Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity (Referral) No.14 Isolation of DNA
Uploaded by
Al-waleed JulkanainOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity (Referral) No.14 Isolation of DNA
Uploaded by
Al-waleed JulkanainCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity (Referral)No.
14
Isolation of DNA
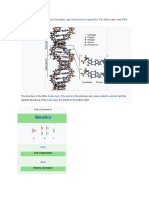
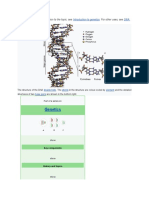
DNA is the chemical name for the molecule that carries genetic instructions in all living
things. The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around one another to form a
shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar
(deoxyribose) and phosphate groups.
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other
organisms. Nearly every cell in a person's body has the same DNA. ... The information in DNA is
stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and
thymine (T).
DNA is made of chemical building blocks called nucleotides. These building blocks
are made of three parts: a phosphate group, a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen
bases. To form a strand of DNA, nucleotides are linked into chains, with the phosphate and
sugar groups alternating.Nov 13, 2019
There are three different DNA types:
● A-DNA: It is a right-handed double helix similar to the B-DNA form. ...
● B-DNA: This is the most common DNA conformation and is a right-handed helix. ...
● Z-DNA: Z-DNA is a left-handed DNA where the double helix winds to the left in a zig-zag
pattern.
DNA is pivotal to our growth, reproduction, and health. It contains the instructions
necessary for your cells to produce proteins that affect many different processes and functions
in your body. Because DNA is so important, damage or mutations can sometimes contribute to
the development of disease.
DNA has three types of chemical component: phosphate, a sugar called deoxyribose,
and four nitrogenous bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Two of the bases,
adenine and guanine, have a double-ring structure characteristic of a type of chemical called a
purine.
DNA has three types of chemical component: phosphate, a sugar called deoxyribose,
and four nitrogenous bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Two of the
bases, adenine and guanine, have a double-ring structure characteristic of a type of chemical
called a purine.
Instruction: Answer the data sheet and question guide in your manual.
You might also like
- What Is DNA? Discovery Diagram DNA Structure Chargaff's Rule DNA Replication Function of DNA Why DNA Is Called A Polynucleotide Molecule?Document5 pagesWhat Is DNA? Discovery Diagram DNA Structure Chargaff's Rule DNA Replication Function of DNA Why DNA Is Called A Polynucleotide Molecule?Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de ElyDocument8 pagesTrabajo de ElyJose luis Arbildo ahuanariNo ratings yet
- DNA EssayDocument1 pageDNA EssaymartaNo ratings yet
- Central Board Od Secondary EducationDocument17 pagesCentral Board Od Secondary EducationSk Samir UddinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - The DNA - Structure, Function, and DiscoveryDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 8 - The DNA - Structure, Function, and Discoverybabylen bahalaNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNADocument1 pageStructure of DNAvuminhtut66No ratings yet
- DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)Document5 pagesDNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)Sagar MohanNo ratings yet
- The Dna - 1Document10 pagesThe Dna - 1Satyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Discovery That Is Considered To Be The Most Breakthrough in The Scientific World in The Past 300 Years IsDocument1 pageThe Scientific Discovery That Is Considered To Be The Most Breakthrough in The Scientific World in The Past 300 Years IsM.H RIFAT KhanNo ratings yet
- Dna 120505163257 Phpapp02Document12 pagesDna 120505163257 Phpapp02Toni Tabi SeunghyunNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: Guided Learning Activity Kit DNA Versus RNADocument20 pagesBiotechnology: Guided Learning Activity Kit DNA Versus RNAKimberly Esmelo100% (1)
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic AcidAaron BautistaNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic AcidQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic AcidQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNADocument2 pagesStructure of DNAGuilbert ZamoraNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument1 pageDNA StructureparaxNo ratings yet
- Heredity: Inheritance and VariationDocument19 pagesHeredity: Inheritance and VariationBelle MateoNo ratings yet
- DNA STRUCTURE and FUNCTIONDocument56 pagesDNA STRUCTURE and FUNCTIONAmari JeonNo ratings yet
- Histology - REspiratory SystemDocument5 pagesHistology - REspiratory SystemNusrat HafeezNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument10 pagesDeoxyribonucleic AcidAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- DNA Diagram Representing The DNA StructureDocument3 pagesDNA Diagram Representing The DNA StructureDoctor Muhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- The History of DnaDocument2 pagesThe History of Dnaduarte54322No ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Introduction To Genetics DNA (Disambiguation)Document3 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Introduction To Genetics DNA (Disambiguation)Lali HajzeriNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Dna Rna ReportDocument13 pagesAristotle Dna Rna ReportSarah Joy RiveraNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenGan Kah KhengNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument1 pageNucleic AcidKaye Tamayo MaldecirNo ratings yet
- Genetics: For A Non-Technical Introduction To The Topic, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument8 pagesGenetics: For A Non-Technical Introduction To The Topic, See - For Other Uses, SeeElenaDiSavoiaNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleDocument20 pagesStructure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleRizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DNA Structure...Document8 pagesIntroduction To DNA Structure...Bhuvan S RamaniNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) : DNA: Structure, Function and DiscoveryDocument18 pagesDeoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) : DNA: Structure, Function and DiscoveryHajar Zarguan (Full stack developer)No ratings yet
- Biology Report - Nucleic AcidDocument12 pagesBiology Report - Nucleic AcidAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- Project Work (DNA)Document6 pagesProject Work (DNA)Abdullah JabbarNo ratings yet
- What Is DNADocument2 pagesWhat Is DNAElweelee ElainNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna Grade 10 TopicsDocument16 pagesDna and Rna Grade 10 TopicsJewel Tan100% (1)
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocument6 pagesDifferences Between DNA and RNAGevo GegantoNo ratings yet
- Digi Page 27-07-2016 GS EnglishDocument1 pageDigi Page 27-07-2016 GS EnglishasdfNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Nucleic Acid 3bDocument2 pagesCytogenetics - Nucleic Acid 3bMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- What Do You Need To KnowDocument6 pagesWhat Do You Need To Knowrecquelle danoNo ratings yet
- Karthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFDocument45 pagesKarthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFkarthikeya kakarlapudiNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Repair.Document23 pagesDNA Replication and Repair.Muhammad sherNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument41 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismPavani AkkalaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Nucleic Acids: Dr. Said Al RiyamiDocument19 pagesBiochemistry of Nucleic Acids: Dr. Said Al RiyamiDodo DadaNo ratings yet
- Cheek CellsDocument3 pagesCheek CellsMikaela CasimiroNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Threads of Life: by Shamatmika Gadre and Kiara Shetty 7BDocument6 pagesThe Genetic Threads of Life: by Shamatmika Gadre and Kiara Shetty 7BShamatmikaNo ratings yet
- Double Helix Structure of DNADocument4 pagesDouble Helix Structure of DNARam SinghNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication PDFDocument7 pagesDNA Replication PDFPiyush ChandraNo ratings yet
- Conclusion Questions: Damontae Hill DNA IsDocument1 pageConclusion Questions: Damontae Hill DNA Isapi-297071461No ratings yet
- What Is DNA - Genetics Home ReferenceDocument3 pagesWhat Is DNA - Genetics Home ReferenceAmit KaushikNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNA Presentation in Colorful Retro Illustrative StyleDocument51 pagesStructure and Function of DNA Presentation in Colorful Retro Illustrative Stylekimmymantos022No ratings yet
- Activity No.1 BSci 101Document3 pagesActivity No.1 BSci 101Shamaica SurigaoNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribo Nucleic AcidDocument26 pagesDeoxyribo Nucleic AcidJoshua EbenezerNo ratings yet
- What Is DNA?: Learn MoreDocument2 pagesWhat Is DNA?: Learn Morenikita bajpaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DNA Fingerprinting (Definition, Importance of DNA Fingerprinting in Forensic Science)Document20 pagesIntroduction To DNA Fingerprinting (Definition, Importance of DNA Fingerprinting in Forensic Science)DeMetrius Sam DanielNo ratings yet
- A New Book 3Document5 pagesA New Book 3api-248758529No ratings yet
- Dna Molecule Model Exercise No. 3 NAME: Shanica E. Surigao Course and Year: Bsed I - ScienceDocument8 pagesDna Molecule Model Exercise No. 3 NAME: Shanica E. Surigao Course and Year: Bsed I - ScienceShamaica SurigaoNo ratings yet
- Components of Dna: Prepared By:Alessandra Gwyneth C.FlorendoDocument14 pagesComponents of Dna: Prepared By:Alessandra Gwyneth C.FlorendoCristie Ann GuiamNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument8 pagesDna ReplicationIrma NeyraNo ratings yet
- Lesson and ActivityDocument3 pagesLesson and ActivityAvigail CvxNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenCristiaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Activity 1 2Document2 pagesPurposive Communication Activity 1 2Al-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Table Form: Initial Data Base For FamilyDocument5 pagesTable Form: Initial Data Base For FamilyAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Family Health Care ProcessDocument13 pagesFamily Health Care ProcessAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Principles of Normal Nutrition: Santiago T.K. de Leon, Jr. RND, MAHED, PSM-FPMDocument56 pagesPrinciples of Normal Nutrition: Santiago T.K. de Leon, Jr. RND, MAHED, PSM-FPMAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum DR TechniqueDocument10 pagesIntrapartum DR TechniqueAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum DR TechniqueDocument10 pagesIntrapartum DR TechniqueAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- MC2 Biochemistry Lecture Notes For BSN First Semester, 2019-2020 Prepared By: SALINA OSIAL - ALFADDocument5 pagesMC2 Biochemistry Lecture Notes For BSN First Semester, 2019-2020 Prepared By: SALINA OSIAL - ALFADAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Protein Digestion Begins When You First Start Chewing. ... Once A Protein Source ReachesDocument2 pagesProtein Digestion Begins When You First Start Chewing. ... Once A Protein Source ReachesAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Care ProcessDocument49 pagesNutrition Care ProcessAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- MMW Chapter-3Document13 pagesMMW Chapter-3Al-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- History and PastDocument2 pagesHistory and PastAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 Reproductive System PDFDocument172 pagesCHAPTER 16 Reproductive System PDFAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Relevance of HistoryDocument2 pagesMeaning and Relevance of HistoryAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesRespiratory SystemAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 Reproductive System PDFDocument172 pagesCHAPTER 16 Reproductive System PDFAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Chemistryofproteinswithclinicalapplications 190621192525 PDFDocument181 pagesChemistryofproteinswithclinicalapplications 190621192525 PDFAl-waleed Julkanain100% (1)
- Qualitative Test of ProteinDocument27 pagesQualitative Test of ProteinAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Effect of Temperature On Enzyme ActivityDocument10 pagesEffect of Temperature On Enzyme ActivityAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet