Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Process of Electrolysis: Worksheet 4.12: Chapter 4: Chemical Changes
Uploaded by
Jump SkillOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Process of Electrolysis: Worksheet 4.12: Chapter 4: Chemical Changes
Uploaded by
Jump SkillCopyright:
Available Formats
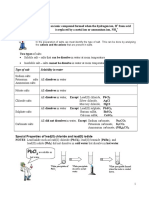
Chapter 4: Chemical changes
The process of electrolysis: Worksheet 4.12
Moving ions
1. Molten sodium chloride is an electrolyte, which means it contains ions that can
move around, and the compound is broken down as the electric current passes
through it. Explain why solid sodium chloride is not an electrolyte and does not
conduct electricity.
Solid ionic compounds do not conduct electricity because the ions are held firmly
2. Label the cathode, the anode, an anion and a cation in the diagram.
3. When a sodium ion, Na+, reaches the negative electrode it becomes an atom.
Explain how this happens.
When an ion reaches the electrode, they either loss or gain an electron depending
on their charge.
4. What happens to chloride ions, Cl−, when they reach the positive electrode?
The atoms join up to make cl2
5. Suggest why the electrolysis of molten compounds is sometimes called ‘electrolytic
decomposition’.
in solution is that the current is carried through the electrolyte by the movement of
ions
6. Molten lead bromide is an electrolyte. Predict what would form at each electrode if
a current was passed through it.
If the current passed through it there would be Pb 2+ ions gain electrons at the cathode
and become Pb atoms. Br - ions lose electrons at the anode and become Br atoms,
which pair up to form Br 2 molecules.
Collins GCSE Science © HarperCollinsPublishers Limited 2016
You might also like
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Chapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4Document9 pagesChapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4AliahYusriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Electrochemistry: Homework QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 20: Electrochemistry: Homework Questionservaldi0% (1)
- Research Paper On D and F Block PDFDocument9 pagesResearch Paper On D and F Block PDFVishwa RahulNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Electrolysis Worksheet with Past Paper QuestionsDocument53 pagesIGCSE Electrolysis Worksheet with Past Paper Questionsaqsa chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases & Salts 1 QP PDFDocument9 pagesAcids, Bases & Salts 1 QP PDFSatria HalimNo ratings yet
- Chemistry VII 1st Term 2014-154563Document6 pagesChemistry VII 1st Term 2014-154563JoannNo ratings yet
- Particles and Atoms MCQ TestDocument5 pagesParticles and Atoms MCQ TestVgyggNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Soluble SaltsDocument23 pagesPreparation of Soluble SaltsFidree AzizNo ratings yet
- Energetics I (Multiple Choice) QPDocument15 pagesEnergetics I (Multiple Choice) QPSalmantt SalmanlohussaNo ratings yet
- Revision -2- on ElectrochemistryDocument12 pagesRevision -2- on ElectrochemistryKiro RemonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4Document4 pagesWorksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4Jeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Oxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsDocument19 pagesOxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsGian Paolo GerzonNo ratings yet
- REDOXDocument67 pagesREDOXLeo PietroNo ratings yet
- VJC 2007Document14 pagesVJC 2007sswee_1No ratings yet
- Unit-8 D - and F - Block ElementsDocument2 pagesUnit-8 D - and F - Block ElementsSaurabhNo ratings yet
- IT Chem F5 SPM Model Paper (BL)Document14 pagesIT Chem F5 SPM Model Paper (BL)Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Class XI Redox Reactions NotesDocument5 pagesClass XI Redox Reactions NoteseasaNo ratings yet
- Chem U5 A2 EdexcelDocument48 pagesChem U5 A2 EdexcelReez SinhaNo ratings yet
- D and F Block ElementsDocument18 pagesD and F Block ElementsLakshmi SinghNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction Reactions ExplainedDocument21 pagesOxidation Reduction Reactions ExplainedKaroline UhlemannNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Assignment-4Document9 pagesPeriodic Table Assignment-4cpramkrishnaNo ratings yet
- True-False - Coordination CompoundsDocument6 pagesTrue-False - Coordination CompoundsrajeshwariNo ratings yet
- Acid and AlkaliDocument9 pagesAcid and Alkali云吸仓鼠吉尼斯保持者No ratings yet
- What Is Atomic Structure?: ProtonsDocument5 pagesWhat Is Atomic Structure?: Protonsjohn mwambuNo ratings yet
- d-BLOCK and f-BLOCKDocument20 pagesd-BLOCK and f-BLOCKHiranmoyNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Topic 4 BondingDocument103 pagesIB Chemistry Topic 4 Bondingzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- 2.04 - 2.06 Redox Reactions, Halogens and Alkali Earth Metals MSDocument28 pages2.04 - 2.06 Redox Reactions, Halogens and Alkali Earth Metals MSJames ChongNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Mark SchemeDocument5 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodic Table Mark SchemeDiyaNo ratings yet
- Periodicity Chemistry Worksheet: A. Periodic TableDocument9 pagesPeriodicity Chemistry Worksheet: A. Periodic TableRhea FrancisNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Form 4 CHAPTER 4-The Periodic TableDocument47 pagesCHEMISTRY Form 4 CHAPTER 4-The Periodic TableAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- IT Chem F4 Final Year Examination (BL)Document13 pagesIT Chem F4 Final Year Examination (BL)Bayane Awang100% (1)
- Task 1: Group 1 - The Alkali MetalsDocument4 pagesTask 1: Group 1 - The Alkali MetalsNeen NaazNo ratings yet
- CC Grade 11 Chemistry Energetics CWDocument3 pagesCC Grade 11 Chemistry Energetics CWMaliq MorrisNo ratings yet
- Born-Haber cycle lesson on calculating lattice energiesDocument21 pagesBorn-Haber cycle lesson on calculating lattice energiesГульдана КуанткановнаNo ratings yet
- Group 1 and 17 Elements Properties and ReactionsDocument5 pagesGroup 1 and 17 Elements Properties and ReactionsLeong Kit WaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations༄ɪɴd᭄乂Sɳιρҽɾ乂100% (1)
- Energy changes in chemical and physical processesDocument8 pagesEnergy changes in chemical and physical processesCitron AkhalaNo ratings yet
- Topical Test 8: Salts: Ujian Topikal 8: GaramDocument7 pagesTopical Test 8: Salts: Ujian Topikal 8: GaramManiArasiChandranNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chapter 8Document60 pagesForm 4 Chapter 8Rabbi 08No ratings yet
- Test Transition Elements 3rd SecondaryDocument1 pageTest Transition Elements 3rd SecondaryAboahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Manipulation of Simple PolynomialsDocument19 pagesChapter 3 - Manipulation of Simple PolynomialseddiechowNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionDocument22 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionCk OoiNo ratings yet
- D and F Block Elements Final RevisionDocument4 pagesD and F Block Elements Final RevisionROWA new year CelebrationNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Homework 3 Reaction RatesDocument4 pagesKinetics Homework 3 Reaction RatesRizkiNo ratings yet
- Topical Test 6: Electrochemistry: Ujian Topikal 6: ElektrokimiaDocument8 pagesTopical Test 6: Electrochemistry: Ujian Topikal 6: ElektrokimiaManiArasiChandranNo ratings yet
- 2021 JC2 Prelim H1 Chemistry Paper 1 QPDocument12 pages2021 JC2 Prelim H1 Chemistry Paper 1 QPShengxin PanNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About SaltsDocument32 pagesEverything You Need to Know About SaltsSabriza Hassan Assa'ariNo ratings yet
- Content: P-Block ElementsDocument8 pagesContent: P-Block ElementssachinkurhekarNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 3Document22 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 3Dhwani ShahNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases Chapter SummaryDocument3 pagesAcids and Bases Chapter SummaryjihuhuNo ratings yet
- Mock Examination 2007 Physics Paper 2Document20 pagesMock Examination 2007 Physics Paper 2api-19650882No ratings yet
- Metals and Its Alloys MCQDocument2 pagesMetals and Its Alloys MCQsrj sNo ratings yet
- 1 Energetics WSDocument28 pages1 Energetics WSGanga GowriNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 The D-And F - Block Elements I. Answer The Following Questions. Each Question Carries One MarkDocument9 pagesUnit 8 The D-And F - Block Elements I. Answer The Following Questions. Each Question Carries One MarkDeva RajNo ratings yet
- Electricity and ChemistryDocument9 pagesElectricity and ChemistryFrancis EssilfieNo ratings yet
- The Electrolytic CellDocument11 pagesThe Electrolytic CellTeandraNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument6 pagesElectrolysisapi-25909541100% (3)
- G-12 - Chapter-2-HandoutDocument16 pagesG-12 - Chapter-2-Handoutbrook debebeNo ratings yet
- GCSE Circle Theorems Cheat SheetDocument30 pagesGCSE Circle Theorems Cheat SheetJump SkillNo ratings yet
- Image Data Representation & Compression LessonDocument3 pagesImage Data Representation & Compression LessonJump Skill0% (2)
- 21a Functions - H - Question PaperDocument11 pages21a Functions - H - Question PaperJump SkillNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 T1a 6 To 9Document25 pagesUnit 1 T1a 6 To 9Jump SkillNo ratings yet
- 21a Functions - H - Question PaperDocument11 pages21a Functions - H - Question PaperJump SkillNo ratings yet
- 21a Functions - H - Question PaperDocument11 pages21a Functions - H - Question PaperJump SkillNo ratings yet
- Resources and Courses: Moocs (Massive Open Online Courses)Document8 pagesResources and Courses: Moocs (Massive Open Online Courses)Jump SkillNo ratings yet