Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STROKE
STROKE
Uploaded by
Khristinez TadejS0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesMassage Stroke
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMassage Stroke
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesSTROKE
STROKE
Uploaded by
Khristinez TadejSMassage Stroke
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
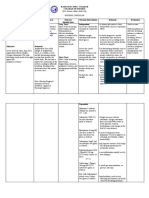
STROKE RATIONALE BENEFITS
1.EFFLEURAGE Used to introduce touch and Warm bodily tissues, making
for applying lubricant them more extensible
Other term –Gliding
Used for assessing and Relaxes the client and
Unbroken gliding movements exploring surface and prepares the area for deeper
repeated following the underlying tissues strokes
contour of the body using
a. Palm Used to begin and end a Soothes an area after deep
b. Knuckles massage to move blood and work
c. Fingertips lymph
d. forearms Addresses places too for
Used to prepare tissue for deep, specific work
deeper massage and flush out
tissues after using other Calm the nervous system
strokes when done slowly
Used on almost every type of Stimulate the nervous system
body surface hence a when done quickly
preferred transition stroke to
use between other strokes Relieve insomnia
Delivered using a lean-and-
drag technique
When working on extremities,
first work area most proximal,
then to distal, stroking in the
heart direction
2. PETRISSAGE stroke of choice to milk the Working out metabolic waste
tissue of metabolic waste and
draw new blood and oxygen Reducing local swelling
Other term-Kneading into the tissues
Improving cellular nutrition
the hands is in C formation]
Mechanically lengthen the
Cycle to rhythmic lifting, it lifts up the skin and the muscle
squeezing and releasing underlying muscle tissue and
tissue firmly knead, wring or squeeze Addressing the tension under
the surface
a. knuckling Lifting, compressing and
releasing of muscle tissue can Reducing muscle soreness
be done in one or both hands and stiffness
intermittently
Softening superficial fascia
The focus is on lifting the
tissue and moving it vertically
or horizontally rather than just
pinching it.
The pressure should be
applied in a rhythmic pattern
to achieve alternate
compression and relaxation of
the muscle
3. FRICTION Often used for areas that have Generating heat
little or no blood supply, such
Other term: Rubbing as ligaments and tendons Loosening stiffness in joints
Deep friction is well suited for Improving the glandular
areas that lack muscle bulk action of the skin
Compressing tissues in such as the ankle, the sides of
several directions;-sliding the head, or the sub-occipital Promoting proper scar
hands, palm, finger, knuckles regions formation
back and forth over skin or
deeper tissue layers. Applied either by pressing Breaking down and freeing
down or around an area or adhesions
Usually dry, with little or with circular or linear
without oil reciprocating movements Softening hyperplasia
Reducing trigger and tender
point formation
4. TAPOTEMENT Has a pleasant stimulating Stimulate nerve endings
effect initially becoming more
Other term: Percussion sedative if continued
Used by respiratory therapist
and nurses to loosen phlegm Aid in decongesting the lungs
congestion in the lungs
Repetitive staccato striking Tone atrophied muscles
movements of hands, The style of percussion
simultaneously or alternately depends on the location Increase local blood flows
using: where it is employed and the
a. Ulnar surface of hands desired effect Access deeper structure such
b. Fingertips as hip rotators
c. Open palm Muscular areas such as the leg
d. Cupped palm and hips may absorb more Create an ultrasound effect
e. Loosely closed fist force in the delivery and thin manually
tissues or delicate areas such
as the face require a smaller Desensitize a hypersensitive
lighter tap area
-
Avoid application immediately
after exercise because this
stroke can activate muscle
spindles and stimulate
cramping
Heavy strokes over the
kidneys in the low-back area is
not advised
May be applied directly to the
skin or through the drape
Begin with light pressure and
moderate strike speed
gradually increase speed and
finally diminish speed and
depth
Delivered rhythmically
allowing hands to spring back
after contact
Percussion delivered with too
much force can bruise a client
5. VIBRATION Done properly you will be able Stimulates muscle spindles
to observe the tissue moving
Other term: shaking near the area on contact Relieves upper respiratory
tract congestion
The client should feel the
onset and removal of pressure Stimulate peristalsis of the
Rapid shaking, quivering, large intestine
trembling or rocking Performing vibration correctly
movements applied with requires coordination and Moves gas in the lower GIT
fingertips of full hand. practice
Stimulate synovial fluid
Is the most physically production in joints
demanding massage stroke
Accesses deeper structure as
Avoid imposing unnatural hip rotators
rhythm
Reduces trigger and tender
point activity
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Rowans Primer of Eeg 2E Second Edition Fields All ChapterDocument67 pagesRowans Primer of Eeg 2E Second Edition Fields All Chapterbetty.ramirez330100% (9)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Massage Therapy NC IIDocument82 pagesMassage Therapy NC IIJeremiash Noblesala Dela Cruz86% (7)
- Lifesci 2G03Document6 pagesLifesci 2G03JamesThoNo ratings yet
- Application Form: Technical Education and Skills Development AuthorityDocument19 pagesApplication Form: Technical Education and Skills Development AuthorityKhristinez TadejSNo ratings yet
- Endangerment SiteDocument1 pageEndangerment SiteKhristinez TadejSNo ratings yet
- Good Morning SirDocument5 pagesGood Morning SirKhristinez TadejSNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of ChildDocument58 pagesGrowth and Development of ChildBasant karn100% (51)
- BookDocument248 pagesBookMostafa GabrNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument16 pagesBlood VesselsAlen OsmanovicNo ratings yet
- Updated NCM 107 Lecture Week 7Document27 pagesUpdated NCM 107 Lecture Week 7Quencee CalaycayNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye: Structure and Function: R M F. LDocument1 pageThe Human Eye: Structure and Function: R M F. LzodiacgeminyNo ratings yet
- Multiple GestationDocument3 pagesMultiple GestationLim Min AiNo ratings yet
- The Kisumu National PolytechnicDocument40 pagesThe Kisumu National PolytechnicphilipNo ratings yet
- TimeTableJanJune2020 PDFDocument160 pagesTimeTableJanJune2020 PDFritik dwivediNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/11Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/11Milinda De SilvaNo ratings yet
- English 1sci17 3trim2Document3 pagesEnglish 1sci17 3trim2Tigane ZinebNo ratings yet
- Ch. 25 Body Defence MechanismsDocument34 pagesCh. 25 Body Defence Mechanisms吴昊No ratings yet
- NCP Anaphylactic ShockDocument6 pagesNCP Anaphylactic ShockKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Bovista LycoperdonDocument4 pagesBovista LycoperdonnitkolNo ratings yet
- SOP Abbot iSTAT User GuideDocument8 pagesSOP Abbot iSTAT User GuideBiomedicaNo ratings yet
- 2015JARG-BraekeleerETAL-Genetic Aspects of Monomorphic Teratozoospermia - A ReviewDocument9 pages2015JARG-BraekeleerETAL-Genetic Aspects of Monomorphic Teratozoospermia - A Reviewkong_666064846No ratings yet
- The Bohr EffectDocument16 pagesThe Bohr EffectZaid SulimanNo ratings yet
- Anthropology Power PointDocument95 pagesAnthropology Power PointWaaqoo Guutuu Waaqoo GuutuuNo ratings yet
- CSEC Form 4 Human and Social Biology NotesDocument4 pagesCSEC Form 4 Human and Social Biology Notessmbdy tbhhh100% (1)
- Homosexuality Study: A Brief Study by Himel ShagorDocument10 pagesHomosexuality Study: A Brief Study by Himel Shagorপ্রাকৃতজন0% (1)
- CHAPTER 12 - Coordination & ResponseDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 12 - Coordination & ResponseHAJAR LENNo ratings yet
- Notes On Breast Cancer 2022Document9 pagesNotes On Breast Cancer 2022Sharvienraaj VelukumaranNo ratings yet
- Neutral ZoneDocument219 pagesNeutral ZoneAbhishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Vol. 17. Basidiomycetes - Marasmieae. Singer, L. 1976Document354 pagesVol. 17. Basidiomycetes - Marasmieae. Singer, L. 1976러카일No ratings yet
- Module 14 BiotechnologyDocument8 pagesModule 14 BiotechnologychristineNo ratings yet
- Clark Zhang: Czhang30@jhmi - EduDocument4 pagesClark Zhang: Czhang30@jhmi - Eduapi-278386371No ratings yet
- Natural Antimicrobial and Bioactive Compounds From Ludwigia Parviflora RoxbDocument6 pagesNatural Antimicrobial and Bioactive Compounds From Ludwigia Parviflora Roxbnguyen ba trungNo ratings yet
- A Review On Methods Application and Properties of Immobilized EnzymeDocument9 pagesA Review On Methods Application and Properties of Immobilized EnzymeSimon LexsNo ratings yet
- tmp64C4 TMPDocument12 pagestmp64C4 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet