Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Generator Ac and DC
Generator Ac and DC
Uploaded by
Vishal Kumar Singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views3 pagesAn electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It works by using a coil of wire and magnets to generate an alternating current (AC) as the coil rotates between the magnets. The key parts are an insulated copper coil, magnets to create a magnetic field, split rings connected to the coil to deliver the current, and brushes connected to the rings that are also connected to a galvanometer to measure the generated current. As the coil rotates, it cuts through the magnetic field, inducing a current that changes direction with each half rotation, producing an alternating current.
Original Description:
Original Title
GENERATOR AC AND DC
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It works by using a coil of wire and magnets to generate an alternating current (AC) as the coil rotates between the magnets. The key parts are an insulated copper coil, magnets to create a magnetic field, split rings connected to the coil to deliver the current, and brushes connected to the rings that are also connected to a galvanometer to measure the generated current. As the coil rotates, it cuts through the magnetic field, inducing a current that changes direction with each half rotation, producing an alternating current.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views3 pagesGenerator Ac and DC
Generator Ac and DC
Uploaded by
Vishal Kumar SinghAn electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It works by using a coil of wire and magnets to generate an alternating current (AC) as the coil rotates between the magnets. The key parts are an insulated copper coil, magnets to create a magnetic field, split rings connected to the coil to deliver the current, and brushes connected to the rings that are also connected to a galvanometer to measure the generated current. As the coil rotates, it cuts through the magnetic field, inducing a current that changes direction with each half rotation, producing an alternating current.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
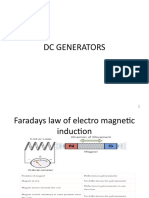
A electric generator is a DEVICE that
converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Examples: Electric Generators , Turbines (for generation
of hydroelectricity) etc, Windmills (for generation of
electricity, etc)
AC Generator
Eklavyalearners.online
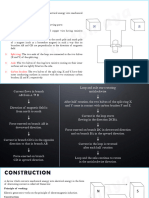
Parts of an AC Electric Generator
o Insulated Copper wire: A rectangular rotating coil of
wire ABCD
o Magnet Poles: A magnet as placed above ie North Pole
and South Pole. This creates a magnetic field as shown
above. The rectangular coil is placed between these
magnets
o Split Rings: Two disjoint C-shaped rings R1 and R2 are
internally attached to the Axle.. Ends of the coil are
connected to R1 and R2. The inner portion of these rins
are made of non-conducting material
o Axle: The split rings are placed on the axle which is
made to rotate freely from an external source.
o Brushes: The outside of the split rings are connected to
conducting brushes B1 and B2. B1 and B2 is kept pressed
on R1 and R2 respectively.
o Galvanometer : To measure current. The outer ends of
the brushes are connected to the galvanometer to
measure the current
Working
o The axle is rotated such that it moves in the clockwise
directions that is AB moves up and CD moves down.
o According to Fleming's Right Hand rule, the induced
current is setup in the coil along B1-> AB -> BC -> CD ->
B2. This means that the external current flows from B2
to B1.
o After half a rotation, arm CD starts moves up and AB
moves down.
o According to Fleming's Right Hand rule, the induced
current is setup in the coil along B2-> AB -> BC -> CD ->
B1. This means that the external current flows from B1
to B2.
o Thus after every half rotation of the coil, the current
changes direction. This is called an AC current.
o AC current(Alternating current) : Changes its direction
after equal intervals of time. It is easier to transmit
this current over long distances due to lesser loses
and hence this is the current that is supplied to our
houses from the electricity department.
o The arrangement is the same as DC Motor except that
the source battery is replaced with a galvanometer.
o The working is also the same.
o The brushes X and Y are fixed.
o Commutators (split rings) P and Q are used to get
unidirectional flow of current. This is DC current
o DC current(Direct current): Does not change direction
with time. Eg: Current from a simple battery/cell
You might also like
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- DC & AC Machines and Speed ControlDocument53 pagesDC & AC Machines and Speed ControlInsane Clown Prince60% (5)
- CH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFDocument2 pagesCH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFVishal Kumar Singh100% (1)
- AC GeneratorDocument37 pagesAC GeneratorS. Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Electric GeneratorDocument5 pagesElectric GeneratorAnonymous jdC36sKP57No ratings yet
- Unit Iv PDFDocument18 pagesUnit Iv PDFMonte CarloNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion IDocument129 pagesEnergy Conversion IKhalil BahrEldinNo ratings yet
- A.C Generator D.C GeneratorDocument16 pagesA.C Generator D.C GeneratorPrashant VanjariNo ratings yet
- Electric MotorDocument4 pagesElectric MotorAnonymous jdC36sKP57No ratings yet
- Unit-I DC GeneratorsDocument45 pagesUnit-I DC GeneratorsParameshwar TummetiNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument24 pagesElectrical MachinesFalguni MathurNo ratings yet
- 2,3. DC Generators & MotorsDocument84 pages2,3. DC Generators & MotorsnakkasrinuNo ratings yet
- DC Generators: by B.Shilpa Reddy Asst - Professor, EEE DeptDocument5 pagesDC Generators: by B.Shilpa Reddy Asst - Professor, EEE DeptAnonymous FzZcDyNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Notes On DC GeneratorDocument40 pagesMicrosoft Word - Notes On DC GeneratorDr. Deepika YadavNo ratings yet
- DC FigureDocument4 pagesDC FigureAbraham AlemNo ratings yet
- Nur Syuhada BT Hashim (b021010370)Document10 pagesNur Syuhada BT Hashim (b021010370)NurSyuhada HashimNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion 1Document74 pagesEnergy Conversion 1sinusah5678No ratings yet
- Physics PprojectDocument6 pagesPhysics PprojectSuman DasNo ratings yet
- Electric GeneratorDocument3 pagesElectric GeneratorABHINAV6969No ratings yet
- DC Generator2021Document28 pagesDC Generator2021Maysara BalakiNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document15 pagesPresentation 1Ajay Talajiya0% (1)
- POWER SUPPLY SYSTEM. ServicesDocument76 pagesPOWER SUPPLY SYSTEM. ServicesnwanabossNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Physics AcDocument2 pagesProject Report On Physics AcAyyappan SudharshanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Experiment.Document5 pagesElectrical Technology Experiment.Joseph KavinNo ratings yet
- Ac & DC Generators NotesDocument9 pagesAc & DC Generators NotesShadyNo ratings yet
- DC Generator, Basic Principle of Operation, Construction & Working PrincipleDocument3 pagesDC Generator, Basic Principle of Operation, Construction & Working PrincipleIzhar Jiskani62% (13)
- Salient and Non Salient Pole GeneratorsDocument7 pagesSalient and Non Salient Pole Generatorsharshil mangeNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document81 pagesModule 1Blesson RoyNo ratings yet
- Ac GeneratorDocument2 pagesAc GeneratorDevansh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 DC Machines IDocument18 pagesTopic 8 DC Machines IThairu MuiruriNo ratings yet
- Beee Unit 2 MeterialDocument18 pagesBeee Unit 2 MeterialnaveenNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorsDocument94 pagesDC GeneratorsWaqas Ashraf KhanNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorDocument35 pagesDC GeneratorMohammed Jalaluddin RayeenNo ratings yet
- Electrical Assignment 15-12-2018Document15 pagesElectrical Assignment 15-12-2018Mudasir SahoNo ratings yet
- Principle of Electric MotorDocument4 pagesPrinciple of Electric MotorAdaitaChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- EEE-183, DC Generators, Working PrinciplesDocument21 pagesEEE-183, DC Generators, Working PrinciplesPiyas ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorDocument11 pagesDC GeneratorTaha khan100% (1)
- Research About DC GeneratorsDocument6 pagesResearch About DC GeneratorsjemahbabesNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument26 pagesUNIT-2 Basic Electrical Engineeringabhi shekNo ratings yet
- cos d sin d d d: NBA t NBA t Φ N VDocument2 pagescos d sin d d d: NBA t NBA t Φ N VchrismarieayopNo ratings yet
- Be8253 - Unit 3Document25 pagesBe8253 - Unit 3balajiNo ratings yet
- 2 Armature ReactionDocument10 pages2 Armature Reactionapi-328781544No ratings yet
- D C Machines-IntroductionDocument25 pagesD C Machines-Introductionprashanth6876050% (2)
- DC GeneratorDocument2 pagesDC GeneratorMohammed AbidNo ratings yet
- ALTERNATORDocument21 pagesALTERNATORRushikesh WandhekarNo ratings yet
- DC Machine L03Document29 pagesDC Machine L03luckyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine & Control SystemsDocument24 pagesElectrical Machine & Control SystemsHatem DheerNo ratings yet
- Explanation of Auto Transformer With Circuit DiagramDocument5 pagesExplanation of Auto Transformer With Circuit DiagramRobin ChadhaNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorsDocument33 pagesDC Generatorsdallisrinivas14No ratings yet
- 1) Explain The Constructional Details of A DC Machine?: Electrical Machines - I Unit - Iv 1Document31 pages1) Explain The Constructional Details of A DC Machine?: Electrical Machines - I Unit - Iv 1abcd sripathiNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorsDocument52 pagesDC GeneratorsDevi Sri PrasadNo ratings yet
- Generating Electrical CurrentDocument6 pagesGenerating Electrical Currentjavierruizleon100% (5)
- EEE Chapter 2 PDFDocument37 pagesEEE Chapter 2 PDFKrishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Three Phase Alternator PDFDocument38 pagesUnit 3 Three Phase Alternator PDFPalak JioNo ratings yet
- 2.3 DC MotorDocument23 pages2.3 DC Motorjohn02cena03No ratings yet
- Unit 1 BEEDocument29 pagesUnit 1 BEEnagendra maddulaNo ratings yet
- Article 93814Document5 pagesArticle 93814how areyouNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Generator or AC Generator or AlternatorDocument6 pagesSynchronous Generator or AC Generator or AlternatorMd. Latifur RahmanNo ratings yet
- ECE 2105 Slide 01Document91 pagesECE 2105 Slide 01saymyname.ptNo ratings yet
- DC Generator Ee301Document16 pagesDC Generator Ee301Fred S. RickNo ratings yet
- DC Motor, AC GeneratorDocument4 pagesDC Motor, AC GeneratorZaynab MominNo ratings yet
- Chancellor Portal - Applied Applications SemesterDocument1 pageChancellor Portal - Applied Applications SemesterVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cust Declaration For Capital Acc LRS NetbankingDocument2 pagesCust Declaration For Capital Acc LRS NetbankingVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Testbooklet2 1Document4 pagesTestbooklet2 1Vishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Lakshya Answer Key Offline Test Series IIDocument1 pageLakshya Answer Key Offline Test Series IIVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- 11th +JEE+2021 2022+L-1+Derivatives PDFDocument70 pages11th +JEE+2021 2022+L-1+Derivatives PDFVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Biology Batch 2 PDFDocument1 pageAnswer Key Biology Batch 2 PDFVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- 5a324131e4b072f270452694 5e99dc6d752dcc4f3e7490bd 1587578641100 PDFDocument10 pages5a324131e4b072f270452694 5e99dc6d752dcc4f3e7490bd 1587578641100 PDFVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Brilliat Coaching Center Class 11 (Assignment) 14 JANUARY 2020Document1 pageBrilliat Coaching Center Class 11 (Assignment) 14 JANUARY 2020Vishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit - V Chapter-22. Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument20 pagesUnit - V Chapter-22. Excretory Products and Their EliminationVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument4 pagesPHYSICSVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Jharkhand Polytechnic Question Paper PECE - B PDFDocument38 pagesJharkhand Polytechnic Question Paper PECE - B PDFVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Lakshya Answer Key Offline Test Series II PDFDocument1 pageLakshya Answer Key Offline Test Series II PDFVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet