Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sulfonamides or Known As The Sulfa Drugs: Trachomatis)
Uploaded by
Kristy Pagaran0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesSulfonamides were the first antibacterial agents, introduced in 1935. They work by inhibiting folic acid synthesis in bacteria, which is necessary for cell growth. Commonly prescribed sulfonamides such as sulfadiazine and sulfisoxazole are used to treat bacterial infections like urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and meningitis. They are effective against some gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria but not pseudomonas or anaerobes. Sulfonamides are absorbed from the intestines and distributed throughout the body before being excreted in urine.
Original Description:
a piece of presentation
Original Title
Sulfonamides Word
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSulfonamides were the first antibacterial agents, introduced in 1935. They work by inhibiting folic acid synthesis in bacteria, which is necessary for cell growth. Commonly prescribed sulfonamides such as sulfadiazine and sulfisoxazole are used to treat bacterial infections like urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and meningitis. They are effective against some gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria but not pseudomonas or anaerobes. Sulfonamides are absorbed from the intestines and distributed throughout the body before being excreted in urine.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesSulfonamides or Known As The Sulfa Drugs: Trachomatis)
Uploaded by
Kristy PagaranSulfonamides were the first antibacterial agents, introduced in 1935. They work by inhibiting folic acid synthesis in bacteria, which is necessary for cell growth. Commonly prescribed sulfonamides such as sulfadiazine and sulfisoxazole are used to treat bacterial infections like urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and meningitis. They are effective against some gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria but not pseudomonas or anaerobes. Sulfonamides are absorbed from the intestines and distributed throughout the body before being excreted in urine.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
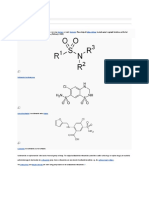
Sulfonamides or known as the sulfa drugs
- Inhibits folic acid synthesis.
- First Antibacterial agent (AMAs)
- Introduced in 1935 by Gerhard Domagk (1895–1964)
Commonly prescribed sulfonamides include:
Sulfadiazine (generic)
Sulfisoxazole (Gantrisin)
Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine)
Contrimoxazole (Septra, Bactrim)
.
Therapeutic Actions
Folic Acid - synthesized by bacteria from the substrate, para-amino-
benzoic acid (PABA), and cell growth
Sulfonamides - competitively inhibit the union of PABA with
pteridine
Targets:
Gram-positive Aerobes ( S. Pyogenes, Pneumococcus, Nocardia)
Gram-negative Aerobes ( E. Coli, Salmonella, Chlamydia
Trachomatis)
No Activity Against Pseudomonas
No Activity against Anaerobes
Indications
Used to treat bacterial and some fungal infections.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) and STD
Bronchitis
Bacterial meningitis
Pneumonia,
Severe burns
Trachoma and other conditions.
vestibular ototoxicity (nausea, vomiting, and vertigo);
Pharmacokinetics:
- Not absorbed from the GI tract. Rapidly absorbed (IM).
-Rapidly distributed into most body tissues and fluids except the brain.
-Excreted via urine, approx 30-90% as unchanged drug.
The two are ANTITUBERCULOSIS AGENT
You might also like
- Nursing NotesDocument6 pagesNursing NotesLinguumNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides: PHRM 304: Antibiotics and Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument36 pagesSulfonamides: PHRM 304: Antibiotics and Chemotherapeutic AgentsApurba Sarker Apu100% (2)
- Sulphonamides PPT 18.02.19Document49 pagesSulphonamides PPT 18.02.19Gunjan Yadav100% (5)
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]From EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Sulfonamides: By: Dr. Shruthi Rammohan Final Year PG Pharmacology RRMCHDocument45 pagesSulfonamides: By: Dr. Shruthi Rammohan Final Year PG Pharmacology RRMCHAli Veer Ali VeerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of SulphonamidesDocument21 pagesPharmacology of SulphonamidesGANESH KUMAR JELLA100% (1)
- Folic Acid Synthesis InhibitorsDocument30 pagesFolic Acid Synthesis InhibitorsPROF DR SHAHMURADNo ratings yet
- Pharma Katzung TablesDocument16 pagesPharma Katzung TablesPrincess Arabia-ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides Trimethoprim and QuinolonesDocument25 pagesSulfonamides Trimethoprim and Quinolonespopat78No ratings yet
- Pharmacology of SulfonamidesDocument37 pagesPharmacology of SulfonamidesDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHM100% (1)
- Sulfonamides or Known As The Sulfa Drugs: Trachomatis)Document2 pagesSulfonamides or Known As The Sulfa Drugs: Trachomatis)Kristy PagaranNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides: First Antibacterial Agent (Amas) Inhibits Folic Acid Synthesis. Introduced in 1935Document3 pagesSulfonamides: First Antibacterial Agent (Amas) Inhibits Folic Acid Synthesis. Introduced in 1935Kristy PagaranNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides: Wednesday, 1 October 2014 10 Am - 12 PMDocument10 pagesSulfonamides: Wednesday, 1 October 2014 10 Am - 12 PMAshamdeep AntaalNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides: Wednesday, 1 October 2014 10 Am - 12 PMDocument9 pagesSulfonamides: Wednesday, 1 October 2014 10 Am - 12 PMecc bafNo ratings yet
- SulfonamidesDocument40 pagesSulfonamidesMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- 15 SulphonamidesDocument1 page15 SulphonamidesSubhashree MahalaNo ratings yet
- Paparella: Volume I: Basic Sciences and Related Disciplines Section 6: Pharmacology Chapter 28: Antibiotics Leonard P. RybakDocument16 pagesPaparella: Volume I: Basic Sciences and Related Disciplines Section 6: Pharmacology Chapter 28: Antibiotics Leonard P. RybakDiana Mihaela BadescuNo ratings yet
- Sulphonamides: DR - Amal Belaid 3Document34 pagesSulphonamides: DR - Amal Belaid 3Mustafa RihanNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamide (Medicine) : (February 2009)Document5 pagesSulfonamide (Medicine) : (February 2009)Garlapati RajeswariNo ratings yet
- SulfonamideDocument2 pagesSulfonamideAbo DowiaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Raghu Prasada M S: MBBS, MD Assistant Professor Dept. of Pharmacology Ssims & RCDocument23 pagesDr. Raghu Prasada M S: MBBS, MD Assistant Professor Dept. of Pharmacology Ssims & RCRaman KumarNo ratings yet
- Sulphonamides KSRpaiDocument31 pagesSulphonamides KSRpaiwolverine12309No ratings yet
- Biseptol & IsoniazidDocument61 pagesBiseptol & IsoniazidYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- Bipedal Edema: Sulfonamide or Sulphonamide Is The Basis of Several Groups of Drugs. The Original AntibacterialDocument16 pagesBipedal Edema: Sulfonamide or Sulphonamide Is The Basis of Several Groups of Drugs. The Original Antibacterialfeliciano_almazoraNo ratings yet
- SulfamideDocument1 pageSulfamideGabriel DineaNo ratings yet
- Chemist Laporan 3.0Document6 pagesChemist Laporan 3.0Bella AstilahNo ratings yet
- SulfonamidesDocument3 pagesSulfonamidesMahdi DiabNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamidebi Da FtorqinolonebiDocument61 pagesSulfonamidebi Da FtorqinolonebiNia IarajuliNo ratings yet
- SulfamethizoleDocument4 pagesSulfamethizoleIlva Kristiāna LangrateNo ratings yet
- SULFONAMIDESDocument25 pagesSULFONAMIDESanaya khan StudentNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid Antag BPTDocument12 pagesFolic Acid Antag BPTfoziiiiiNo ratings yet
- Theme 22. Synthetic Chemotherapeutic Drugs: General Structure of Streptocides Paraaminobenzoic AcidDocument12 pagesTheme 22. Synthetic Chemotherapeutic Drugs: General Structure of Streptocides Paraaminobenzoic Acidfatima ALArrayedhNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamidesandcotrimoxazole 130910115011 Phpapp02Document20 pagesSulfonamidesandcotrimoxazole 130910115011 Phpapp02SanketNandaniNo ratings yet
- Antifolate Drugs 17970Document19 pagesAntifolate Drugs 17970TES SENNo ratings yet
- Anti-Folate DrugsDocument4 pagesAnti-Folate Drugssarguss14100% (2)
- Quinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist, and Urinary Tract AntisepticsDocument29 pagesQuinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist, and Urinary Tract AntisepticsAliImadAlKhasakiNo ratings yet
- PHARM Yoshimura SulfonamidesAndDHFRInhibitor 2 PDFDocument23 pagesPHARM Yoshimura SulfonamidesAndDHFRInhibitor 2 PDFDhaif dhaifNo ratings yet
- Sulphonamides & Co - Trimoxazole BamsDocument46 pagesSulphonamides & Co - Trimoxazole BamsKasturiRangan SrivatsaNo ratings yet
- Cardiotonic AgentsDocument3 pagesCardiotonic AgentsKristy PagaranNo ratings yet
- ZGMG 56 FDDGDocument22 pagesZGMG 56 FDDG11 spartusNo ratings yet
- Dentistry Anti TB, Viral, Fungal, Parasitic 2020Document38 pagesDentistry Anti TB, Viral, Fungal, Parasitic 2020Visayan Alliah GailNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Agents-Sulfonamides 032305Document139 pagesAntibacterial Agents-Sulfonamides 032305Odiit StephenNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides and Sulfonamide Combinations : Continued On Next PageDocument4 pagesSulfonamides and Sulfonamide Combinations : Continued On Next PageIfan ZulfantriNo ratings yet
- Sulphonamides PDFDocument11 pagesSulphonamides PDFAbhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Antifolate Drugs: Sulfonamides: Pharmacology IvDocument22 pagesAntifolate Drugs: Sulfonamides: Pharmacology IvShashidharan MenonNo ratings yet
- Antifolate DrugsDocument2 pagesAntifolate DrugsJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- StandartDocument14 pagesStandartEder AlbertoNo ratings yet
- 2 Vol. 12 Issue 5 May 2021 IJPSR RE 3860Document13 pages2 Vol. 12 Issue 5 May 2021 IJPSR RE 3860VinayNo ratings yet
- 03 Sulphonamides 2Document25 pages03 Sulphonamides 2Abeer SarayraNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial SDocument40 pagesAntibacterial SAiman SohailNo ratings yet
- Sulphonamides & TrimethoprimDocument32 pagesSulphonamides & TrimethoprimShiva KarthikNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides, Cotrimoxazole and QuinolonesDocument2 pagesSulfonamides, Cotrimoxazole and QuinolonesNtettNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides - Dr. Ejaz AliDocument49 pagesSulfonamides - Dr. Ejaz AliMubashir Ali100% (1)
- Antibiotics/Anti-infective: Classes of Drugs That Act As Anti-InfectivesDocument6 pagesAntibiotics/Anti-infective: Classes of Drugs That Act As Anti-InfectivesJL D. BusiaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Tuberculosis Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPediatric Tuberculosis Drug StudyEvelyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- BP601T Unit 4-6Document222 pagesBP601T Unit 4-6Solomon GyampohNo ratings yet
- Pharm DR Ahmed Abd AlrahmanDocument24 pagesPharm DR Ahmed Abd AlrahmanAmrAliTahaNo ratings yet
- SulfadimidinasDocument5 pagesSulfadimidinasfranciscorodriguez15No ratings yet
- Sulfonamides, Trimethoprim, & Quinolones: Camille E. Beauduy, Pharmd, & Lisa G. Winston, MDDocument15 pagesSulfonamides, Trimethoprim, & Quinolones: Camille E. Beauduy, Pharmd, & Lisa G. Winston, MDRegine Coeli Menta LansanganNo ratings yet
- 7 Case ScenarioDocument3 pages7 Case ScenarioLucas JelmarNo ratings yet



![Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/475660044/149x198/2c7fc45015/1691161640?v=1)