Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI Edition
Uploaded by
Noman MaqsoodOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI Edition
Uploaded by
Noman MaqsoodCopyright:
Available Formats
NEW!
Textbook Solutions Expert Q&A Study Pack Practice
Find solutions for your homework Search
home / study / science / chemistry / chemical engineering / chemical engineering solutions manuals / fundamentals of chemical engineering thermodynamics, si edition / 1st edition / chapter 11 / problem
20p
Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Post a question
Thermodynamics, SI Edition (1st Edition)
Answers from our experts for your tough
homework questions
See this solution in the app Enter question
Chapter 11, Problem 20P Bookmark Show all steps: ON
Continue to post
Problem
0 questions remaining
The azeotrope of a binary mixture, being an important point on a mixture phase diagram, is often
used for parameter estimation. To that end, use the azeotropic information for the acetone (1) +
Snap a photo from your
cyclohexane (2) system at 308.15 K to determine the A parameter of the 1-parameter Margules phone to post a question
equation. Then plot the Pxy predictions from this model and compare it to the experimental data We'll send you a one-time
in Table. Note that you will need to plot the experimental data first to estimate the location of the
download link
azeotrope.
888-888-8888 Text me
By providing your phone number, you agree to receive
a one-time automated text message with a link to get
the app. Standard messaging rates may apply.
My Textbook Solutions
Fundamental Automation, Fundamental
Table Vapor-liquid equilibrium of acetone (1) + cyclohexane (2) at 308.15 K. s of... Production... s of Logic...
1st Edition 4th Edition 7th Edition
View all solutions
Step-by-step solution
Step 1 of 17
Denote “1” as component of acetone and “2” as component of cyclohexane.
Comment
Step 2 of 17
Show the data of mole fraction of component 1 in liquid and vapor phase with system pressure
as in Table (1).
P (kPa)
19.625 0 0
37.877 0.098 0.482
45.476 0.198 0.601
47.969 0.283 0.635
49.489 0.387 0.665
50.316 0.489 0.686
50.969 0.598 0.709
51.302 0.7 0.732
51.409 0.771 0.754
50.196 0.895 0.841
45.863 1 1
Comment
Step 3 of 17
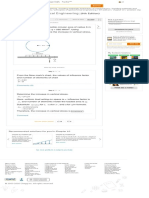
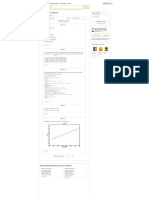
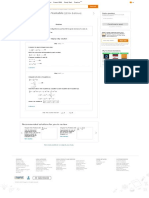
Use the above data and plot the pressure versus as in Figure (1).
Comment
Step 4 of 17
From Figure (1) the azetrope is about and .
From this calculation, point out to parameterize the model.
Comment
Step 5 of 17
Use the 1-Parameter Margules Equation and express the activity coefficient of component 1 and
2.
Here, parameter is A, activity coefficient of component 1 and 2 is respectively.
Comment
Step 6 of 17
Express the activity coefficient of pure component i.
…… (3)
Here, system pressure is P, mole fraction of component i in vapor phase is , mole fraction of
component i in liquid phase is , and vapor pressure of component i is .
Comment
Step 7 of 17
Express the vapor pressure using Antoine equation.
…… (4)
From Appendix E, “Antoine Equations”, write the following properties for component 1 and 2.
Parameters Acetone (1) Cyclohexane (2)
A 7.11714 6.84130
B 1210.595 1201.53
C 229.664 222.65
Comment
Step 8 of 17
From Equation (4), substitute for T, 7.11714 for A, 1210.595 for B, and
229.664 for C and calculate the vapor pressure for component 1.
Comment
Step 9 of 17
From Equation (4), substitute for T, 6.84130 for A, 1210.53 for B, and 222.65
for C and calculate the vapor pressure for component 2.
Comments (1)
Step 10 of 17
From Equation (3), substitute 46.55 kPa for , 0.74 for , 51.5 kPa for P, and 0.74 for
and calculate the activity coefficient for the component 1.
Comment
Step 11 of 17
From Equation (3), substitute 18.52 kPa for , 0.26 for , 51.5 kPa for P, and 0.26 for
and calculate the activity coefficient for the component 2.
Comment
Step 12 of 17
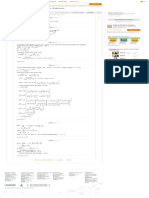
Write the relationship to use for the excess molar Gibbs free energy.
Here, gas constant is R and temperature is T.
Substitute 2.780 for , 1.106 for , 0.74 for , and 0.74 for .
Comment
Step 13 of 17
Write the excess molar Gibbs free energy for 1-parameter Margules equation.
Here, parameter is A.
Substitute 0.34039 for , 0.74 for , and 0.26 for .
Comment
Step 14 of 17
Presently we are prepared to foresee the conduct at any composition of interest and plot the
model forecasts. We will utilize this A quality to find the activity coefficients at the desired
composition. We will go from x1 = 0 to x1 = 1 in additions of 0.05.
Comment
Step 15 of 17
Use the Modified Raoult’s law, calculate the pressure.
…… (5)
Express the modified Raoult’s law for combined component of 1 and 2.
…… (6)
Comment
Step 16 of 17
Use Equation (5), express the value of .
…… (7)
Along these lines, for each estimation of , we will settle for the activity coefficient from the
model and decide both the pressure and vapor stage composition from the model.
Comment
Step 17 of 17
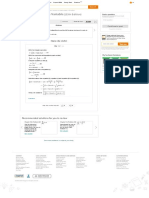
Plot the pressure P versus and versus for the model (lines) using Equation (6) and (7)
and Table (1) data as in Figure (2).
Comment
Was this solution helpful? 2 1
Recommended solutions for you in Chapter 11
Chapter 11, Solution 5E Chapter 11, Problem 29P
The mole fraction of In a process analysis
component-(1) in liquid application, you are
mixture is 0.20. The working with the di-n-
vapor pressure of propyl ether (1) and 2-
component-(1) is 10 kPa propanol (2) system at
and that for... 25°C. Youthink...
See solution See solution
See more problems in subjects you study
COMPANY LEGAL & POLICIES CHEGG PRODUCTS AND SERVICES CHEGG NETWORK CUSTOMER SERVICE
About Chegg Advertising Choices Cheap Textbooks Online Tutoring EasyBib Customer Service
Become a Tutor Cookie Notice Chegg Coupon Sell Textbooks Internships.com Give Us Feedback
Chegg For Good General Policies Chegg Play Solutions Manual Studyblue Help with Chegg Tutors
College Marketing Intellectual Property Rights Chegg Study Help Study 101 Thinkful Help with eTextbooks
Corporate Development Terms of Use College Textbooks Textbook Rental Help to use EasyBib Plus
Investor Relations Chegg Tutors Terms of Service eTextbooks Used Textbooks Manage Chegg Study
Jobs Global Privacy Policy Chegg Math Solver Digital Access Codes Subscription
Join Our Affiliate Program DO NOT SELL MY INFO Mobile Apps Chegg Money Return Your Books
Media Center Honor Code Textbook Return Policy
Site Map
© 2003-2020 Chegg Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI EditionDocument1 pageFundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI EditionNoman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI EditionDocument1 pageFundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI EditionNoman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Solved - Chapter 10 Problem 28P Solution - Classical Mechanics 0th EditionDocument6 pagesSolved - Chapter 10 Problem 28P Solution - Classical Mechanics 0th EditionRyuNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis and Design, SI EditionDocument5 pagesPower System Analysis and Design, SI EditionAkimeNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering: (5th Edition)Document4 pagesFoundations of Materials Science and Engineering: (5th Edition)IdridNo ratings yet
- Pregunta 6. Tarea 3Document3 pagesPregunta 6. Tarea 3Josebeth UlateNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: (7th Edition)Document5 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: (7th Edition)Alia TasNo ratings yet
- Solved Solve Problem 8.10 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Document1 pageSolved Solve Problem 8.10 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- TSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 36P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionDocument1 pageTSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 36P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionxomuxNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.41. Given q2 3800 LBFT, x1 18 ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.41. Given q2 3800 LBFT, x1 18 ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - A Mixture 25 Mol N Pentane 45 Mol N Hexane and 3... PDFDocument6 pagesSolved - A Mixture 25 Mol N Pentane 45 Mol N Hexane and 3... PDFYasmin KayeNo ratings yet
- Solved A Hot Water Stream at 80°C Enters A Mixing Chamber With CheggDocument3 pagesSolved A Hot Water Stream at 80°C Enters A Mixing Chamber With Cheggsalim.22en1No ratings yet
- TSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 34P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionDocument1 pageTSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 34P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionxomuxNo ratings yet
- Local Media2138585013869044277Document3 pagesLocal Media2138585013869044277panger moooNo ratings yet
- Loose Leaf For Mechanics of Materials: (7th Edition)Document5 pagesLoose Leaf For Mechanics of Materials: (7th Edition)TonkaNo ratings yet
- Solved - If The Salmon River Temperature in Problem 7-33 Decreas...Document2 pagesSolved - If The Salmon River Temperature in Problem 7-33 Decreas...mabmi17No ratings yet
- For The Radial Power System Shown in Figure 1.17, ...Document6 pagesFor The Radial Power System Shown in Figure 1.17, ...Ayush Gupta 4-Year B.Tech. Electrical Engineering100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics: (7th Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics: (7th Edition)Hassanein HeidarNo ratings yet
- A Liquid Delivery SystemDocument3 pagesA Liquid Delivery SystemEhtisham ZiaNo ratings yet
- Solved - A Stage Extraction Process Is Depicted in Fig. P9.13. I...Document3 pagesSolved - A Stage Extraction Process Is Depicted in Fig. P9.13. I...Galuh Saputra 5No ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.46. A Flexible Circular Area of Radi...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.46. A Flexible Circular Area of Radi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - Three Groups of Students From The Geotechnical EngineerDocument5 pagesSolved - Three Groups of Students From The Geotechnical Engineerabdullahiomar2020100% (1)
- Solved - A Prototype Automobile Is Designed To Travel at 65 km2Fh Cheggcom PDFDocument3 pagesSolved - A Prototype Automobile Is Designed To Travel at 65 km2Fh Cheggcom PDFNabihah AzanNo ratings yet
- Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design: (9th Edition)Document3 pagesShigley's Mechanical Engineering Design: (9th Edition)mahdi najehNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.49. For The Linearly Increasing Vert...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.49. For The Linearly Increasing Vert...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: (7th Edition)Document4 pagesFluid Mechanics: (7th Edition)Asfand Yar QureshiNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.43. A Strip Load of Q 1450 lbft2 ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.43. A Strip Load of Q 1450 lbft2 ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 7.25. During An Auger Hole Test To Dete...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 7.25. During An Auger Hole Test To Dete...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Estimate The Hydraulic Conductivity of A Saturated Clay...Document1 pageSolved Estimate The Hydraulic Conductivity of A Saturated Clay...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To The Cross Section of The Earth Dam Shown in Fi...Document1 pageSolved Refer To The Cross Section of The Earth Dam Shown in Fi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved A 10-M-Thick Layer of Stiff Saturated Clay Is Underlain...Document1 pageSolved A 10-M-Thick Layer of Stiff Saturated Clay Is Underlain...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Repeat Problem 10.3 For The Element Shown in Figure 10....Document1 pageSolved Repeat Problem 10.3 For The Element Shown in Figure 10....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Repeat Problem 8.8 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Document1 pageSolved Repeat Problem 8.8 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals and Applications: (3rd Edition)Document8 pagesFluid Mechanics Fundamentals and Applications: (3rd Edition)W DDNo ratings yet
- Solved - Chapter 10 Problem 14P Solution - Classical Mechanics 0th EditionDocument3 pagesSolved - Chapter 10 Problem 14P Solution - Classical Mechanics 0th EditionRyuNo ratings yet
- Question: Pr.1 (45 Points) Boiling of Saturated Water at 137.78 C Occurs oDocument3 pagesQuestion: Pr.1 (45 Points) Boiling of Saturated Water at 137.78 C Occurs owaqasNo ratings yet
- Question: Water (Temperature 68F) Is Pumped From A Reservoir To A StoragDocument1 pageQuestion: Water (Temperature 68F) Is Pumped From A Reservoir To A StoragNiell Anakeen dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Solved - Chapter 8 Problem 31P Solution - MATLAB 4th EditionDocument2 pagesSolved - Chapter 8 Problem 31P Solution - MATLAB 4th EditionSalahuddin D. EdolNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Problem 8.4. Using The Flow Net Drawn, Calcula...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Problem 8.4. Using The Flow Net Drawn, Calcula...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Fluid Mechanics: (11th Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Fluid Mechanics: (11th Edition)كرار عبدالحسين قاسمNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Consider The Hypothetical Eutectic Phase Diagram F...Document3 pagesConsider The Hypothetical Eutectic Phase Diagram F...IdridNo ratings yet
- Solved - Steam at 6000 Kpa and 500°C Enters A Steady-Flow Turbin...Document2 pagesSolved - Steam at 6000 Kpa and 500°C Enters A Steady-Flow Turbin...Irfan Nazir NoriNo ratings yet
- Solved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An Alu-I... PDFDocument3 pagesSolved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An Alu-I... PDFTafseer-e-QuranNo ratings yet
- Solved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An AluDocument3 pagesSolved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An AluTafseer-e-QuranNo ratings yet
- Solved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An Alu-I... PDFDocument3 pagesSolved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An Alu-I... PDFTafseer-e-QuranNo ratings yet
- Solved - During A Plant Visit, It Was Noticed That A 12-M-Long S...Document1 pageSolved - During A Plant Visit, It Was Noticed That A 12-M-Long S...Shaiful IzzatNo ratings yet
- Solved A Pervious Soil Layer Is Sandwiched Between Two Impervi...Document1 pageSolved A Pervious Soil Layer Is Sandwiched Between Two Impervi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.47. A Flexible Rectangular Area Is S...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.47. A Flexible Rectangular Area Is S...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Question: Exercise (Test Your Understanding) A Beam of Yellow Light WithDocument3 pagesQuestion: Exercise (Test Your Understanding) A Beam of Yellow Light WithMuhammad SatrioNo ratings yet
- Solved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Document1 pageSolved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - Determine The Real Root of F (X) 5x3 - 5x2 + 6x - 2 - (...Document6 pagesSolved - Determine The Real Root of F (X) 5x3 - 5x2 + 6x - 2 - (...Angel Maliel Limon CaceresNo ratings yet
- Student Solutions Manual, Volume 1 For Serway/Jewett's Physics For Scientists and EngineersDocument5 pagesStudent Solutions Manual, Volume 1 For Serway/Jewett's Physics For Scientists and EngineersMalik AsadNo ratings yet
- Solved - The Following Is A Set of VLE Data For The System Aceto...Document10 pagesSolved - The Following Is A Set of VLE Data For The System Aceto...Ehtisham ZiaNo ratings yet
- 6.9 For The La For The Plane Strain Elements Shown...Document4 pages6.9 For The La For The Plane Strain Elements Shown...EdilunarNo ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics: (0th Edition)Document1 pageClassical Mechanics: (0th Edition)ChaseNo ratings yet
- Solved For A Given Sandy Soil, Emax 0.75 and Emin 0.52. If...Document1 pageSolved For A Given Sandy Soil, Emax 0.75 and Emin 0.52. If...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved Figure 9.29 Shows The Zone of Capillary Rise Within A C... Chegg - Com 2Document1 pageSolved Figure 9.29 Shows The Zone of Capillary Rise Within A C... Chegg - Com 2Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Finite Element Analysis: Formulation, Verification and ValidationFrom EverandIntroduction to Finite Element Analysis: Formulation, Verification and ValidationNo ratings yet
- Calculus of A Single Variable: (11th Edition)Document1 pageCalculus of A Single Variable: (11th Edition)Noman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Calculus of A Single Variable: (11th Edition)Document1 pageCalculus of A Single Variable: (11th Edition)Noman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- 431 ProjectDocument8 pages431 ProjectNoman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Calculus of A Single Variable: (11th Edition)Document1 pageCalculus of A Single Variable: (11th Edition)Noman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Nozzles - Process Design, From The OutsideDocument12 pagesNozzles - Process Design, From The OutsideperoooNo ratings yet
- The Need For International Accounting StandardsDocument1 pageThe Need For International Accounting StandardsYuvaraj RajNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3Nate LoNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lecture NotesDocument120 pagesDBMS Lecture NoteshawltuNo ratings yet
- Phillips Curve and Okun's LawDocument3 pagesPhillips Curve and Okun's LawSheldon JosephNo ratings yet
- MikroTik Course Outline UpdatedDocument2 pagesMikroTik Course Outline UpdatedAbdul KuddusNo ratings yet
- 3hac13347 1Document18 pages3hac13347 1CJ MallickNo ratings yet
- Unmatched Power. Unmatched Creative Freedom.: Nvidia Quadro P6000Document1 pageUnmatched Power. Unmatched Creative Freedom.: Nvidia Quadro P6000Família FranciscoNo ratings yet
- BARACARBDocument2 pagesBARACARBYudha Satria50% (2)
- Company Profile: Our BeginningDocument1 pageCompany Profile: Our BeginningSantoshPaul CleanlandNo ratings yet
- Soil Fabric LoggingDocument4 pagesSoil Fabric LoggingCaraUnggahNo ratings yet
- GrimaldiDocument104 pagesGrimaldiRicardo MartinsNo ratings yet
- Dan Fue Leung v. IACDocument2 pagesDan Fue Leung v. IACCedricNo ratings yet
- Completion Fluids BaroidDocument26 pagesCompletion Fluids Baroidcrown212No ratings yet
- 5TH International Conference BrochureDocument5 pages5TH International Conference Brochureanup patwalNo ratings yet
- Session 6 OligopolyDocument43 pagesSession 6 OligopolyROKGame 1234No ratings yet
- 7Document11 pages7Va PolNo ratings yet
- Manuale NanoVIP3 Rel. 1.5 en (UK)Document76 pagesManuale NanoVIP3 Rel. 1.5 en (UK)ECNo ratings yet
- Mba Thesis EsamiDocument67 pagesMba Thesis EsamiMarket Chain AlliancesNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips Chapter 12 Sonic Logs Lecture Notes For Pet 370 Spring 2012 Prepared by Thomas W Engler PHD PeDocument21 pagesSilo - Tips Chapter 12 Sonic Logs Lecture Notes For Pet 370 Spring 2012 Prepared by Thomas W Engler PHD PeIntanNurDaniaNo ratings yet
- Application of Power Electronic Converters in Electric Vehicles andDocument22 pagesApplication of Power Electronic Converters in Electric Vehicles andfekadu gebeyNo ratings yet
- NTP Dummy ConfigDocument1 pageNTP Dummy Configastir1234No ratings yet
- Opportunities For Enhanced Lean Construction Management Using Internet of Things StandardsDocument12 pagesOpportunities For Enhanced Lean Construction Management Using Internet of Things StandardsBrahian Roman CabreraNo ratings yet
- CE 332 Environmental Engineering-Lab I (Lab Manual) : Department of Civil EngineeringDocument75 pagesCE 332 Environmental Engineering-Lab I (Lab Manual) : Department of Civil EngineeringjulesNo ratings yet
- BIR Rule on Taxing Clubs OverturnedDocument2 pagesBIR Rule on Taxing Clubs OverturnedLucky JavellanaNo ratings yet
- Nirman SahayakDocument32 pagesNirman SahayakRoti100% (1)
- Maintenance Manual For AC LHB CoachesDocument729 pagesMaintenance Manual For AC LHB Coachesdiiiiips100% (14)
- Operator E-Jets News Rel 030Document16 pagesOperator E-Jets News Rel 030jivomirNo ratings yet
- Community Service ProposalDocument3 pagesCommunity Service ProposalAbdurahman AbdulhakimNo ratings yet
- Marquez Vs Comelec GR 112889Document1 pageMarquez Vs Comelec GR 112889JFA100% (1)