Professional Documents
Culture Documents
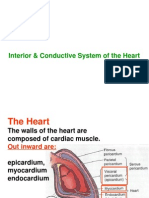
The Most Superficial Layer of The Pericardium
Uploaded by
Sara0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views6 pages.
Original Title
HEART 2018
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views6 pagesThe Most Superficial Layer of The Pericardium
Uploaded by
Sara.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
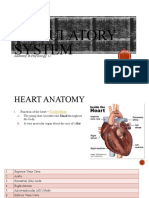
HEART – TRAINING TEST b.
is occupied by the right and left ventricles
c. faces anteriorly, inferiorly and to the left
1. Pericardium and heart lie within 12. Pectinnate muscles
a. anterior mediastinum a. are located within the right and left auricles
b. posterior mediastinum b. are located within the right and left
c. superior mediastinum ventricles
d. middle mediastinum 13. Ligamentum arteriosum runs
2. Visceral layer of serous pericardium is a. between tracheal bifurcation and aortic arch
a. the most superficial layer of the pericardium b. between pulmonary bifurcation and aortic arch
b. inner lining of the heart 14. Anterior interventricular sulcus contains
c. known as epicardium a. branch of left coronary artery
d. known as endocardium b. branch of right coronary artery
3. Oblique pericardial sinus is space c. middle cardiac vein
a. posterior to heart 15. Epicardium
b. posterior to aorta and pulmonary trunk a. covers heart myocardium
c. anterior to aorta and pulmonary trunk b. lines heart chambers
d. anterior to heart c. covers heart valves
4. The right ventricle of heart 16. Coronary sinus opens into
a. pumps blood to aorta a. right ventricle
b. pumps blood to pulmonary trunk b. left ventricle
c. receives blood from pulmonary circulation c. right atrium
d. contains openings for four pulmonary veins d. left atrium
5. Acute margin 17. Valve of the inferior vena cava
a. is left margin of the heart a. during fetal life directs blood into interatrial
b. is right ventricular magin of the heart septum
c. is formed mainly by the left ventricle b. directs blood into right atrioventicular opening
d. is formed mainly by the right atrium c. directs blood into left atrioventricular opening
6. Coronary sulcus 18. Initial part of the right coronary artery
a. separates atria from ventricles a. passes between right auricle and right ventricle
b. contains anterior interventricular artery in coronary groove
c. contains posterior interventricular artery b. passes behind pulmonary trunk
d. contains middle cardiac vein 19. Great cardiac vein goes parallel the
7. Circumflex branch a. posterior interventricular branch of right
a. passes in anterior interventricular groove coronay artery
b. passes in posterior interventricular groove b. anterior interventricular branch of left coronary
c. is from right coronary artery artery
d. passes in coronary sulcus 20. Major branches of the left coronary artery are
8. Coronary sinus a. posterior interventricular and left marginal
a. empties into the right atrium b. circumflex and anterior interventricular
b. contains arterial blood c. circumflex and posterior interventricular
c. receives blood from all small cardiac veins d. anterior and posterior interventricular
9. Fossa ovalis is depression in 21. Acute margin of heart is supplied by branch of
a. interventricular septum a. right coronary artery
b. interatrial septum b. left coronary artery
10. Anterior and posterior papillary muscles 22. Smallest cardiac veins
a. lie within the right atrium a. drain into coronary sinus
b. lie within the left atrium b. drain directly into right atrium
c. are attached to aortic valve c. drain through cardiac wall directly into all four
d. lie within ventricles of heart heart chambers
11. Base of the heart 23. Chordae tendinae
a. is occupied by the left atrium and right atrium a. lie within both atrias
b. are attached to semilunar valves c. transmits electrical impulses from left ventricle
c. are attached to tricuspid and mitral valves to right ventricle
24. During ventricular systole 32. Atriventricular bundle of His
a. tricuspid and bicuspid valve are closed a. passes through the right fibrous trigone
b. tricuspid and bicuspid valve are open b. passes through the right fibrous trigone
c. aortic valve is closed 33. AV node is located
d. pulmonary valve is closed a. in the lower part of the interatrial septum near
25. Mitral valve the opening of the coronary sinus
a. is between right atrium and right ventricle b. in supraventricular crest
b. is between aorta and left ventricle c. in terminal crest (crista terminalis)
c. is between left atrium and left ventricle 34. SA (sinoatrial node) node is situated
d. has three cusps a. in the wall of myocardium of the left atrium
26. First heart sound (S1) results from b. in the wall of myocardium of the right atrium
a. closing of the mitral and tricuspid valves c. between the atria and ventricles
b. closing of the aortic and pulmonary valves 35. Papillary muscles
c. opening of mitral and tricuspid valves a. are attached to the cusps of the semilunar
d. opening of aortic and pulmonary valves valves
27. Ausculation site for the aortic valve is b. are contracted during ventricular diastole
a. left fifth intercostal space, on the apex c. are attached to the cusps of the atrioventricular
b. left second intercostal space (in upper left valves
sternal border) 36. Superficial cardiac plexus
c. right second intercostal space (in upper a. lies beneath aortic arch, in front of the right
right sternal border) pulmonary artery
d. left fourth intercostal space b. is situated between aortc arch and trachea
28. Septomarginal trabecula (moderator band) c. generates electrical impulses for heart
a. lies in left ventricle contraction
b. lies in left atrium 37. Ligamentum arteriosum
c. extends from interventricular septum to a. is closely related to the left recurrent laryngeal
posterior papillary muscle nerve
d. conveys right branch of atrioventricular b. lies between aortic arch and pulmonary trunk
bundleof the conducting system c. is a vestige of the ductus arteriosus
29. Supraventricular crest d. all above is true
a. is muscular ridge of the left ventricle 38. Right fibrous trigone of cardiac fibrous skeleton
b. separates the outflow from inflow tracts of a. is termed the central fibrous body
the right ventricle b. is between mitral valve anulus, aortic fibrous
c. separates outflow tract and pulmonary annulus and pulmonary fibrous annulus
trunk of the right ventricle 39. Fibrous skeleton of the heart
d. is located on the internal wall of the left a. electrically isolates the atria from the ventricles
atrium b. consists of three fibrous rings
30. Right fibrous trigone c. includes three fibrous trigones
a. forms link between pulmonary, mitral, and 40. Mitral valve
tricuspid valve a. is right atrioventricular valve
b. forms link between pulmonary, aortic, and b. has three cusps
tricuspid valve c. has right and left cusp
c. forms link between aortic, mitral, and tricuspid d. has anterior and posterior cusp
valve 41. During left ventricular diastole
31. Atriventricular bundle of His a. Mitral valve closes
a. transmits electrical impulses from SA node to AV b. Mitral valve opens
node c. Aortic valve closes
b. transmits electrical impulses from AV node to d. Aortic valve opens
the ventricles of heart
42. Sternopericardial ligaments a. is filled by deoxygenated blood
a. fix the fibrous pericardium to posterior b. contains opening for sinus coronarius
mediastinum c. receives pulmonary veins
b. connect periacardium to central tendon of d. contains fossa ovalis
diaphragm
c. lie within the anterior mediastinum
d. blends with tunica adventitia of ascending aorta
43. Pericardiacophrenic artery
a. accompanies vagus nerve
b. supplies the fibrous pericardium
c. is branch of thoracic aorta
d. provides arterial supply to myocardium
44. Transverse pericardial sinus is transverse
communication between the left and right parts of
pericardial space,
a. lies posterior to the heart
b. lies anterior to the heart
c. lies in front of the aorta and pulmonary trunk
d. lies behind the aorta and pulmonary trunk
45. Base of the heart
a. involves the left ventricle
b. involves the right ventricle
c. involves the left atrium
d. forms lower border of the heart
46. Apex of the heart is positioned deep to the
a. left fifth intercostal space, 8cm from midsternal
line
b. right fifth intercostal space, 8cm from
midsternal line
c. right second intercostal space, 1cm from
midsternal line
d. left second intercostal space, 1cm from
midsternal line
47. Apex of the heart is formed by
a. right ventricle
b. right atrium
c. left atrium
d. left ventricle
48. Obtuse margin of the heart is formed mostly by the
a. left atrium
b. left ventricle
c. right atrium
d. right ventricle
49. Sinus of venae cavae is
a. space of the right atrium, anterior to crista
terminalis
b. space of the right atrium, posterior to the crista
terminalis
c. component of the left atrium
d. is covered by musculi pectinati
50. Left atrium
h. lie within ventricles of heart
11. Base of the heart
d. is occupied by the left atrium and right atrium
e. is occupied by the right and left ventricles
CORRECT ANSWERS
f. faces anteriorly, inferiorly and to the left
1. Pericardium and heart lie within 12. Pectinnate muscles
a. anterior mediastinum c. are located within the right and left auricles
b. posterior mediastinum d. are located within the right and left
c. superior mediastinum ventricles
d. middle mediastinum 13. Ligamentum arteriosum runs
2. Visceral layer of serous pericardium is c. between tracheal bifurcation and aortic arch
e. the most superficial layer of the pericardium d. between pulmonary bifurcation and aortic arch
f. inner lining of the heart 14. Anterior interventricular sulcus contains
g. known as epicardium d. branch of left coronary artery
h. known as endocardium e. branch of right coronary artery
3. Oblique sinus of the pericardial cavity is space f. middle cardiac vein
e. posterior to heart 15. Epicardium
f. posterior to aorta and pulmonary trunk d. covers heart myocardium
g. anterior to aorta and pulmonary trunk e. lines heart chambers
h. anterior to heart f. covers heart valves
4. The right ventricle of heart 16. Coronary sinus opens into
e. pumps blood to aorta e. right ventricle
f. pumps blood to pulmonary trunk f. left ventricle
g. receives blood from pulmonary circulation g. right atrium
h. contains openings for four pulmonary veins h. left atrium
5. Acute margin 17. Valve of the inferior vena cava
e. is left margin of the heart d. during fetal life directs blood into interatrial
f. is right ventricular magin of the heart septum
g. is formed mainly by the left ventricle e. directs blood into right atrioventicular opening
h. is formed mainly by the right atrium f. directs blood into left atrioventricular opening
6. Coronary sulcus 18. Initial part of the right coronary artery
e. separates atria from ventricles c. passes between right auricle and right ventricle
f. contains anterior interventricular artery in coronary groove
g. contains posterior interventricular artery d. passes behind pulmonary trunk
h. contains middle cardiac vein 19. Great cardiac vein goes parallel the
7. Circumflex branch c. posterior interventricular branch of right
e. passes in anterior interventricular groove coronay artery
f. passes in posterior interventricular groove d. anterior interventricular branch of left coronary
g. is from right coronary artery artery
h. passes in coronary sulcus 20. Major branches of the left coronary artery are
8. Coronary sinus e. posterior interventricular and left marginal
d. empties into the right atrium f. circumflex and anterior interventricular
e. contains arterial blood g. circumflex and posterior interventricular
f. receives blood from all small cardiac veins h. anterior and posterior interventricular
9. Fossa ovalis is depression in 21. Acute margin of heart is supplied by branch of
c. interventricular septum c. right coronary artery
d. interatrial septum d. left coronary artery
10. Anterior and posterior papillary muscles 22. Smallest cardiac veins
e. lie within the right atrium d. drain into coronary sinus
f. lie within the left atrium e. drain directly into right atrium
g. are attached to aortic valve
f. drain through cardiac wall directly into all four d. transmits electrical impulses from SA node to AV
heart chambers node
23. Chordae tendinae e. transmits electrical impulses from AV node to
d. lie within both atrias the ventricles of heart
e. are attached to semilunar valves f. transmits electrical impulses from left ventricle
f. are attached to tricuspid and mitral valves to right ventricle
24. During ventricular systole 32. Atriventricular bundle of His
e. tricuspid and bicuspid valve are closed c. passes through the right fibrous trigone
f. tricuspid and bicuspid valve are open d. passes through the right fibrous trigone
g. aortic valve is closed 33. AV node is located
h. pulmonary valve is closed d. in the lower part of the interatrial septum near
25. Mitral valve the opening of the coronary sinus
e. is between right atrium and right ventricle e. in supraventricular crest
f. is between aorta and left ventricle f. in terminal crest (crista terminalis)
g. is between left atrium and left ventricle 34. SA (sinoatrial node) node is situated
h. has three cusps d. in the wall of myocardium of the left atrium
26. First heart sound (S1) results from e. in the wall of myocardium of the right atrium
e. closing of the mitral and tricuspid valves f. between the atria and ventricles
f. closing of the aortic and pulmonary valves 35. Papillary muscles
g. opening of mitral and tricuspid valves d. are attached to the cusps of the semilunar
h. opening of aortic and pulmonary valves valves
27. Ausculation site for the aortic valve is e. are contracted during ventricular diastole
e. left fifth intercostal space, on the apex f. are attached to the cusps of the atrioventricular
f. left second intercostal space (in upper left valves
sternal border) 36. Superficial cardiac plexus
g. right second intercostal space (in upper d. lies beneath aortic arch, in front of the right
right sternal border) pulmonary artery
h. left fourth intercostal space e. is situated between aortc arch and trachea
28. Septomarginal trabecula (moderator band) f. generates electrical impulses for heart
e. lies in left ventricle contraction
f. lies in left atrium 37. Ligamentum arteriosum
g. extends from interventricular septum to e. is closely related to the left recurrent laryngeal
posterior papillary muscle nerve
h. conveys right branch of atrioventricular f. lies between aortic arch and pulmonary trunk
bundleof the conducting system g. is a vestige of the ductus arteriosus
29. Supraventricular crest h. all above is true
e. is muscular ridge of the left ventricle 38. Right fibrous trigone of cardiac fibrous skeleton
f. separates the outflow from inflow tracts of c. is termed the central fibrous body
the right ventricle d. is between mitral valve anulus, aortic fibrous
g. separates outflow tract and pulmonary annulus and pulmonary fibrous annulus
trunk of the right ventricle 39. Fibrous skeleton of the heart
h. is located on the internal wall of the left d. electrically isolates the atria from the ventricles
atrium e. consists of three fibrous rings
30. Right fibrous trigone f. includes three fibrous trigones
d. forms link between pulmonary, mitral, and 40. Mitral valve
tricuspid valve e. is right atrioventricular valve
e. forms link between pulmonary, aortic, and f. has three cusps
tricuspid valve g. has right and left cusp
f. forms link between aortic, mitral, and tricuspid h. has anterior and posterior cusp
valve 41. During left ventricular diastole
31. Atriventricular bundle of His a. mitral valve closes
b. mitral valve opens f. space of the right atrium, posterior to the crista
c. aortic valve closes terminalis
d. aortic valve opens g. component of the left atrium
h. is covered by musculi pectinati
42. Sternopericardial ligaments
e. fix the fibrous pericardium to posterior 50. Coronary sulcus contains
mediastinum a. middle cardiac vein
f. connect periacardium to central tendon of b. anterior interventricular artery
diaphragm c. posterior interventricular artery
g. lie within the anterior mediastinum d. small cardiac vein
h. blends with tunica adventitia of ascending aorta 51. Sinus of venae cavae is
43. Pericardiacophrenic artery i. space of the right atrium, anterior to crista
e. accompanies vagus nerve terminalis
f. supplies the fibrous pericardium j. space of the right atrium, posterior to the crista
g. is branch of thoracic aorta terminalis
h. provides arterial supply to myocardium k. component of the left atrium
44. Transverse pericardial sinus is transverse l. is covered by musculi pectinati
communication between the left and right parts of 52. Left atrium
pericardial space, e. is filled by deoxygenated blood
e. lies posterior to the heart f. contains opening for sinus coronarius
f. lies anterior to the heart g. receives pulmonary veins
g. lies in front of the aorta and pulmonary trunk h. contains fossa ovalis
h. lies behind the aorta and pulmonary trunk
45. Base of the heart
e. involves the left ventricle
f. involves the right ventricle
g. involves the left atrium
h. forms lower border of the heart
46. Apex of the heart is positioned deep to the
e. left fifth intercostal space, 8cm from midsternal
line
f. right fifth intercostal space, 8cm from
midsternal line
g. right second intercostal space, 1cm from
midsternal line
h. left second intercostal space, 1cm from
midsternal line
47. Apex of the heart is formed by
e. right ventricle
f. right atrium
g. left atrium
h. left ventricle
48. Obtuse margin of the heart is formed mostly by the
e. left atrium
f. left ventricle
g. right atrium
h. right ventricle
49. Sinus of venae cavae is
e. space of the right atrium, anterior to crista
terminalis
You might also like
- Thorax MCQDocument15 pagesThorax MCQIbNu OmEr71% (7)
- Thorax Practice ExaminationDocument12 pagesThorax Practice ExaminationNatnael GetahunNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The ThoraxDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The ThoraxdocaliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Exam 1 Thorax Part 2 With Answers PDFDocument13 pagesAnatomy Exam 1 Thorax Part 2 With Answers PDFUu UuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Quest.Document9 pagesAnatomy Quest.Ade AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Cardiac and Pulmonary Pre Block Anatomy Quiz QuestionsDocument12 pagesCardiac and Pulmonary Pre Block Anatomy Quiz Questionstlecesne100% (1)
- Buku Anatomi Nervus Arteri Jantung PDFDocument99 pagesBuku Anatomi Nervus Arteri Jantung PDFmuhammad firdausNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Quick ReviewDocument2 pagesQuiz 2 Quick ReviewFranklinSappNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Blood VesselsDocument3 pagesAbdomen Blood VesselsMiki AberaNo ratings yet
- C. Cardiac Notch: Evaluation Exam (Lungs Heart)Document4 pagesC. Cardiac Notch: Evaluation Exam (Lungs Heart)MARIA RADELINE LUNo ratings yet
- Anatomy CardioDocument4 pagesAnatomy CardioAgung IndraNo ratings yet
- Sika Ti HeartDocument5 pagesSika Ti Heartkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- Interior of The Heart (129)Document19 pagesInterior of The Heart (129)Anonymous t5TDwdNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 12 MCQs ThoraxDocument23 pagesAnatomy 12 MCQs ThoraxFernando Junior Parra Uchasara100% (1)
- Anatomy Quest.Document11 pagesAnatomy Quest.Ade AlcarazNo ratings yet
- CVS 217 QaDocument125 pagesCVS 217 QaDoaa Zakaria AliNo ratings yet
- (ANAT) - LQ 3-CompiledDocument8 pages(ANAT) - LQ 3-CompiledKaezzy Ila TabungarNo ratings yet
- Thorax Past QuestionsDocument11 pagesThorax Past QuestionsNwaoha Chibuzor AnthonyNo ratings yet
- New Rich Text DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Rich Text DocumentAnonimaNo ratings yet
- Cardiocascular System Review QuestionsDocument9 pagesCardiocascular System Review QuestionsArjay Español0% (1)
- REFERENCE: Clinically Oriented Anatomy 3 By: Keith Moore Questions: Back, Vertebral Column and Contents Multiple ChoicesDocument9 pagesREFERENCE: Clinically Oriented Anatomy 3 By: Keith Moore Questions: Back, Vertebral Column and Contents Multiple ChoiceschristinejoanNo ratings yet
- 1 FullllDocument19 pages1 FullllMah ShawdNo ratings yet
- PM702 Practice Test 2Document13 pagesPM702 Practice Test 2Darek ChenNo ratings yet
- Thorax Practice ExamDocument14 pagesThorax Practice ExamAisha YolaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test: D. The Chordae TendineaeDocument5 pagesPre-Test: D. The Chordae TendineaeTrisha Dianne RaquenioNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition EllisDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition Elliscanebrutalfniy66No ratings yet
- Ana&Physio of CV SystemDocument4 pagesAna&Physio of CV SystemNadia Andrea Paz AmoraNo ratings yet
- 0103 10am Anatomy of The Heart and PericardiumDocument9 pages0103 10am Anatomy of The Heart and PericardiumGeorge Q. YangNo ratings yet
- 1Document5 pages1Dr-Mohammed ȜlaaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Anatomy-thorax-Abdo-PelvisDocument100 pagesMCQ Anatomy-thorax-Abdo-PelvisMatt McCannNo ratings yet
- THE Circulatory System: Anatomy & Physiology 12Document15 pagesTHE Circulatory System: Anatomy & Physiology 12Vanesa VorpsiNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 4th Edition by Ellis Chapters 12-15-18 Not IncludedDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 4th Edition by Ellis Chapters 12-15-18 Not Includednuggetessayistypcu100% (41)
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - .docx; filename= UTF-8''ახალი-ტესტებიDocument13 pages- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - .docx; filename= UTF-8''ახალი-ტესტებიLALITH SAI KNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Ratio 7Document9 pagesAnatomy Ratio 7Jimell ObradorNo ratings yet
- An100 - Sem1 Cat1 2021 2022 1Document11 pagesAn100 - Sem1 Cat1 2021 2022 1Anna BiroNo ratings yet
- MCQS Snell Anatomy 9th EditionDocument65 pagesMCQS Snell Anatomy 9th EditionUsama198750% (2)
- In Lab, What Nerve Will You Find Adhered To The Fibrous Pericardium?Document4 pagesIn Lab, What Nerve Will You Find Adhered To The Fibrous Pericardium?Amar AlkhafajiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledAbdulateef AdebisiNo ratings yet
- Thorax McqsDocument23 pagesThorax McqsBassamSheryanNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document4 pagesModule 1Aya AbdelgaleelNo ratings yet
- ACD 15 - Pericardium & External HeartDocument8 pagesACD 15 - Pericardium & External Heartpranky neyneyNo ratings yet
- AA CVS Questions FinalDocument21 pagesAA CVS Questions FinalMahmoud hilmyNo ratings yet
- Lab 2: Anatomy of The Heart: General ConsiderationsDocument19 pagesLab 2: Anatomy of The Heart: General ConsiderationsDisshiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy mcq12-23Document3 pagesAnatomy mcq12-23germeen ashmallahNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument8 pagesAnatomyAbdelrahman SelimaNo ratings yet
- Embryology: HeartDocument46 pagesEmbryology: HeartRahul K. JagaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Mcqs (2) - 1Document13 pagesAnatomy Mcqs (2) - 1Yashfa Yasin - PharmDNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy MCQDocument7 pagesNeuroanatomy MCQNishanthy Pirabakar0% (1)
- A. Parasympathetic Stimulation of The HeartDocument20 pagesA. Parasympathetic Stimulation of The HeartmuryumNo ratings yet
- The Heart TransDocument15 pagesThe Heart TransAmelie Sta RomanaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2Document15 pagesAnatomy 2christinejoanNo ratings yet
- 2004Document5 pages2004api-3757921No ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument11 pagesAnatomyoddone_outNo ratings yet
- 1 SEMESTER 18/19: Median Nerve-Carpal Tunnel Weakens Lateral 3 Digits Sensory Loss ParalysisDocument60 pages1 SEMESTER 18/19: Median Nerve-Carpal Tunnel Weakens Lateral 3 Digits Sensory Loss ParalysisInsaf AhamedNo ratings yet
- Veine Cave SuperieureDocument17 pagesVeine Cave Superieuredorleansrikelme1234No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy QuestionsDocument21 pagesHuman Anatomy Questionsსალომე მუმლაძე “Slay” TMANo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemDiona SpecialNo ratings yet
- Comparative Cardiac Imaging: A Case-based GuideFrom EverandComparative Cardiac Imaging: A Case-based GuideJing Ping SunNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsFrom EverandAnatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- Laboratory Manual For Practical Exercises Properties of Organic CompoundsDocument18 pagesLaboratory Manual For Practical Exercises Properties of Organic CompoundsSaraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Practical Exercises Amino AcidsDocument5 pagesLaboratory Manual For Practical Exercises Amino AcidsSaraNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Laboratory Manual For Practical Exercises ProteinsDocument5 pagesProteins: Laboratory Manual For Practical Exercises ProteinsSaraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Practical Exercises Acids and BasesDocument15 pagesLaboratory Manual For Practical Exercises Acids and BasesSaraNo ratings yet
- Presención Tema 10 Investigación 2Document4 pagesPresención Tema 10 Investigación 2SaraNo ratings yet
- Volumetric AnalysisDocument15 pagesVolumetric AnalysisSaraNo ratings yet
- Presención Tema 10 Investigación 2Document4 pagesPresención Tema 10 Investigación 2SaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8.3: Secondary Scale Techniques: Comparative Scaling Techniques Paired Comparison ScalingDocument5 pagesChapter 8.3: Secondary Scale Techniques: Comparative Scaling Techniques Paired Comparison ScalingSaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Analysis of Mulicountry DataDocument2 pagesChapter 9: Analysis of Mulicountry DataSaraNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 - Wireframe Geometry Creation and Editing - Rev ADocument33 pagesExercise 3 - Wireframe Geometry Creation and Editing - Rev AdevNo ratings yet
- Āyāt Al-Aḥkām, Ayat Al-AhkamDocument6 pagesĀyāt Al-Aḥkām, Ayat Al-AhkamRasoul NamaziNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Benefits of Language LearningDocument11 pagesCognitive Benefits of Language LearningIlhamdi HafizNo ratings yet
- Roy B. Kantuna, MPRM, CESE: (For Midterm) (Instructor)Document8 pagesRoy B. Kantuna, MPRM, CESE: (For Midterm) (Instructor)Athena Mae DitchonNo ratings yet
- REACH ArticlesDocument12 pagesREACH ArticlesChristian SugasttiNo ratings yet
- Aeroacoustic Optimization of Wind Turbine Airfoils by Combining Thermographic and Acoustic Measurement DataDocument4 pagesAeroacoustic Optimization of Wind Turbine Airfoils by Combining Thermographic and Acoustic Measurement DatamoussaouiNo ratings yet
- Inertia Physics: Defi Ni Ti OnDocument2 pagesInertia Physics: Defi Ni Ti OnSentoash NaiduNo ratings yet
- ART Threaded Fastener Design and AnalysisDocument40 pagesART Threaded Fastener Design and AnalysisAarón Escorza MistránNo ratings yet
- 02 Geotechnical Investigation (General)Document35 pages02 Geotechnical Investigation (General)Miftahul JannaNo ratings yet
- Orifice Plate Calculator Pressure Drop CalculationsDocument4 pagesOrifice Plate Calculator Pressure Drop CalculationsAnderson Pioner100% (1)
- Advantage Dis OqpskDocument5 pagesAdvantage Dis OqpskHarun AminurasyidNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior Exam 2 Practice QuestionsDocument1 pageOrganizational Behavior Exam 2 Practice QuestionsSydney EverettNo ratings yet
- Review Problems Chapter 6Document8 pagesReview Problems Chapter 6Yue FeiNo ratings yet
- Brunswick Manual Preinstalacion GSXDocument33 pagesBrunswick Manual Preinstalacion GSXroberto dominguezNo ratings yet
- HLTARO001 HLTAROO05 Student Assessment Booklet 1 1Document68 pagesHLTARO001 HLTAROO05 Student Assessment Booklet 1 1Amber PreetNo ratings yet
- Draft Technical Notes SGLG 2023 - National OrientationDocument109 pagesDraft Technical Notes SGLG 2023 - National OrientationZane ZyneNo ratings yet
- Sheet - PDF 3Document4 pagesSheet - PDF 3Nazar JabbarNo ratings yet
- Math 2 MakilingDocument28 pagesMath 2 MakilingAnnabelle Poniente HertezNo ratings yet
- Ath9k and Ath9k - HTC DebuggingDocument4 pagesAth9k and Ath9k - HTC DebuggingHam Radio HSMMNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Entre P Dec 7Document12 pagesLesson Plan Entre P Dec 7yannie isananNo ratings yet
- NS2-DVN-2540.Rev4 - Profomal Packing List BLR Piping Hanger Support Beam-Unit 2 - 20200710Document27 pagesNS2-DVN-2540.Rev4 - Profomal Packing List BLR Piping Hanger Support Beam-Unit 2 - 20200710PHAM PHI HUNGNo ratings yet
- Sources of InnovationDocument22 pagesSources of Innovationm umair zahirNo ratings yet
- Julia Kristeva IntroDocument7 pagesJulia Kristeva IntroShweta SoodNo ratings yet
- Wireless Cellular and LTE 4g Broadband PDFDocument26 pagesWireless Cellular and LTE 4g Broadband PDFAE videosNo ratings yet
- Case Study - of Chapel of San Pedro CalungsodDocument5 pagesCase Study - of Chapel of San Pedro CalungsodJosielynNo ratings yet
- BS en 13369-2018 - TC - (2020-11-30 - 09-45-34 Am)Document164 pagesBS en 13369-2018 - TC - (2020-11-30 - 09-45-34 Am)Mustafa Uzyardoğan100% (1)
- Annual Implementation Plan FinalDocument3 pagesAnnual Implementation Plan FinalMichelle Ann Narvino100% (2)
- Group 6G Revised Research Manuscript 1Document57 pagesGroup 6G Revised Research Manuscript 1Mc Rollyn VallespinNo ratings yet
- Alup Allegro 37 AC IE3 400V 4-13bar 50Hz Metric Technical Data ENDocument2 pagesAlup Allegro 37 AC IE3 400V 4-13bar 50Hz Metric Technical Data ENBosznay ZoltánNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Test Plan (ITP) For Spherical Storage Tanks: Dehloran Olefin PlantDocument9 pagesInspection and Test Plan (ITP) For Spherical Storage Tanks: Dehloran Olefin PlantbahmanNo ratings yet