuitry in "machine tool applications", "Aircraft
control systems" and " similar operations" occurs because of such factors as accuracy,
positioeness, flexibility, high power-to-weight ratio, fast starting, stopping, and reaersal
m;r-: s:::-.:i u.hich with smoothness and precision and simplicity of operations.
operating pressure in hydraulic systems lies between 1 and 35 MPa; in
e E';.: : :.-nponents - The
some special applications the operating pressure may go upto 70 MPa.
For the same power requirement, the weight and size of the hydraulic unit
I',rr -- - can be made smaller by increasing the supply pressure. Very large force can be
obtained rnith hydraulic systems.
With hyraulic systems, rapid-acting, accurate positioning of heautl loads is possible.
- A combination of electronic and hydraulic systems is widely used because it
TPB: :
- combines the advantages of both electronic control and hydraulic power.
tlrE; : - =: o Hydraulic controllers employ a liquid control meditmt to proitide an output signal which
.1 i: : is a function of an input error signal.
t.
niF \ 3,7lance Hydraulic
control
valve
Crr::-, =-enentS.
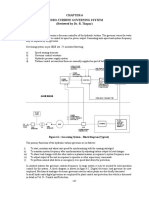
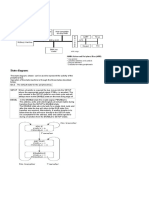
Fig. 1.13. Schematics of an hydraulic control system.
Fig. 1.13 shows the schematics of a hydraulic control system; the major components
!I:]J . -- i\-er than that are :
Error detector; an amplifier; a hydraulic control aakte; an actuator.
PDF compression, OCR, web optimization using a watermarked evaluation copy of CVISION PDFCompressor
You might also like
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideFrom EverandHydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Condition MonitoringDocument10 pagesCondition MonitoringRoy Samia100% (1)
- 8992 0104 65 Diagrams and Drawings PDFDocument75 pages8992 0104 65 Diagrams and Drawings PDFChachou MohamedNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary TransformerDocument22 pagesAuxiliary TransformerعليفاضلNo ratings yet
- MICROPROCESSOR-BASED COMPRESSOR CONTROLDocument16 pagesMICROPROCESSOR-BASED COMPRESSOR CONTROLSANTOSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Hydro-Turbine Governing SystemDocument27 pagesChapter-6 Hydro-Turbine Governing SystemChristian Llanes-de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic System For Airbus 330 AirlinerDocument5 pagesHydraulic System For Airbus 330 Airlinerrihhh hh100% (1)
- Ammeter and Voltmeter PDFDocument29 pagesAmmeter and Voltmeter PDFKristian TarucNo ratings yet
- Control EngineeringDocument144 pagesControl EngineeringRommel Roldan100% (1)
- ME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument79 pagesME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticselabalajiNo ratings yet
- SiemensEnergy IndustrialHeatPumpsDocument25 pagesSiemensEnergy IndustrialHeatPumpsHélder FernandoNo ratings yet
- WESCO 33/11kV Primary Substation SpecificationDocument65 pagesWESCO 33/11kV Primary Substation SpecificationNima MahmoudpourNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics & SCRDocument55 pagesPower Electronics & SCRsoumyaranjan_kar34No ratings yet
- Anna University CAD Lab Record BookDocument93 pagesAnna University CAD Lab Record BookRameez Farouk100% (3)
- Thermistor Project1 PDFDocument5 pagesThermistor Project1 PDFYan Mg MgNo ratings yet
- Thermistor Project1 PDFDocument5 pagesThermistor Project1 PDFYan Mg MgNo ratings yet
- TMHP51 Hydraulic Servo Systems Rydberg 2008Document46 pagesTMHP51 Hydraulic Servo Systems Rydberg 2008sherisha100% (1)
- Capitulo 1Document29 pagesCapitulo 1Ramón AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- ClosedDocument9 pagesClosedfikadu435No ratings yet
- Discrete Sliding Mode Controller For Pressure Control With An Electrohydraulic ServovalveDocument5 pagesDiscrete Sliding Mode Controller For Pressure Control With An Electrohydraulic Servovalvejhoar1987No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Component ModellingDocument18 pagesHydraulic Component ModellingRajesh MalikNo ratings yet
- Final design of dynamic systems modeled and analyzedDocument5 pagesFinal design of dynamic systems modeled and analyzedJESUS DAVID FRANCO GOMEZNo ratings yet
- انظمة نيوماتيكيهDocument86 pagesانظمة نيوماتيكيهraneem bassamNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power Control FundamentalsDocument21 pagesFluid Power Control FundamentalsBassel DaradkehNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Observer-Based Robust Control For Hydraulic Velocity Control SystemDocument10 pagesResearch Article: Observer-Based Robust Control For Hydraulic Velocity Control SystemNehal ANo ratings yet
- History of Fluid PowerDocument7 pagesHistory of Fluid PowerNEELIMANo ratings yet
- Electro-Hydraulic Servo System'sDocument9 pagesElectro-Hydraulic Servo System'smirza kasimNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power and Energy Systems: A. Khodabakhshian, R. HooshmandDocument8 pagesElectrical Power and Energy Systems: A. Khodabakhshian, R. HooshmandNabin AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Report 1: Comparison Between Electric, Hydraulic and Pneumatic Drive SystemsDocument7 pagesReport 1: Comparison Between Electric, Hydraulic and Pneumatic Drive SystemsMohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- Mobile Hydraulic Control Technology TrendsDocument6 pagesMobile Hydraulic Control Technology TrendsNelson PaicoNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of A Transmission Hydraulic SystemDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of A Transmission Hydraulic SystemMTĐTK BKHNNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Governing Systems and Electronic Governor Retrofit by Josephs. Lamberson and Jack ReedDocument8 pagesSteam Turbine Governing Systems and Electronic Governor Retrofit by Josephs. Lamberson and Jack ReedEr Mahendra KeshriNo ratings yet
- Seminar ProjectDocument30 pagesSeminar ProjectANWAR MOHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Leakage Compensation For Actuator Speed Control in Electro Hydraulic SystemsDocument11 pagesExperimental Study of Leakage Compensation For Actuator Speed Control in Electro Hydraulic SystemsJohn WilleyNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Basic Hydraulic Linear Circuit: Mechanical Engineering Department Djj40153 Pneumatics and HyraulicsDocument6 pagesLab Report: Basic Hydraulic Linear Circuit: Mechanical Engineering Department Djj40153 Pneumatics and Hyraulicszairil izuwanNo ratings yet
- Temperature Control Solution With PLC: October 2016Document5 pagesTemperature Control Solution With PLC: October 2016Lu Pham KhacNo ratings yet
- Robust Adaptive Backstepping Control Design For A Nonlinear Hydraulic-Mechanical SystemDocument8 pagesRobust Adaptive Backstepping Control Design For A Nonlinear Hydraulic-Mechanical SystemlimakmNo ratings yet
- 058 ReducedspeedDocument5 pages058 ReducedspeedKleber BonamimNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Drives, Actuators and ControlDocument80 pagesCh4 Drives, Actuators and ControlcactuswillsaNo ratings yet
- Pre and Post CompensationDocument10 pagesPre and Post CompensationRitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient Hydraulic and Regenerative Cap - SICFP - 2005 - K-E RydbergDocument13 pagesEnergy Efficient Hydraulic and Regenerative Cap - SICFP - 2005 - K-E RydbergNemoz ZrNo ratings yet
- Improving Hydraulic Steering Gear Response with PI ControlDocument9 pagesImproving Hydraulic Steering Gear Response with PI Controlaj310790No ratings yet
- Electrical Control System Components Topic 5 - 2Document33 pagesElectrical Control System Components Topic 5 - 2Vedant .ChavanNo ratings yet
- Proportion AirDocument7 pagesProportion AirNayagi Industrial TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Electrical Control of Hydraulic SystemsDocument46 pagesElectrical Control of Hydraulic SystemsJagan FaithNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Electro-Hydraulic Turbine Control (EHTC) SystemDocument8 pagesSimulation of Electro-Hydraulic Turbine Control (EHTC) SystemShwethaNo ratings yet
- Model Hsra-2 Hydraulic Actuator TBDocument2 pagesModel Hsra-2 Hydraulic Actuator TBjoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics NotesDocument193 pagesHydraulics NotesKunal KabraNo ratings yet
- Iecon 2010 5675042Document6 pagesIecon 2010 5675042godspower brunoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Control and Protection General Considerations Technology DevelopmentDocument13 pagesChapter-1 Control and Protection General Considerations Technology DevelopmentmsnsaikiranNo ratings yet
- cp:19971881Document8 pagescp:19971881Xuan Man NguyenNo ratings yet
- Interactive Analysis of Closed Loop Electro-Hydraulic Control SystemsDocument11 pagesInteractive Analysis of Closed Loop Electro-Hydraulic Control SystemsJ Cristhian QuispeNo ratings yet
- Analysis Ofh-Infinity Controllers in Fuel Cell Powered Uninterruptible Power Supply SystemDocument4 pagesAnalysis Ofh-Infinity Controllers in Fuel Cell Powered Uninterruptible Power Supply SystemMurali DharanNo ratings yet
- The BAE SYSTEMS Hawk 200 Hydraulic System Notes 04Document5 pagesThe BAE SYSTEMS Hawk 200 Hydraulic System Notes 04Afzaal Ahmad khanNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Control System For Energy Saving in Locomotive Service PlantDocument4 pagesAir Compressor Control System For Energy Saving in Locomotive Service PlantZainal ArifinNo ratings yet
- An Artificial Intelligence Based Control For Micro Hydro Power PlantsDocument11 pagesAn Artificial Intelligence Based Control For Micro Hydro Power PlantsLaxmi PriyaNo ratings yet
- 01chapter1 PDFDocument9 pages01chapter1 PDFJboar TbenecdiNo ratings yet
- Design of Universal Test Rig and Virtual Experimentation of Hydraulic Circuit For TestingDocument6 pagesDesign of Universal Test Rig and Virtual Experimentation of Hydraulic Circuit For TestingAhmed EldessoukyNo ratings yet
- 34 Campian PDFDocument6 pages34 Campian PDFFolpoNo ratings yet
- 34 Campian PDFDocument6 pages34 Campian PDFFolpoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document26 pagesLecture 1ahmedelebyaryNo ratings yet
- Ejc 15 560-577Document18 pagesEjc 15 560-577jhon cenaNo ratings yet
- MECHATRONICS ACTUATORSDocument5 pagesMECHATRONICS ACTUATORSNavin H YadavNo ratings yet
- 2004 Jun FuzzyDocument5 pages2004 Jun FuzzyCumhur ÖzbaşNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 Introduction To Pneumatics and Hydraulics SystemDocument60 pagesCH - 1 Introduction To Pneumatics and Hydraulics SystemEyasu demsewNo ratings yet
- 10.1002@asjc.2021Document11 pages10.1002@asjc.2021hamidamza4No ratings yet
- Energetic Processes in Follow-Up Electrical Control Systems: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationFrom EverandEnergetic Processes in Follow-Up Electrical Control Systems: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationNo ratings yet
- or by 7. 1. 2. 3. 4. of 5. Oil in of Tenr: RamDocument1 pageor by 7. 1. 2. 3. 4. of 5. Oil in of Tenr: RamYan Mg MgNo ratings yet
- O o o O: 1.2.22. Lndustrial 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 1. 2. 3. Res:.: 4. 5Document1 pageO o o O: 1.2.22. Lndustrial 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 1. 2. 3. Res:.: 4. 5Yan Mg MgNo ratings yet
- Electrical ConnectionDocument5 pagesElectrical ConnectionYan Mg MgNo ratings yet
- Of This: A With Tobe in Stability Criterion Stability Is Stability of +NN - RS"' + Nyquist Me:: ApproxiiDocument2 pagesOf This: A With Tobe in Stability Criterion Stability Is Stability of +NN - RS"' + Nyquist Me:: ApproxiiYan Mg MgNo ratings yet
- Linkage 3.11: User's GuideDocument76 pagesLinkage 3.11: User's GuidezulNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document19 pagesCH 4Yan Mg MgNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Data Display Principles of Interfacing Techniques and Data AcquisitionsDocument40 pagesTechniques of Data Display Principles of Interfacing Techniques and Data AcquisitionsYan Mg MgNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Data Analysis PDFDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Data Analysis PDFMuhammad Anaz'sNo ratings yet
- Project: Automatic Dcfan Controller Using ThermistorDocument18 pagesProject: Automatic Dcfan Controller Using ThermistorYan Mg MgNo ratings yet
- Lab BookDocument216 pagesLab BookrkNo ratings yet
- FMATLAB Fuzzy design with matlabDocument8 pagesFMATLAB Fuzzy design with matlabYan Mg MgNo ratings yet
- What is an OPC ServerDocument1 pageWhat is an OPC ServerYan Mg MgNo ratings yet
- Dual Axis Solar Tracking System CircuitDocument9 pagesDual Axis Solar Tracking System CircuitSatish BhatNo ratings yet
- Parameterization and Validation of Road and Driver ModelsDocument47 pagesParameterization and Validation of Road and Driver ModelsWNo ratings yet
- SW DK TM4C123G Ug 2.1.0.12573Document22 pagesSW DK TM4C123G Ug 2.1.0.12573trungkiena6No ratings yet
- Control PlaneDocument42 pagesControl PlanemakislaskosNo ratings yet
- COMPANIES ACT SHARES & SECURITIESDocument143 pagesCOMPANIES ACT SHARES & SECURITIESrachel tsetsewaNo ratings yet
- Xen Hypervisor ArchitectureDocument14 pagesXen Hypervisor ArchitectureRavi Teja CherukuriNo ratings yet
- DJSCE Placement Report 2014-15Document3 pagesDJSCE Placement Report 2014-15sujeet guptaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Chapter 1 - The Worlds of Database SystemsDocument31 pages1.1 - Chapter 1 - The Worlds of Database SystemsPhạm Nhựt HàoNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Networks: CMSC 35246: Deep LearningDocument166 pagesConvolutional Neural Networks: CMSC 35246: Deep LearningDiego AntonioNo ratings yet
- 10 3 22 Updated List of Tvet Schools and Trades To Be Chosen by s3 Candidates 2022 1Document72 pages10 3 22 Updated List of Tvet Schools and Trades To Be Chosen by s3 Candidates 2022 1jeffbosire19No ratings yet
- DARCY CV - UpdatedDocument3 pagesDARCY CV - UpdatedRodel CandelarioNo ratings yet
- FSY FSM Electronic Speed Controller DatasheetDocument6 pagesFSY FSM Electronic Speed Controller DatasheetAndre VargasNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument5 pagesOSI Modelcemerlang satuNo ratings yet
- Brochure Club V SeriesDocument8 pagesBrochure Club V SeriesAlberto PanameñoNo ratings yet
- Vector SynthesisDocument19 pagesVector SynthesisGiorgio Magnanensi100% (1)
- IRM 6 Website DefacementDocument2 pagesIRM 6 Website DefacementtaekNo ratings yet
- APB protocol on EMACSDocument3 pagesAPB protocol on EMACSviswanath SomanchiNo ratings yet
- Radar Word Meaning Translation ListDocument1 pageRadar Word Meaning Translation ListMohamed AlmandalawyNo ratings yet
- Voltage Source Inverter Drive: Ece 504 - Experiment 2Document17 pagesVoltage Source Inverter Drive: Ece 504 - Experiment 2Olimpiu StoicutaNo ratings yet
- The Smart Transformer: Impact On The Electric Grid and Technology ChallengesDocument16 pagesThe Smart Transformer: Impact On The Electric Grid and Technology ChallengesAmal MonichanNo ratings yet
- Fdas765 Data SheetDocument2 pagesFdas765 Data SheettanadfNo ratings yet
- Cisco 2621 Gateway-PBX Interoperability: Ericsson MD-110 With T1 PRI SignalingDocument11 pagesCisco 2621 Gateway-PBX Interoperability: Ericsson MD-110 With T1 PRI Signalinginr0000zhaNo ratings yet
- Apache Hive DDL DML, QueriesDocument4 pagesApache Hive DDL DML, QueriesRahul Singh100% (1)
- ATGSuppJavaMailerSetup12 7246 FNDCPGSC23637Document73 pagesATGSuppJavaMailerSetup12 7246 FNDCPGSC23637rap0777No ratings yet
- Senior Digital Marketing Director in Denver CO Resume Clark RappDocument6 pagesSenior Digital Marketing Director in Denver CO Resume Clark RappClarkRappNo ratings yet