Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gynecology - Vaginal Bleeding
Uploaded by
Ansley Madala0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views1 pageGynecology - Vaginal Bleeding
Uploaded by
Ansley MadalaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
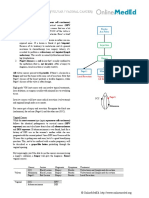
Gynecology [VAG BLEEDING 1: INTRO]
Introduction and Age Differential 11 51
Vaginal bleeding should occur in reproductive aged females and
should be at regular intervals - 21-35 days between cycles. Premenstrual Reproductive Postmenopausal
Menarche occurs around age 11 and has some trouble getting
started (normal). Menopause is around 51 and has some trouble
Foreign Body (MC) Pregnancy (MC) Atrophy (MC)
turning off (normal). When bleeding is heavy (menorrhagia),
Sexual Abuse Anatomy Endometrial Ca
irregular (metrorrhagia), or occurs in either premenarchal or
Precocious Puberty DUB HRT
postmenopausal females there may be a problem.
Sarcoma Botyroides
Bleeding exists along an age spectrum, with the most common Speculum Exam UPT Endometrial
causes of bleeding differing in each age group. Sampling
In premenarchal girls who are bleeding suspect foreign bodies
(most common) and sexual abuse. These girls needs a speculum
exam, often under anesthesia. Premenarchal Girls Vaginal Bleeding: covered in Puberty
In a post menopausal woman bleeding is cancer until proven
otherwise, ruled out with endometrial sampling. It’s usually
NOT cancer - simple atrophy is the most common. Hormone Postmenopausal women: covered in Endometrial cancer
replacement therapy can also induce bleeding.
For the reproductive aged female with meno, metro, or
menometrorrhagia it is far more complicated; we will follow the
neumonic “PAD”: Pregnancy, Anatomy, Dysfunctional Uterine Pregnancy: Covered in Vaginal Bleeding Pregnancy
Bleeding. Start by ruling out pregnancy with a UPT. Anatomy: Covered in Vaginal Bleeding Anatomy
DUB/AUB: Covered in Vaginal Bleeding Anatomy
Acute Uterine Bleeding
Women bleed. Some women can bleed a lot. They soak tampons,
and this may lead to an anemia. Anemia of chronic blood loss
(effectively iron deficiency anemia) can be treated with iron
supplementation and then finding out what is causing the heavy
bleeding. That’s what the vaginal bleed lectures are about.
But if a woman comes in with heavy, life-threatening bleeding,
the treatment course is quite different. The treatment parallels a
GI bleed.
The primary goal is stability: 2 large bore IVs, intravenous fluid
bolus, type and cross, transfuse as needed. To turn off uterine
bleeding, IV estrogen is administered.
If IV estrogen cannot obtain control of the bleeding, surgical
intervention is required, and escalates in severity.
Intracavitary balloon tamponade applies pressure and is
temporizing. D&C doesn’t impact subsequent menses, and might
take care of the problem acutely. Uterine artery embolization
(or ligation) is used when a vascular pathology is suspected (like
AVM or fibroids), and Hysterectomy is definitive, but the most
aggressive.
Women should be discharged on iron and some sort of
suppressive therapy (like OCPs) if she kept her uterus.
© OnlineMedEd. http://www.onlinemeded.org
You might also like
- Hysterectomy A-Z: Why, When, How and What afterFrom EverandHysterectomy A-Z: Why, When, How and What afterRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Gynecology - Vaginal BleedingDocument1 pageGynecology - Vaginal BleedingEugen MNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDocument8 pagesDysfunctional Uterine BleedingJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Threatened AbortionDocument4 pagesThreatened AbortionKate VillalonNo ratings yet
- Endometriosis: by Jane LyttletonDocument8 pagesEndometriosis: by Jane Lyttletonitsik12886No ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument2 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingeinlancherNo ratings yet
- Slide PUADocument55 pagesSlide PUAWinda LiraNo ratings yet
- Gynecologic Pain and Vaginal Bleeding: Jamie L. Collings and Nicholas A. BormDocument11 pagesGynecologic Pain and Vaginal Bleeding: Jamie L. Collings and Nicholas A. BormAnton ArifinNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Common Gynecological Complaints - Sundhed - DKDocument7 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Common Gynecological Complaints - Sundhed - DKPavel BerlinschiNo ratings yet
- Artículo Menopausia 2Document17 pagesArtículo Menopausia 2daniela otaNo ratings yet
- Postmenopausal Bleeding - StatPearls - NCBI BooksDocument11 pagesPostmenopausal Bleeding - StatPearls - NCBI BooksKalaivathanan VathananNo ratings yet
- Management Abnormal Uterine Bleeding SLCOG PDFDocument13 pagesManagement Abnormal Uterine Bleeding SLCOG PDFDoc IasNo ratings yet
- 651 1809 1 PBDocument8 pages651 1809 1 PBPadma LekshmiNo ratings yet
- Uterine Fibroids & EndometriosisDocument82 pagesUterine Fibroids & EndometriosisDuncan Jackson67% (3)
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument8 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingEcbNo ratings yet
- 16 Prolapse IndonesianDocument17 pages16 Prolapse IndonesianDwi MahendraNo ratings yet
- Post Menstrual BleedingDocument4 pagesPost Menstrual BleedingGinger SodarNo ratings yet
- OBGYN Revision NotesDocument9 pagesOBGYN Revision NotesJoanne Bowers100% (3)
- Impey Obs and Gynae Revision Notes PDFDocument9 pagesImpey Obs and Gynae Revision Notes PDFRoiseNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Dysfungsion Uterine BleedingDocument3 pagesTreatment of Dysfungsion Uterine BleedingAd RyanNo ratings yet
- Wafa Obgyn Smle2021Document171 pagesWafa Obgyn Smle2021Heba AhmedNo ratings yet
- Anum Noori (PNR1811029) Obstetric EmergenciesDocument63 pagesAnum Noori (PNR1811029) Obstetric Emergenciesvaishali TMU studentNo ratings yet
- Common Problems in Women S Health 19Document33 pagesCommon Problems in Women S Health 19afifahsalsabilaaaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument6 pagesAbnormal Uterine Bleedingcatcat669111No ratings yet
- The Pregnant Trauma PatientDocument77 pagesThe Pregnant Trauma PatientValdy Giovano ThomasNo ratings yet
- Obs-Gynae CP Final (2nd Batch)Document89 pagesObs-Gynae CP Final (2nd Batch)Dipesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Makalah Rule of Ultrasound in Management of Uterine LeiomyomaDocument23 pagesMakalah Rule of Ultrasound in Management of Uterine LeiomyomaKristabella GianinaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: - Rou'a Eyad - Rahaf EyadDocument35 pagesAbnormal Uterine Bleeding: - Rou'a Eyad - Rahaf EyadYazeed Asrawi0% (1)
- Ob GynDocument13 pagesOb GynDianne Geremy RojoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument28 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingirmaarmiyahNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Utrine Bleeding ManagementDocument75 pagesAbnormal Utrine Bleeding ManagementwaleedaliNo ratings yet
- Case 3 AlexiDocument17 pagesCase 3 AlexiHenry HNo ratings yet
- Bleeding During PregnancyDocument8 pagesBleeding During Pregnancyfernandezrachelle44No ratings yet
- Perimenopausal Bleeding and Bleeding After MenopauseDocument5 pagesPerimenopausal Bleeding and Bleeding After MenopauseAnonymous KwWTUPjXNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Vaginal Bleeding 3Document2 pagesGynecology - Vaginal Bleeding 3Ansley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Disorders in The Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesDisorders in The Reproductive SystemBeatriz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Embarazo EctópicoDocument8 pagesEmbarazo EctópicoCristhian MendezNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument55 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingRiskyWulandariNo ratings yet
- Local Media7887757728146616486Document13 pagesLocal Media7887757728146616486IRA MONIQUE CABADENNo ratings yet
- Uterus NeoDocument11 pagesUterus NeoHester Marie SimpiaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Adnexal MassDocument2 pagesGynecology Adnexal MassgeNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB)Document45 pagesAbnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB)asdf0% (1)
- Gender Term List 16-1Document30 pagesGender Term List 16-1rr48843No ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy: ReviewDocument6 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: ReviewIgha MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding: Clinical UpdateDocument3 pagesDysfunctional Uterine Bleeding: Clinical Updateragil putra jNo ratings yet
- 14 - AmenorrhoeaDocument26 pages14 - AmenorrhoeaHimanshu MehtaNo ratings yet
- Uterine FibroidsDocument30 pagesUterine Fibroidsbabudocs1No ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument23 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingTakeru Ferry100% (2)
- TBL4, VTE in Pregnancy and Puerperium. RashidDocument5 pagesTBL4, VTE in Pregnancy and Puerperium. Rashidmedical chroniclesNo ratings yet
- The Woman With Postmenopausal Bleeding: Gynaecological MalignanciesDocument5 pagesThe Woman With Postmenopausal Bleeding: Gynaecological MalignanciesWahyu AriyawatiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Woman and Family Experiencing A Postpartal ComplicationDocument43 pagesNursing Care of A Woman and Family Experiencing A Postpartal ComplicationVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument64 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingAakriti GargNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhage in Early and Late Pregnancy (Dr. Hariyasa)Document29 pagesHemorrhage in Early and Late Pregnancy (Dr. Hariyasa)elokNo ratings yet
- Clinical: Section 3 of 10Document36 pagesClinical: Section 3 of 10coleNo ratings yet
- Benign Ovarian Tumors & EndometriosisDocument21 pagesBenign Ovarian Tumors & EndometriosisnoreenfatimamaanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Gynecology Uterine BleedingDocument7 pagesComprehensive Gynecology Uterine BleedingRem AlfelorNo ratings yet
- 8.office Diagnosis and Management of Abnromal Uterine Bleeding - PublishedDocument16 pages8.office Diagnosis and Management of Abnromal Uterine Bleeding - PublishedRonald Ivan WijayaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument23 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingTakeru Ferry100% (1)
- Uterine Fibroid - Viva VoceDocument77 pagesUterine Fibroid - Viva VoceK Haynes Raja100% (1)
- Gynecology - VaginalVulvar CancerDocument1 pageGynecology - VaginalVulvar CancerAnsley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Vaginal Bleeding 3Document2 pagesGynecology - Vaginal Bleeding 3Ansley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Secondary AmenorrheaDocument2 pagesGynecology - Secondary AmenorrheaAnsley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Cancer IntroDocument1 pageGynecology - Cancer IntroAnsley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Adnexal MassDocument2 pagesGynecology - Adnexal MassAnsley MadalaNo ratings yet
- Doxazosin MesylateDocument2 pagesDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Why Cell Phone Towers Are So Bad For Your Health?Document6 pagesWhy Cell Phone Towers Are So Bad For Your Health?Dr. Sirish100% (1)
- Ahlskog Et Al. Mayo Clin Proc 2011Document9 pagesAhlskog Et Al. Mayo Clin Proc 2011Thais AmandaNo ratings yet
- Marijuana: What Is Cannabis?Document24 pagesMarijuana: What Is Cannabis?kamal asghar100% (1)
- Acid Base BalanceDocument44 pagesAcid Base BalanceKenny JapNo ratings yet
- NHM UP CHO Previous PapersDocument30 pagesNHM UP CHO Previous PapersRajeev PalNo ratings yet
- Consolidation Bo MaizatulDocument4 pagesConsolidation Bo MaizatulChris Tine ChiaNo ratings yet
- Horner'S Syndrome - : Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationDocument3 pagesHorner'S Syndrome - : Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationVictorija Evania Lucille DeldioNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument2 pagesHypothyroidismwael orabiNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis NP: Deficit of KnowledgeDocument2 pagesUrolithiasis NP: Deficit of Knowledgevictor zhefaNo ratings yet
- DosesDocument16 pagesDosesAli Adnan AfridiNo ratings yet
- Prostatitis and Male Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: What Is The Prostate?Document10 pagesProstatitis and Male Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: What Is The Prostate?emagooNo ratings yet
- AK - Guidelines Severity Classification GAADocument53 pagesAK - Guidelines Severity Classification GAANadya GhifaniNo ratings yet
- LYMPHOMADocument12 pagesLYMPHOMAश्रीकृष्ण हेङ्गजूNo ratings yet
- List of 37 Critical IllnessDocument13 pagesList of 37 Critical IllnessdexterNo ratings yet
- Gabapentin Can Significantly Improve Dystonia Severity and Quality of Life in ChildrenDocument8 pagesGabapentin Can Significantly Improve Dystonia Severity and Quality of Life in ChildrenDr-Asit Kumar ParidaNo ratings yet
- New Case - Firza Humaira RespiDocument21 pagesNew Case - Firza Humaira RespiHardiyanti HermanNo ratings yet
- Itas2010 - Indiantakayasu'S Arteritis Activity ScoreDocument2 pagesItas2010 - Indiantakayasu'S Arteritis Activity ScoreLp Saikumar DoradlaNo ratings yet
- Internation Classification ICSD III BetaDocument8 pagesInternation Classification ICSD III BetaRikizu HobbiesNo ratings yet
- Telemed Written Report 4Document5 pagesTelemed Written Report 4Gabriel MillaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument66 pagesUntitledPhilip Edward OsborneNo ratings yet
- A. Transverse Ligament: B. Ligamentum TeresDocument30 pagesA. Transverse Ligament: B. Ligamentum TeresUsmle seekerNo ratings yet
- Eye 10 Years-1Document4 pagesEye 10 Years-1deepNo ratings yet
- Best of Five Mcqs For The Endocrinology and Diabetes Sce Atul Kalhan Full ChapterDocument67 pagesBest of Five Mcqs For The Endocrinology and Diabetes Sce Atul Kalhan Full Chapterdeanna.haire453100% (5)
- Precise Location of Chinese Scalp Acupuncture Areas Requires Identification of Two Imaginary Lines On The HeadDocument9 pagesPrecise Location of Chinese Scalp Acupuncture Areas Requires Identification of Two Imaginary Lines On The Headubirajara3fernandes3100% (4)
- NCM 116Document32 pagesNCM 116Yeany IddiNo ratings yet
- PARAQUAT POISIONING 3rd Block Imed COMPLIEDDocument15 pagesPARAQUAT POISIONING 3rd Block Imed COMPLIEDMohil PratapNo ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument5 pagesNeonatal SepsisBhawna PandhuNo ratings yet
- Training Manual Hypertensive Disorder in Pregnancy 3rd Edition 2018 PDFDocument140 pagesTraining Manual Hypertensive Disorder in Pregnancy 3rd Edition 2018 PDFJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- The Emerging Spectrum of COVID-19 Neurology: Clinical, Radiological and Laboratory FindingsDocument36 pagesThe Emerging Spectrum of COVID-19 Neurology: Clinical, Radiological and Laboratory FindingsDino AdijayaNo ratings yet
- The Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeFrom EverandThe Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (84)
- I Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionFrom EverandI Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (42)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (267)
- The Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameFrom EverandThe Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (88)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Secret of the Golden Flower: A Chinese Book Of LifeFrom EverandThe Secret of the Golden Flower: A Chinese Book Of LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (171)
- Summary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (61)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (329)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (256)
- The Fun Habit: How the Pursuit of Joy and Wonder Can Change Your LifeFrom EverandThe Fun Habit: How the Pursuit of Joy and Wonder Can Change Your LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)