Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Infectious Disease - Sepsis
Uploaded by
Ansley MadalaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Infectious Disease - Sepsis
Uploaded by
Ansley MadalaCopyright:
Available Formats
Infectious Disease [SEPSIS]
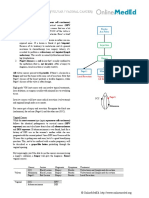
Introduction SIRS Criteria
An infection usually causes a local inflammatory response with Temperature > 38 or < 36
symptoms. Lung infections cause a cough, while UTIs cause Tachycardia > 90
dysuria. But when an infection jumps the shark and goes systemic Respiratory RR > 20 or PCO2 < 32
WBC > 12 or < 4
- effects are felt systemically - start thinking of sepsis. Sepsis
itself doesn’t require septicemia (bacteria in the blood) and
therefore may be culture negative, but the systemic effects of SIRS “Types”
inflammatory mediators can wreak havoc on the body. SIRS 2 or more criteria met, Ø source
Sepsis SIRS source
SIRS Criteria Severe Sepsis Sepsis with low blood pressure or elevated
The Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) must lactic that is responsive to fluids
meet 2 of 4 criteria that signal physiologic responses to Septic Shock Sepsis with low blood pressure or elevated
inflammation. Inflammatory mediators will cause ↑ CO (↑ HR) lactate that is non-responsive to fluid.
MODS Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome, the
either directly on the heart or reflexively from vasodilation.
patient is circling the drain with septic
Tachypnea follows. Fever is a product of IL-6 + TNF-α. Finally, shock and multiple organs failing
the response to infection is ↑ WBC (leukocytosis). But, because
some infections may ↓ WBC or a person can have sepsis in the
presence of HIV, both count. Evaluation beyond sepsis involves Organs in Dysfunction
looking for end organ damage: 1) Renal Failure (↑ Cr and Hypotension
BUN), 2) liver failure with coags and an LFT 3) Blood Vessels
with a blood pressure, 4) Brain with mental status checks, and 5)
Heart with an ECG or Troponins. Still further, one needs to
AMS
evaluate for tissue hypoxemia with a lactic acid level. Depending
on the number and severity of organ dysfunction, the patient is
stratified into a sepsis “type.” (SIRS, Sepsis, Severe Sepsis,
Septic Shock, MODS). Creatinine
Therapy
Regardless of “type,” the treatment is the same: Early Goal
Directed Therapy. This takes place in the first six hours of LFTs, Coags
hospitalization (early) and is designed to ↑ Tissue Perfusion, ↓
Tissue Hypoxia, and control the source. Controlling the source
begins by eliminating sources of infection (IV sites, Abscess Other Lactate
Drainage, and Wound Debridement) and starting empiric
antibiotics for the suspected agent. Blood Cultures should be
drawn prior to antibiotics, but do NOT delay the treatment with
broad-spectrum antibiotics. In order to meet tissue perfusion
demands certain criteria should be monitored. To maintain Early Goal Directed Therapy
perfusion (MAP > 65, CVP 8-16) a 30cc/kg bolus is the first CVP 10-12mmHg
MAP >65mmHg
step. If responsive, nothing more needs be done. Failure of the
Uoutput >0.5cc/kg/hr
fluid challenge will require the need for pressors. To maintain SvcO2 >70%
oxygenation (oxygen deliver > oxygen consumption, or SvO2 > 1) Give 30cc/kg IV Bolus
70%) both oxygen and blood (if Hgb < 7) should be given. 2) Remove all source of infection
3) O2 as needed
4) Pressors if fluid bolus fails
5) Empiric abx while waiting for cultures
© OnlineMedEd. http://www.onlinemeded.org
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- WHO GPW12 Leadership PrioritiesDocument1 pageWHO GPW12 Leadership Prioritiesrahma watiNo ratings yet
- Arora PLAB 2 90 Day Planner - MinDocument12 pagesArora PLAB 2 90 Day Planner - Minmalmegrim100% (1)
- Gynecology - VaginalVulvar CancerDocument1 pageGynecology - VaginalVulvar CancerAnsley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Vaginal BleedingDocument1 pageGynecology - Vaginal BleedingAnsley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Vaginal Bleeding 3Document2 pagesGynecology - Vaginal Bleeding 3Ansley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Secondary AmenorrheaDocument2 pagesGynecology - Secondary AmenorrheaAnsley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Cancer IntroDocument1 pageGynecology - Cancer IntroAnsley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Adnexal MassDocument2 pagesGynecology - Adnexal MassAnsley MadalaNo ratings yet
- DDX of Generalized OedemaDocument33 pagesDDX of Generalized Oedemazaw wai aungNo ratings yet
- S C R S C: Ymptom Lusters Elated To Pecific AncersDocument6 pagesS C R S C: Ymptom Lusters Elated To Pecific AncersDip Ayan MNo ratings yet
- Mitochondrial MyopathiesDocument20 pagesMitochondrial MyopathiescristobalchsNo ratings yet
- Advances in Puppy & KittenDocument6 pagesAdvances in Puppy & KittenLeo TuahNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction - JAMA (2023)Document12 pagesHeart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction - JAMA (2023)cheve glzNo ratings yet
- English For PharmacyDocument20 pagesEnglish For PharmacyMas Yaimin100% (2)
- 1 Glomerular DiseasesDocument127 pages1 Glomerular DiseasesCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Epigastric PainDocument4 pagesEpigastric PainRezqi N FirdaNo ratings yet
- Shape of The Plot - HomeDocument6 pagesShape of The Plot - Homeastrology111No ratings yet
- Limb IschaemiaDocument40 pagesLimb Ischaemiaqaaneta bint-e-najafNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis CAPDocument4 pagesCase Analysis CAPKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Quiz On School Health NursingDocument7 pagesQuiz On School Health Nursingchoobi0% (2)
- TCBSDocument13 pagesTCBSMohammad Aklis AzmiNo ratings yet
- Amethyst Biomat Far Infrared Rays Stimulate Permanent Weight LossDocument2 pagesAmethyst Biomat Far Infrared Rays Stimulate Permanent Weight LossJenNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On AlendronateDocument12 pagesA Drug Study On AlendronateTrio San LuisNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology - GallbladderDocument2 pagesGastroenterology - GallbladderEugen MNo ratings yet
- Soap Note 4 DominguezDocument5 pagesSoap Note 4 Dominguezapi-320062911100% (1)
- (PDF) Mcqs in Microbiology - Mohammed Bilal - Academia - Edu PDFDocument1 page(PDF) Mcqs in Microbiology - Mohammed Bilal - Academia - Edu PDFM AdnanNo ratings yet
- Neurobehavioral DisordersDocument5 pagesNeurobehavioral DisordersAsmaaAliAmmarNo ratings yet
- International Sports Science Conference 2014Document99 pagesInternational Sports Science Conference 2014talktoyeshaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal HyperthyroidismDocument30 pagesNeonatal HyperthyroidismVishal SidanaNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and DiagnosisDocument14 pagesLumbar Spinal Stenosis: Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and DiagnosisAnastasia TjanNo ratings yet
- BorreliaDocument93 pagesBorreliarehana100% (1)
- BARLA S. J. Emmanuel ETHNO MEDICINAL BELIEFS AND PRACTICES AMONG TRIBALS OF JHARKHANDDocument20 pagesBARLA S. J. Emmanuel ETHNO MEDICINAL BELIEFS AND PRACTICES AMONG TRIBALS OF JHARKHANDsaurabhshubhamNo ratings yet
- Normal Lab ValuesDocument3 pagesNormal Lab ValuesHNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Diabetes MellitusDocument23 pagesDiagnosis of Diabetes MellitusNkosinathi ShongweNo ratings yet
- The Causes and Effects of Alzheimer's Disease: The Silent DiseaseDocument35 pagesThe Causes and Effects of Alzheimer's Disease: The Silent DiseaseNina Canares100% (2)
- Gastritis - Etiology and Diagnosis - UpToDateDocument10 pagesGastritis - Etiology and Diagnosis - UpToDateLizbeth Navarrete SierraNo ratings yet