0% found this document useful (0 votes)
179 views16 pagesBinomial Heaps: Operations and Analysis
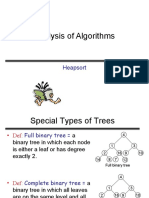
Binomial heaps allow for efficient minimum extraction by representing a heap as a collection of binomial trees. Binomial trees have the shape of a full binary tree where the root has degree 0 and each node's children have degree one less than the parent. Operations like extract-min, delete, and merge on binomial heaps can be performed in O(log n) time by using union-find and properties of binomial trees.
Uploaded by
Nishant MishraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
179 views16 pagesBinomial Heaps: Operations and Analysis
Binomial heaps allow for efficient minimum extraction by representing a heap as a collection of binomial trees. Binomial trees have the shape of a full binary tree where the root has degree 0 and each node's children have degree one less than the parent. Operations like extract-min, delete, and merge on binomial heaps can be performed in O(log n) time by using union-find and properties of binomial trees.
Uploaded by
Nishant MishraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd