Professional Documents
Culture Documents
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Uploaded by
Aseel K. SelmiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Uploaded by
Aseel K. SelmiCopyright:
Available Formats
High-performance
liquid chromatography (HPLC)
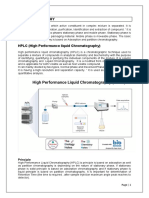
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a chromatographic technique used to split a mixture
of compounds in the fields of analytical chemistry, biochemistry and industrial. The main purposes for
using HPLC are for identifying, quantifying, and purifying the individual components of the mixture.
HPLC play a crucial role in the field of pharmaceutical industries and analysis, since it is used to test the
products and to detect the raw ingredient used to make them i.e., qualitative, and quantitative analysis.
Furthermore, the importance of HPLC uses in these fields falls under the stringent regulations
established by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This forces all pharmaceutical companies to
detect the quality of their products by using the HPLC before before marketing.
HPLC Types:
Partition chromatography.
Normal–phase chromatography.
Displacement chromatography.
Reversed-phase chromatography (RPC)
Size-exclusion chromatography.
Ion-exchange chromatography.
Bioaffinity chromatography.
Aqueous normal-phase chromatography.
UPLC refers to ultra-performance liquid chromatography, which enhance mainly in three areas: “speed,
resolution and sensitivity. The separation and quantification in UPLC are done under very high pressure
(up to 100M Pa).
Both HPLC and UPLC are liquid chromatography techniques used to separate the different com- ponents
found in mixtures. However, UPLC operates at higher pressures (15,000 psi) and allows for lower particle
sizes in columns, while HPLC operates at lower pressures (max <6000 psi).
HPLC brands:
Waters- USA
Agilent- USA
Dionex- USA
Perkin Elmer- USA
Shimadzu- Japan
You might also like
- Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography and Its ApplicationsFrom EverandUltra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography and Its ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Research HPLCDocument10 pagesResearch HPLCdm409449No ratings yet
- Application of HPLC in Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument8 pagesApplication of HPLC in Pharmaceutical IndustryLaraib ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- HPLCDocument2 pagesHPLCApoorva ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- HPLCDocument13 pagesHPLCvinsonNo ratings yet
- HPLCDocument12 pagesHPLCkushalNo ratings yet
- Standardization of Herbal DrugsDocument10 pagesStandardization of Herbal DrugsManoj TambeNo ratings yet
- PPT-finalDocument21 pagesPPT-finalRamu KetkarNo ratings yet
- Dommeti Pujitha Mrs. G.MANGADEVI (M.Pharm) : Presented BY (Reg. No:19JQ1S1603)Document40 pagesDommeti Pujitha Mrs. G.MANGADEVI (M.Pharm) : Presented BY (Reg. No:19JQ1S1603)LikithaNo ratings yet
- Applications of HPLC in Clinical DiagnosticsDocument2 pagesApplications of HPLC in Clinical Diagnosticsmanan259050% (2)
- 01 IntroductinDocument57 pages01 IntroductinPhariNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document11 pagesDocument 1Nitin RathodNo ratings yet
- HPLC Method Development and ValidationDocument8 pagesHPLC Method Development and ValidationParina Fernandes100% (1)
- Application of HPLCDocument11 pagesApplication of HPLCIts KazmiNo ratings yet
- HPLC MechanismDocument10 pagesHPLC MechanismvinsonNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument1 pageChromatographyamehak244No ratings yet
- HPLC Applications - Quick Separation Guide: October 2020Document9 pagesHPLC Applications - Quick Separation Guide: October 2020Fasttrack TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Quality Control in Pharmaceuticals: Residual Solvents Testing and AnalysisDocument29 pagesQuality Control in Pharmaceuticals: Residual Solvents Testing and Analysisexs19058No ratings yet
- University of Zakho Faculty of Science Department of ChemistryDocument29 pagesUniversity of Zakho Faculty of Science Department of ChemistryAhmed AmirNo ratings yet
- Ana TechDocument6 pagesAna TechNoor ul HudaNo ratings yet
- Purifi Cation, Purity Analysis, and Impurity Analysis Solutions For Pharmaceutical Research and DevelopmentDocument19 pagesPurifi Cation, Purity Analysis, and Impurity Analysis Solutions For Pharmaceutical Research and DevelopmentArmando Saldaña100% (1)
- Introduction of HPLCDocument11 pagesIntroduction of HPLCInga Budadoy NaudadongNo ratings yet
- A Review On Stability Indicating HPLC Method DevelopmentDocument19 pagesA Review On Stability Indicating HPLC Method DevelopmentppiccoliniNo ratings yet
- Kar ThickDocument80 pagesKar ThickTAMILAN XEROX VtmNo ratings yet
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)Document16 pagesHigh Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)Jojo ChanNo ratings yet
- Review Article An Overview of Impurity Profiling On Antihypertensive Life Saving Drugs by Using Recent Hyphenated TechniqueDocument25 pagesReview Article An Overview of Impurity Profiling On Antihypertensive Life Saving Drugs by Using Recent Hyphenated TechniqueAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- 250 259 (Ijpra)Document10 pages250 259 (Ijpra)fkamaliyahNo ratings yet
- Recent Applications of HPLC in Food Analysis: A Mini ReviewDocument6 pagesRecent Applications of HPLC in Food Analysis: A Mini ReviewIjaems JournalNo ratings yet
- Applications of High Performance Liquid ChromatographyDocument3 pagesApplications of High Performance Liquid ChromatographyKavisa GhoshNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument146 pagesChromatographyKennyKalyangoHuiosNo ratings yet
- Analytical MethodsDocument2 pagesAnalytical MethodsAkshay TandleNo ratings yet
- Different Grades of ChemicalsDocument1 pageDifferent Grades of ChemicalsRemo GagalNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument19 pagesIntroductionbabuNo ratings yet
- Forman Christian College UniversityDocument21 pagesForman Christian College UniversityHadeel Naeem Faiz ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Prathiash Topic ApprovalDocument7 pagesPrathiash Topic Approvalprathiash royNo ratings yet
- Dynamic ExtractionsDocument4 pagesDynamic ExtractionsediwskiNo ratings yet
- VALIDATION MASTER PLAN (Repaired)Document56 pagesVALIDATION MASTER PLAN (Repaired)aman pathania100% (3)
- A Novel USP-HPTLC Protocol Compliant Method For The Simultaneous Quantification of E-102, E-124, and E-133 Azo Dyes in Consumer GoodsDocument8 pagesA Novel USP-HPTLC Protocol Compliant Method For The Simultaneous Quantification of E-102, E-124, and E-133 Azo Dyes in Consumer GoodsArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- HPLC Pharma 25-1-09-Numbered-All PrintDocument19 pagesHPLC Pharma 25-1-09-Numbered-All PrintshulalevinNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation by AshwiniDocument19 pagesDevelopment and Validation by AshwiniPhArMaCyGrAdUaTeSNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument13 pagesChromatographySalmana QadeerNo ratings yet
- Analytical Method Development and Validation For The Simultaneous Estimationof Budesonide and Formoterol in Bulk and Dosage Form Using RP-HPLC MethodDocument12 pagesAnalytical Method Development and Validation For The Simultaneous Estimationof Budesonide and Formoterol in Bulk and Dosage Form Using RP-HPLC MethodBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Grshmal Btech 4th SemDocument11 pagesGrshmal Btech 4th Semprototypes6341No ratings yet
- Oil Debate Chromatography PPT 2Document17 pagesOil Debate Chromatography PPT 2Eridha TriwardhaniNo ratings yet
- HPLC Method Devolopment and Validation For EverolimusDocument20 pagesHPLC Method Devolopment and Validation For EverolimusthesisNo ratings yet
- Stability Indicating AssayDocument28 pagesStability Indicating AssayJugal Kishore Arya100% (2)
- Hypanated Technieqes Degradation StudyDocument8 pagesHypanated Technieqes Degradation StudySachin PishawikarNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between HPLC and HPTLCDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between HPLC and HPTLCMubarak PatelNo ratings yet
- Xantan GumDocument5 pagesXantan Gumjulie_lindaNo ratings yet
- Azam Sad at Mon Tazer I 2018Document7 pagesAzam Sad at Mon Tazer I 2018cuauhtlahtoatzinNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument30 pagesAnalysisSai SaiNo ratings yet
- Method Development and Validation For The Simultaneous Estimation of DMM & DTT by Using RP-HPLC MethodDocument56 pagesMethod Development and Validation For The Simultaneous Estimation of DMM & DTT by Using RP-HPLC MethodSaravanan RamNo ratings yet
- 6 15v5i4 2 PDFDocument6 pages6 15v5i4 2 PDFRiska She Blue Lover'szNo ratings yet
- A Review HPLC Method Development and ValidationDocument6 pagesA Review HPLC Method Development and ValidationEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- HPLC: Principle and Maintenance With ApplicationDocument9 pagesHPLC: Principle and Maintenance With ApplicationEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- Importance of RP-HPLC in Analytical Method Development: A ReviewDocument8 pagesImportance of RP-HPLC in Analytical Method Development: A ReviewAnthony HalimNo ratings yet
- Method Development and Validation A ReviewDocument31 pagesMethod Development and Validation A ReviewElami TuncelNo ratings yet
- HPLC Clobetasol+Acid Salicilic PDFDocument11 pagesHPLC Clobetasol+Acid Salicilic PDFElena BobrovNo ratings yet
- Principles of ChromatographyDocument20 pagesPrinciples of Chromatographyg2kwc6bhfpNo ratings yet