Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hemostasis
Uploaded by
Jaira RiegoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hemostasis
Uploaded by
Jaira RiegoCopyright:
Available Formats
Riego, Jaira O.
September 16, 2020
D21A
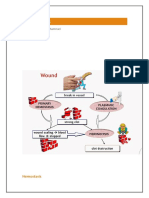
Hemostasis is the process that controls bleeding at the site of injury. The bleeding
discontinues because of the formation of blood clots that seals the injured part. The process
involves platelets and clotting fragments which are always in the blood in their inactive forms and
activates when there is an injury. These fragments, especially, platelets in their activated form
are involve in all stages of hemostasis. In the muscles most immediate response to injury, called
vascular spasm, they secrete chemicals that make blood vessels to narrow and lessen blood loss.
It also activate with the pain receptors and substances from the endothelium, a simple squamous
epithelium that lines the surface of blood vessels. These platelets are being bonded to each other
and to the endothelium that form platelet plug. Platelets also release substances to attract other
platelets and participate during blood clotting. The place where the platelets bond together is
called the site for coagulation or clotting. Blood coagulation is composed of platelet plug, from
the bond of platelets to the epithelium, and protein strands called fibrin. Coagulation is a chain
reaction from which one clotting factor is needed to activate the other one. Coagulation pathways
can be classified into 2 types – Extrinsic pathway and Intrinsic pathway. The Extrinsic pathway is
quicker than the intrinsic pathway and involves factor VII. The intrinsic pathway is activated by
platelets, exposed endothelium. This pathway is slower than the extrinsic pathway, but more
important. It involves factors XII, XI and IX. When both pathways meet, it is called common
pathway. It produces Thrombin, which has central role in the coagulation cascade and leads
insoluble Fibrogen to produce Fibrin. Thrombin also contributes to the activation of platelets.
Once the repair is done, coagulation must be dissolved to restore blood flow and this process is
called as fibrinolysis.
The liver is responsible for producing most clotting factors, and requires Vitamin K for this
production. This leads to excessive bleeding when someone has been diagnosed of deficiency
with some clotting factors, liver diseases and Vitamin-K deficiency. Unwanted coagulation can be
fetal, known as Thrombosis. It is the most common cause of block arteries that leads to heart
attacks, strokes and such. This problems can be prevented with the platelets repellent property
of the endothelium, anticoagulant factors such as serpins and APC/protein S and Fibrinolysis
cascade and fluidity of normal blood flow. There are also drugs that can prevent thrombosis like
aspirin , clopidgorel, heparin and warfarin.
You might also like
- Vasoconstriction: HemostasisDocument1 pageVasoconstriction: Hemostasisclau lizNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Blood and Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Blood and Cardiovascular SystemCharise LigoresNo ratings yet
- HemostasisDocument2 pagesHemostasisMian Talha KamalNo ratings yet
- 1) VasoconstrictionDocument7 pages1) VasoconstrictionDwi Wahyu WulandariNo ratings yet
- Blood Coagulation Drug EffectsDocument18 pagesBlood Coagulation Drug EffectsLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Guyton Chapter 36Document6 pagesGuyton Chapter 36g_komolafe100% (1)
- Hemostasis and ThrombosisDocument23 pagesHemostasis and ThrombosisFiqrotul Umam100% (1)
- Etymology and Pronunciation: HemostasisDocument5 pagesEtymology and Pronunciation: HemostasismayaNo ratings yet
- Pengantar HemostasisDocument12 pagesPengantar HemostasisPretty AngeliaNo ratings yet
- Platelets: By: Tarek Khaleefa Alwaan. Supervised ByDocument9 pagesPlatelets: By: Tarek Khaleefa Alwaan. Supervised ByAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates By: Tarek Khaleefa Alwaan. Supervised By: Dr. MustafaDocument9 pagesCarbohydrates By: Tarek Khaleefa Alwaan. Supervised By: Dr. MustafaAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- grp52 DHF DseDocument17 pagesgrp52 DHF DsekcdgrvnNo ratings yet
- CoagulationDocument2 pagesCoagulationFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- HP SeminarDocument10 pagesHP Seminarishrathjalal1999No ratings yet
- What Is HaemostasisDocument1 pageWhat Is Haemostasisshamn15No ratings yet
- 1-2 Hemostasis PhysiologyDocument48 pages1-2 Hemostasis PhysiologyHussein Al Saedi100% (2)
- Pathology T5Document58 pagesPathology T5Theone DacaNo ratings yet
- MK Hematology - Bleeding DisordersDocument60 pagesMK Hematology - Bleeding DisordersMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Mechanism of HemostasisDocument7 pagesUnderstanding the Mechanism of HemostasisArmella AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis: Written By: Fayzah Alshammari Date: 06-11-2021Document4 pagesHemostasis: Written By: Fayzah Alshammari Date: 06-11-2021fayzah alshammariNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis - MechanismDocument5 pagesHemostasis - MechanismАнна КатраженкоNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - BloodDocument5 pagesLecture 6 - Bloodadnan yaqoobNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and Blood CoagulationDocument11 pagesHemostasis and Blood CoagulationRinta MoonNo ratings yet
- SGD 1 LBM Ke 3.2Document15 pagesSGD 1 LBM Ke 3.2RaisNo ratings yet
- Platelets: Structure, Function and Hemostasis (35 charactersDocument35 pagesPlatelets: Structure, Function and Hemostasis (35 charactersЛариса ТкачеваNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Current Research in Biosciences and Plant BiologyDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Current Research in Biosciences and Plant BiologyAndius SetiawanNo ratings yet
- LBM 3 Hematopoietin Master - AndriDocument8 pagesLBM 3 Hematopoietin Master - AndriAndri Tri AtmojoNo ratings yet
- Haemostasis MechanismDocument15 pagesHaemostasis MechanismThakur KanchanNo ratings yet
- Coagulation and The Clotting CascadeDocument13 pagesCoagulation and The Clotting CascadeCLAUDIANo ratings yet
- Blood Clotting: The Extrinsic PathwayDocument6 pagesBlood Clotting: The Extrinsic PathwayHammaki MumariNo ratings yet
- HEMOSTASISDocument12 pagesHEMOSTASISKim Mae ComendadorNo ratings yet
- Describe The Role of Vascular Spasm in HaemostasisDocument4 pagesDescribe The Role of Vascular Spasm in Haemostasisnoob1314No ratings yet
- First The Blood Vessel Gets SmallerDocument2 pagesFirst The Blood Vessel Gets SmallervonashNo ratings yet
- Anemia Evaluation and Transfusion GuidelinesDocument4 pagesAnemia Evaluation and Transfusion GuidelinesGisselle PauloNo ratings yet
- Epbl 2 (Deep Venous Thrombosis)Document7 pagesEpbl 2 (Deep Venous Thrombosis)Noor Ul AminNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis: or Bleeding Blood Blood Vessel Hemorrhage Wound Healing CoagulationDocument1 pageHemostasis: or Bleeding Blood Blood Vessel Hemorrhage Wound Healing CoagulationFokus SholikinNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anesthesiolog1 BLOODDocument14 pagesClinical Anesthesiolog1 BLOODIsra JavedNo ratings yet
- Cougulation CascadeDocument3 pagesCougulation CascadeZeg ZejNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders-7777 - копия 3Document24 pagesBleeding Disorders-7777 - копия 3minakshi bossNo ratings yet
- Blood Lec 4Document18 pagesBlood Lec 4islamtareqa121No ratings yet
- Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pagesLearning ObjectivesjmcvicenteNo ratings yet
- Biology of HemostasisDocument20 pagesBiology of HemostasisVeronica TomaselloNo ratings yet
- 1 Blood HemostasisDocument32 pages1 Blood Hemostasisarlinda noviana100% (1)
- Hemostasis - Stopping of The Flow oDocument1 pageHemostasis - Stopping of The Flow oSweet Melody Cho Than Sin HtunNo ratings yet
- Blood Components PlateletsDocument3 pagesBlood Components PlateletsDavidNo ratings yet
- Block Iv: Module I: Case 2: " Hematopoietic System" "To Ooze or Not To Ooze" HemostasisDocument3 pagesBlock Iv: Module I: Case 2: " Hematopoietic System" "To Ooze or Not To Ooze" HemostasisRoscelie KhoNo ratings yet
- The Vascular Phase: HaemostasisDocument12 pagesThe Vascular Phase: HaemostasisagestaraswitaNo ratings yet
- What Is HemostasisDocument5 pagesWhat Is HemostasissupahvyNo ratings yet
- Process of Blood CoagulationDocument1 pageProcess of Blood CoagulationhariniNo ratings yet
- Aula Af 2 PDFDocument49 pagesAula Af 2 PDFtobiasmanuel179No ratings yet
- HemostasisDocument2 pagesHemostasisdea syafiraNo ratings yet
- Blood Coagulation and HaemostasisDocument76 pagesBlood Coagulation and HaemostasisArun MamachanNo ratings yet
- Positive Feedback in Childbirth and CoagulationDocument2 pagesPositive Feedback in Childbirth and CoagulationEugene Lucino CodisNo ratings yet
- Basic HemostasisDocument4 pagesBasic HemostasisMarvin SimbulanNo ratings yet
- Overview of Hemostasis - UpToDateDocument50 pagesOverview of Hemostasis - UpToDateTrung LêNo ratings yet
- SEED No 1 - COAG - Principles of HaemostasisDocument4 pagesSEED No 1 - COAG - Principles of HaemostasisM Yusuf Ali RNo ratings yet
- Blood HomeoDocument2 pagesBlood HomeoM.RautNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Coagulation ProcessDocument16 pagesPhysiology of Coagulation ProcessIlyas HalimNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemJaira RiegoNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemJaira RiegoNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemJaira RiegoNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus Infundibulum: (Adenohypophysis)Document3 pagesHypothalamus Infundibulum: (Adenohypophysis)jaira_joshbieNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument1 pageHeartJaira RiegoNo ratings yet
- Test Tenses en AnswersDocument4 pagesTest Tenses en AnswersAmit Kumar LalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Futures MarketsDocument9 pagesChapter 22 - Futures MarketsminibodNo ratings yet
- Running A Profitable Construction Company:revisited Break-Even AnalysisDocument13 pagesRunning A Profitable Construction Company:revisited Break-Even AnalysisSrivishnu VardhanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of An Effective CounselorDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of An Effective CounselorAbbas KhanNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument3 pagesReportPrecious Anne MacalinoNo ratings yet
- The Role of Social Media On Leisure Preferences - A Research On The Participants of Outdoor Recreation Activities (#263492) - 230009Document10 pagesThe Role of Social Media On Leisure Preferences - A Research On The Participants of Outdoor Recreation Activities (#263492) - 230009Stella PadillaNo ratings yet
- The DB2 Engine - The Life Cycle of A SQL StatementDocument70 pagesThe DB2 Engine - The Life Cycle of A SQL StatementPrashant LenkaNo ratings yet
- 11Document24 pages11anil.gelra5140100% (1)
- Cyber Security Module 1Document4 pagesCyber Security Module 1silentnightNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro I - 2011 TahaDocument27 pagesCiv Pro I - 2011 TahaACDCNo ratings yet
- Md. Touhidul Islam: Professional ProfileDocument4 pagesMd. Touhidul Islam: Professional ProfileYaseen Fida HossainNo ratings yet
- SMRP SAMPLE Guide To The Maintenance and ReliabiliDocument17 pagesSMRP SAMPLE Guide To The Maintenance and ReliabiliSaul sanchez MantillaNo ratings yet
- Karma Connection in Marriage PDFDocument27 pagesKarma Connection in Marriage PDFAavesh TapdeNo ratings yet
- The Authors Guild vs. Google, Inc. Facts: Plaintiffs, Who Are Authors of Published Books UnderDocument15 pagesThe Authors Guild vs. Google, Inc. Facts: Plaintiffs, Who Are Authors of Published Books UnderElead Gaddiel S. AlbueroNo ratings yet
- Hesi v2Document125 pagesHesi v2kandiezein88No ratings yet
- OD 017 V4 Drawing DocumentationDocument26 pagesOD 017 V4 Drawing DocumentationVijendra BariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Fluid StaticsDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Fluid StaticsguhanNo ratings yet
- Commercial Invoice: Exporter/Shipper Importer/ConsigneeDocument1 pageCommercial Invoice: Exporter/Shipper Importer/ConsigneePrem ChanderNo ratings yet
- Competition Commission of India Economics Study Material Amp NotesDocument3 pagesCompetition Commission of India Economics Study Material Amp NotesRaghav DhillonNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2 Stat20053 Descriptive Statistics - CompressDocument2 pagesAssessment 2 Stat20053 Descriptive Statistics - CompressDon RatbuNo ratings yet
- Astherielleseraphine Mercadejas 38 ReportDocument3 pagesAstherielleseraphine Mercadejas 38 ReportHaelenna CubalanNo ratings yet
- NATO Intelligence Exploitation of The InternetDocument104 pagesNATO Intelligence Exploitation of The Internetmauro.pennacchietti100% (1)
- Environmental Sustainability Assessment of An Academic Institution in Calamba CityDocument29 pagesEnvironmental Sustainability Assessment of An Academic Institution in Calamba CityAmadeus Fernando M. PagenteNo ratings yet
- Industrial Relations and Trade Unions MainDocument32 pagesIndustrial Relations and Trade Unions MainKishore MuppaneniNo ratings yet
- The Lair of Arachas - A Mausritter AdventureDocument8 pagesThe Lair of Arachas - A Mausritter AdventureGladstone PinheiroNo ratings yet
- The Snouters - Form and Life of - Harald StumpkeDocument126 pagesThe Snouters - Form and Life of - Harald StumpkeAlberto Humanes MuñozNo ratings yet
- Soderstrom - Circuit Modeling of Cyanex 272Document17 pagesSoderstrom - Circuit Modeling of Cyanex 272Anonymous OnoowoNo ratings yet
- Guardian Reading - Avon Cosmetics Sellers Prosper in AfricaDocument4 pagesGuardian Reading - Avon Cosmetics Sellers Prosper in Africamiguelillo84eireNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: How Cells Grow and DivideDocument21 pagesThe Cell Cycle: How Cells Grow and DivideAqsa YaminNo ratings yet
- Sieyes What Is The Third Estate PDFDocument10 pagesSieyes What Is The Third Estate PDFhunt3rV100% (1)