Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quantitative Analysis: CPA CCP Cifa
Uploaded by
Timo PaulOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quantitative Analysis: CPA CCP Cifa
Uploaded by
Timo PaulCopyright:
Available Formats
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
CPA
CCP
CIFA
s
te
PART II
no
e
pl
am
0 S
89 -
Section 4
7 nya
73 Ke
07 ea
07 om
S
STUDY TEXT
KASNEB JULY 2018 SYLLABUS
Revised on: January 2019
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
CONTENT
1. Basic mathematical techniques
Functions
- Functions, equations and graphs: Linear, quadratic, cubic, exponential and logarithmic
- Application of mathematical functions in solving business problems
Matrix algebra
- Types and operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, transposition, and inversion)
- Application of matrices: statistical modelling, Markov analysis, input- output analysis
and general applications
Calculus
- Differentiation
• Rules of differentiation (general rule, chain, product, quotient)
• Differentiation of exponential and logarithmic functions
• Higher order derivatives: Turning points (maxima and minima)
• Ordinary derivatives and their applications
• Partial derivatives and their applications
• Constrained Optimisation; lagrangian multiplier
s
te
no
- Integration
e
pl
• Rules of integration
am
• Applications of integration to business problems
0 S
89 -
7 nya
2. Probability
73 Ke
Set theory
07 ea
- Types of sets 07 om
- Set description: Enumeration and descriptive properties of sets
S
- Operations of sets: Union, intersection, complement and difference
- Venn diagram
Probability theory and distribution Probability theory
- Definitions: Event, outcome, experiment, sample space
- Types of events: Elementary, compound, dependent, independent, mutually exclusive,
exhaustive, mutually inclusive
- Laws of probability: Additive and multiplicative rules - Baye's Theorem
- Probability trees
- Expected value, variance, standard deviation and coefficient of variation using
frequency and probability
Probability distributions
- Discrete and continuous probability distributions (uniform, normal, binomial, poisson
and exponential)
- Application of probability to business problems
www.someakenya.co.ke Contact: 0707 737 890 Page 2
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
3. Hypothesis testing and estimation
- Hypothesis tests on the mean (when population standard deviation is unknown)
- Hypothesis tests on proportions
- Hypothesis tests on the difference between means (independent samples)
- Hypothesis tests on the difference between means (matched pairs)
- Hypothesis tests on the difference between two proportions
4. Correlation and regression analysis
Correlation analysis
• Scatter diagrams
• Measures of correlation -product moment and rank correlation coefficients (Pearson
and Spearman)
Regression analysis
• Assumptions of linear regression analysis
• Coefficient of determination, standard error of the estimate, standard error of the
slope, t and F statistics
• Computer output of linear regression
• T-ratios and confidence interval of the coefficients
• Analysis of Variances (ANOVA)
s
te
• Simple and multiple linear regression analysis
no
e
pl
5. Time series
am
- Definition of time series
0 S
- Components of time series (circular, seasonal, cyclical, irregular/ random, trend)
89 -
7 nya
- Application of time series
73 Ke
- Methods of fitting trend: free hand, semi-averages, moving averages, least squares
07 ea
methods 07 om
- Models- additive and multiplicative models
S
- Measurement of seasonal variation using additive and multiplicative models
- Forecasting time series value using moving averages, ordinary least squares method and
exponential smoothing
- Comparison and application of forecasts for different techniques
6. Linear programming
- Definition of decision variables, objective function and constraints
- Assumptions of linear programming
- Solving linear programming using graphical method
- Solving linear programming using simplex method
- Sensitivity analysis and economic meaning of shadow prices in business situations
- Interpretation of computer assisted solutions
- Transportation and assignment problems
7. Decision theory
- Decision process
www.someakenya.co.ke Contact: 0707 737 890 Page 3
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
- Decision making environment - deterministic situation (certainty), analytical
hierarchical approach (AHA), risk and uncertainty, stochastic situations (risk), situations
of uncertainty
- Decision making under uncertainty - maximin, maximax, minimax regret, Hurwicz
decision rule, Laplace decision rule
- Decision making under risk - expected monetary value, expected opportunity loss,
minimising risk using coefficient of variation, expected value of perfect information
- Decision trees - sequential decision, expected value of sample information
- Limitations of expected monetary value criteria
8. Game theory
- Assumptions of game theory
- Zero sum games
- Pure strategy games (saddle point)
- Mixed strategy games (joint probability approach)
- Dominance, graphical reduction of a game
- Value of the game.
- Non zero sum games
- Limitations of game theory
s
te
no
9. Network planning and analysis
e
pl
- Basic concepts - network, activity, event
am
- Activity sequencing and network diagram
0 S
- Critical path analysis (CPA)
89 -
7 nya
- Float and its importance
73 Ke
- Crashing of activity/project completion time
07 ea
- Project evaluation and review technique (PERT) 07 om
- Resource scheduling (levelling) and Gantt charts
S
- Limitations and advantages of CPA and PERT
10. Queuing theory
- Components/elements of a queue: arrival rate, service rate, departure, customer
behaviour, service discipline,' finite and infinite queues, traffic intensity
- Elementary single server queuing systems
- Finite capacity queuing systems
- Multiple server queues
11. Simulation
- Types of simulation
- Variables in a simulation model
- Construction of a simulation model
- Monte Carlo simulation
- Random numbers selection
- Simple queuing simulation: Single server, single channel "first come first served"
(FCFS) model
- Application of simulation models
www.someakenya.co.ke Contact: 0707 737 890 Page 4
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
CONTENT PAGE
Topic 1: Basic mathematical techniques……………………………………………… …..…6
Topic 2: Probability………………………………………………………………………….100
Topic 3: Hypothesis testing and estimation…………………………………………………151
Topic 4: Correlation and regression analysis…………………………………………….….162
Topic 5: Time series……………………………………………………………………..…..199
s
te
Topic 6: Linear programming………………………………………………………………..227
no
Topic 7: Decision theory………………………………………………………………..……280
e
pl
Topic 8: Game theory………………………………………………………...……………...301
am
Topic 9: Network planning and analysis………………………………………… ….……..310
0 S
Topic 10: Queuing theory………………………………………………...…………..….…..330
89 -
7 nya
Topic 11: Simulation…………………………………………………...……………….……345
73 Ke
Topic 12: Emerging issues and trends
07 ea
07 om
S
www.someakenya.co.ke Contact: 0707 737 890 Page 5
You might also like
- Using the Standards - Number & Operations, Grade 8From EverandUsing the Standards - Number & Operations, Grade 8No ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis: CPA CCP CifaDocument5 pagesQuantitative Analysis: CPA CCP CifaTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis Sample NotesDocument5 pagesQuantitative Analysis Sample NotesKelvin mwaiNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques - SampleDocument61 pagesQuantitative Techniques - SampleMarcellin MarcaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative AnalysisDocument366 pagesQuantitative AnalysisLazarus AmaniNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics I (CO)Document2 pagesBusiness Mathematics I (CO)Sakib HossenNo ratings yet
- Computer Mathematics - Sample NotesDocument41 pagesComputer Mathematics - Sample Notesmwitirodgers839No ratings yet
- F6Document3 pagesF6Syed Ali HaiderNo ratings yet
- 1 Function Approximation Complete BeamerDocument256 pages1 Function Approximation Complete BeamerVSNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Analysis and Design of AlgorithmsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Analysis and Design of AlgorithmsLion KenanNo ratings yet
- Course Ouline SIT 064Document3 pagesCourse Ouline SIT 064abuumaiyoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Mathematics - Applications and InterpretationDocument17 pagesSyllabus Mathematics - Applications and InterpretationSanaNo ratings yet
- JML ArimaDocument37 pagesJML Arimapg aiNo ratings yet
- Mt105a CisDocument2 pagesMt105a CisAli ImranNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Machine LearningDocument52 pagesMathematics For Machine LearningVaibhav PathakNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Numerical Modeling and Device Modeling OutlineDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Numerical Modeling and Device Modeling OutlineCorey HeffernanNo ratings yet
- Testing The CAPM: Statistical Framework For Estimation and TestingDocument32 pagesTesting The CAPM: Statistical Framework For Estimation and Testingmbilal1985No ratings yet
- Rao1988 PDFDocument10 pagesRao1988 PDFantonio ScacchiNo ratings yet
- MTech Ind Maths SyllabusDocument8 pagesMTech Ind Maths SyllabusRudra RathodNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Numerical Methods: 19-23 September 2005Document3 pagesIntroduction To Numerical Methods: 19-23 September 2005Venkadesh KannanNo ratings yet
- Structural Equation Modeling: MGMT 291 Sep 28, 2009Document38 pagesStructural Equation Modeling: MGMT 291 Sep 28, 2009sahojjatNo ratings yet
- Pengantar: Time Series AnalysisDocument41 pagesPengantar: Time Series AnalysisAdam Alexander BriaNo ratings yet
- Outline: Linear Algebra and Calculus: Nternational Chool of ConomicsDocument5 pagesOutline: Linear Algebra and Calculus: Nternational Chool of ConomicsElgün AbdullayevNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technology Degree Course Full Module Wise DescriptionDocument138 pagesBachelor of Technology Degree Course Full Module Wise DescriptionPappanNo ratings yet
- Stage-2 S-203 - Business Mathematics & StatisticsDocument3 pagesStage-2 S-203 - Business Mathematics & StatisticsMuhammad AamirNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning Questions and Answers For InterviewDocument20 pagesMachine Learning Questions and Answers For InterviewVijaykumarNo ratings yet
- Cours MSP SPC Complement Cartes de Controle 2015 2016Document109 pagesCours MSP SPC Complement Cartes de Controle 2015 2016ilyaswinnersNo ratings yet
- Everything You Wanted To Know ProbabilityDocument66 pagesEverything You Wanted To Know ProbabilityjjNo ratings yet
- Forecasting in Business Research Using The ARIMA Box-Jenkins MethodologyDocument15 pagesForecasting in Business Research Using The ARIMA Box-Jenkins MethodologymugwadiinnocentNo ratings yet
- Sat Math Subject Test PDFDocument4 pagesSat Math Subject Test PDFRobert LascarNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free STATISTICS 2Document14 pagesWuolah Free STATISTICS 2pabloenriquerh28No ratings yet
- Estimating DSGE Models With DynareDocument45 pagesEstimating DSGE Models With DynareGilbert ADJASSOUNo ratings yet
- Advanced Topics in Digital Processing, 7.5 ECTS CreditsDocument5 pagesAdvanced Topics in Digital Processing, 7.5 ECTS CreditsAli AwanNo ratings yet
- NDElectives (Mathematics)Document8 pagesNDElectives (Mathematics)Amrith ChallengerNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER AIDED ANALYSIS AND MODELLING LecturesDocument41 pagesCOMPUTER AIDED ANALYSIS AND MODELLING LecturesBen Anim100% (1)
- Ecet Bit BankDocument75 pagesEcet Bit BankTejaswi Sai Vishwanath RavipatiNo ratings yet
- Algebra (Math 1314) TopicsDocument2 pagesAlgebra (Math 1314) TopicsAletta Gregg CataloniaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Introduction To System Dynamics, Causal Loop Diagrams PDFDocument97 pagesLecture 5 - Introduction To System Dynamics, Causal Loop Diagrams PDFAlee TeenaNo ratings yet
- New SyllabusDocument5 pagesNew SyllabusIpsha GuhaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Deleted and Added Portion For JEE Main 2024Document2 pagesMathematics Deleted and Added Portion For JEE Main 2024S MALATHINo ratings yet
- ModellingDocument10 pagesModellingG U RajuNo ratings yet
- Indian Statistical Institute Delhi CentreDocument19 pagesIndian Statistical Institute Delhi CentreVaibhav AroraNo ratings yet
- Mpba G512 2464 20240109101049Document3 pagesMpba G512 2464 20240109101049purnimaNo ratings yet
- 4903 English PDFDocument8 pages4903 English PDFAdityaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document21 pagesLecture 4Dimpho Sonjani-SibiyaNo ratings yet
- ACT 7105 - EconometricsDocument2 pagesACT 7105 - Econometricsr.h.anik1596No ratings yet
- Course Outline: Subject: Eco. BBA - 1207 Subject: (Basic Mathematics I) Semester: BBA 1Document3 pagesCourse Outline: Subject: Eco. BBA - 1207 Subject: (Basic Mathematics I) Semester: BBA 1Muhammad HameedNo ratings yet
- Wa0052.Document73 pagesWa0052.IbinNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra and Vector CalculusDocument3 pagesLinear Algebra and Vector CalculusRoki BullNo ratings yet
- Box-Jenkins Methodology Forecasting BasicsDocument11 pagesBox-Jenkins Methodology Forecasting BasicsAdil Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus and Linear Algebra: Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesVector Calculus and Linear Algebra: Gujarat Technological Universitygecg ICNo ratings yet
- QA Notes QTWFTZDocument299 pagesQA Notes QTWFTZRyan LynnNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Forecasting and Time Series - Advanced TopicsDocument54 pagesUnit 7 - Forecasting and Time Series - Advanced TopicsRajdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- NET Syllabus 2023Document5 pagesNET Syllabus 2023Himanshu SahuNo ratings yet
- World: Lecture NotesDocument58 pagesWorld: Lecture NotesPower System Analysis-1No ratings yet
- Real Analysis Lesson PlanDocument1 pageReal Analysis Lesson PlanUdaya ShivaniNo ratings yet
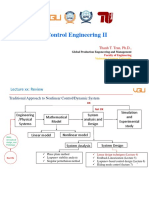
- Control Engineering II: Thanh T. Tran, PH.D.Document36 pagesControl Engineering II: Thanh T. Tran, PH.D.Thiên BùiNo ratings yet
- No. Unit Name Marks Lesson Marks No. Unit Name Marks Lesson MarksDocument1 pageNo. Unit Name Marks Lesson Marks No. Unit Name Marks Lesson MarksVEDISH SHARMANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Part 1 - Arima (Box-Jenkin) - 2023Document20 pagesChapter 11 Part 1 - Arima (Box-Jenkin) - 2023chau.nguyenminh2003No ratings yet
- 1-2 Syllabus 2010-2011Document42 pages1-2 Syllabus 2010-2011kiranbondNo ratings yet
- Common Mistakes in The Use of PronounsDocument3 pagesCommon Mistakes in The Use of PronounsMuhammad YounisNo ratings yet
- Relative Pronouns ExerciseDocument6 pagesRelative Pronouns ExerciseTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect vs. Simple PastDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect vs. Simple PastNimnaadie PremarathneNo ratings yet
- Gap Filling Grammar Exercise - 2Document6 pagesGap Filling Grammar Exercise - 2Timo PaulNo ratings yet
- Connecting Words ExerciseDocument7 pagesConnecting Words ExerciseNimnaadie PremarathneNo ratings yet
- Subject and Object Pronouns ExerciseDocument5 pagesSubject and Object Pronouns ExerciseNimnaadie PremarathneNo ratings yet
- Combine Using Relative PronounsDocument2 pagesCombine Using Relative PronounsRihabSallam100% (2)
- Subject and Object Pronouns ExerciseDocument5 pagesSubject and Object Pronouns ExerciseNimnaadie PremarathneNo ratings yet
- 7096-Article Text-28748-1-10-20130326 PDFDocument9 pages7096-Article Text-28748-1-10-20130326 PDFTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- Business Law: Study TextDocument59 pagesBusiness Law: Study TextTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions ExerciseDocument4 pagesConjunctions Exerciseiwibab 2018No ratings yet
- Management Information Systems Sample NotesDocument9 pagesManagement Information Systems Sample NotesTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- Company Law: Study TextDocument11 pagesCompany Law: Study TextTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: Study TextDocument10 pagesFinancial Management: Study TextTimo Paul100% (1)
- Indirect Speech Exercise: 1. He Told Me That He Me The Other DayDocument6 pagesIndirect Speech Exercise: 1. He Told Me That He Me The Other DaybharatNo ratings yet
- KASNEB-fa-may-2015 Teacher - Co .KeDocument7 pagesKASNEB-fa-may-2015 Teacher - Co .KeTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- Kasneb Financial Accounting For More Free Past Papers Visit May 2014 Question OneDocument6 pagesKasneb Financial Accounting For More Free Past Papers Visit May 2014 Question OneTimo Paul100% (1)
- KASNEB-law-may-2015 Teacher - Co .KeDocument2 pagesKASNEB-law-may-2015 Teacher - Co .KeTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- Tag Questions PDFDocument6 pagesTag Questions PDFTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- Phrasal Verbs ExerciseDocument6 pagesPhrasal Verbs ExerciseKaterina MartNo ratings yet
- Kasneb Introduction To Law For More Free Past Papers Visit November 2011 Question OneDocument2 pagesKasneb Introduction To Law For More Free Past Papers Visit November 2011 Question OneTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- Kasneb Fa May 2013Document6 pagesKasneb Fa May 2013xanax_1984No ratings yet
- For More Free Revision Papers Visit Kasneb LAW May 23rd 2014 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Question OneDocument2 pagesFor More Free Revision Papers Visit Kasneb LAW May 23rd 2014 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Question OneTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- PTE NOTES PHYSICAL EDUCATION Teacher - Co - .KeDocument64 pagesPTE NOTES PHYSICAL EDUCATION Teacher - Co - .KeTimo Paul93% (15)
- Practical Chemistry 4Document56 pagesPractical Chemistry 4Timo PaulNo ratings yet
- Kasneb Introduction To Law For More Free Past Papers Visit November 2012 Question OneDocument2 pagesKasneb Introduction To Law For More Free Past Papers Visit November 2012 Question OneTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- Kasneb Entrepreneurship and Communication For More Free Past Papers Visit May 2014 Section 1 Question OneDocument1 pageKasneb Entrepreneurship and Communication For More Free Past Papers Visit May 2014 Section 1 Question OneTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- PTE SOCIAL STUDIES REVISION NOTES Q - A Teacher - Co - .KeDocument18 pagesPTE SOCIAL STUDIES REVISION NOTES Q - A Teacher - Co - .KeTimo Paul83% (6)
- On The Performance of Lottery Winning Strategies: A Case Study of Oyo State Lottery, NigeriaDocument14 pagesOn The Performance of Lottery Winning Strategies: A Case Study of Oyo State Lottery, NigeriaPablo EscobarNo ratings yet
- Employee Attrition Project 2Document210 pagesEmployee Attrition Project 2Aakriti VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Latihan Analisis VariansDocument4 pagesLatihan Analisis VariansJessica Loong100% (1)
- Background and AimsDocument35 pagesBackground and Aimsapi-308874632No ratings yet
- DOE Wizard - Process and Mixture FactorsDocument46 pagesDOE Wizard - Process and Mixture FactorsAnonymous FZNn6rBNo ratings yet
- BUSI 410 Business Analytics: Module 25: Store24 (A) - Managing Employee RetentionDocument20 pagesBUSI 410 Business Analytics: Module 25: Store24 (A) - Managing Employee RetentionsnehalNo ratings yet
- RSM Minitab TutorialDocument41 pagesRSM Minitab Tutorialrpadhra8803100% (5)
- Dsbda LabDocument76 pagesDsbda LabDarth Vader100% (1)
- Determination of The Potential of Kamias (Averrhoa Bilimbi) Flowers For Tea DevelopmentDocument4 pagesDetermination of The Potential of Kamias (Averrhoa Bilimbi) Flowers For Tea DevelopmentMary Ann SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- MALEIA at Al Full PAPER SEACF 18 FREIDocument12 pagesMALEIA at Al Full PAPER SEACF 18 FREIshacquytto22No ratings yet
- The Role of Human Resource Planning On Performance of Public Water Utilities in TanzaniaDocument7 pagesThe Role of Human Resource Planning On Performance of Public Water Utilities in TanzaniaRZ RashedNo ratings yet
- Research PlanDocument11 pagesResearch PlanGrey GaleNo ratings yet
- Common Statistical Tests Are Linear ModelsDocument1 pageCommon Statistical Tests Are Linear ModelsLourrany BorgesNo ratings yet
- Handy Reference Sheet 2 - HRP 259 Calculation Formula's For Sample DataDocument15 pagesHandy Reference Sheet 2 - HRP 259 Calculation Formula's For Sample DataRosetta RennerNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 9Th 9Th Edition Frederick J Gravetter Full ChapterDocument51 pagesEssentials of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 9Th 9Th Edition Frederick J Gravetter Full Chapterjames.lenz339100% (6)
- Introduction To Blocking: Nuisance Factor: A Factor That Probably Has An Effect On The Response, But Is Not A FactorDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Blocking: Nuisance Factor: A Factor That Probably Has An Effect On The Response, But Is Not A Factorstatistics on tips 2020No ratings yet
- Obstacles and Implementation of Accounting Software System in Small Medium Enterprises (SMEs) : Case of South Asian Perspective.Document9 pagesObstacles and Implementation of Accounting Software System in Small Medium Enterprises (SMEs) : Case of South Asian Perspective.ijsab.comNo ratings yet
- STAB27Document51 pagesSTAB27Bharani DharanNo ratings yet
- V5n3itrac14 3 PDFDocument9 pagesV5n3itrac14 3 PDFvivek pandeyNo ratings yet
- Doe QuizDocument10 pagesDoe QuizManish RawatNo ratings yet
- Listeners' Attitudes Toward Children With Voice ProblemsDocument8 pagesListeners' Attitudes Toward Children With Voice ProblemsparismonamourNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Various Tests Applied On Quantitative ResearchDocument7 pagesComparative Analysis of Various Tests Applied On Quantitative ResearchInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- QNT 561, Week 5 Exercises, Chapter 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 17Document14 pagesQNT 561, Week 5 Exercises, Chapter 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 17Danielle KingNo ratings yet
- Time Cost RelationshipDocument13 pagesTime Cost RelationshipgthpmcsamrasNo ratings yet
- AnovaDocument2 pagesAnovaDewi HardiantiNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryDocument8 pagesJournal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Malaysian Guidelines For Bioavailability and Bioequivalence StudiesDocument28 pagesMalaysian Guidelines For Bioavailability and Bioequivalence StudiesKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life, Integrative Community Therapy, FamilyDocument11 pagesQuality of Life, Integrative Community Therapy, FamilyMaria Anita QueirozNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@978 3 030 24271 837Document14 pages10.1007@978 3 030 24271 837QabsooNo ratings yet
- DAFMDocument13 pagesDAFMMedha SinghNo ratings yet