Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI Edition
Uploaded by
Noman MaqsoodOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI Edition
Uploaded by
Noman MaqsoodCopyright:
Available Formats
NEW!
Textbook Solutions Expert Q&A Study Pack Practice
Find solutions for your homework Search
home / study / science / chemistry / chemical engineering / chemical engineering solutions manuals / fundamentals of chemical engineering thermodynamics, si edition / 1st edition / chapter 11 / problem
21p
Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Post a question
Thermodynamics, SI Edition (1st Edition)
Answers from our experts for your tough
homework questions
See this solution in the app Enter question
Chapter 11, Problem 21P 2 Bookmarks Show all steps: ON
Continue to post
Problem
0 questions remaining
Consider the experimental data in Table for the ethyl acetate (1) + cyclohexane (2) system at
293.15 K. Please fit this system to the 2-parameter Margules equation and plot the Pxy curve for
Snap a photo from your
the system (along with the experimental data and Raoult’s Law predictions). Also, plot the natural phone to post a question
logarithm of activity coefficients and the excess molar Gibbs free energy (divided by RT) both on We'll send you a one-time
the same curve.
download link
888-888-8888 Text me
By providing your phone number, you agree to receive
a one-time automated text message with a link to get
the app. Standard messaging rates may apply.
My Textbook Solutions
Table Vapor-liquid equilibrium of ethyl acetate (1) + cyclohexane (2) at 293.15 K.
Fundamental Automation, Fundamental
s of... Production... s of Logic...
1st Edition 4th Edition 7th Edition
View all solutions
Step-by-step solution
Step 1 of 16
Calculate the liquid mole fraction of component 2 or cyclohexane .
…… (1)
Here, liquid mole fraction of component 1 or ethanol is .
Substitute 0 for in Equation (1)
Comment
Step 2 of 16
Calculate the vapor mole fraction of component 2 or cyclohexane .
…… (2)
Here, vapor mole fraction of component 1 or ethanol is .
Substitute 0 for in Equation (2).
Comment
Step 3 of 16
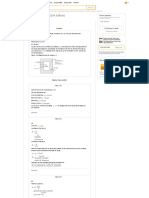
Express the vapor pressure using Antoine equation.
…… (3)
Here, temperature in degree Celsius is , and Antoine coefficients are .
From Appendix E, “Antoine Equations”, write the following properties for component 1 and 2 as in
Table (1).
Parameters Ethyl acetate Cyclohexane
A 7.10 6.84
B 1244.9 1201.5
C 217.8 222.6
Comment
Step 4 of 16
Show the unit conversion of temperature from Kelvin to degree Celsius.
Comment
Step 5 of 16
Calculate vapor pressure of component 1
Substitute for T, 7.10 for A, 1244.9 for B, and 217.8 for C in Equation (3).
Comment
Step 6 of 16
Calculate vapor pressure of component 2
Substitute for T, 6.84 for A, 1201.5 for B, and 222.6 for C in Equation (3).
Comment
Step 7 of 16
Calculate the activity coefficient of component 1 .
…… (4)
Here, pressure is .
Comment
Step 8 of 16
Calculate the activity coefficient of component 2 .
…… (5)
Here, pressure is .
Comment
Step 9 of 16
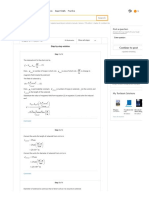
Determine the experimental value of the excess molar Gibbs free energy.
…… (6)
Here, gas constant is , and temperature is .
Take the value of gas constant as .
Comment
Step 10 of 16
Determine the model values of the excess molar Gibbs free energy.
…… (7)
Here, Margules parameters are .
Comment
Step 11 of 16
Calculate the objective function .
…… (8)
To minimize the objective function with respect to , take the values of Margules
parameters are as respectively with an value of .
Comment
Step 12 of 16
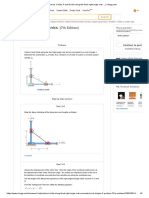
Now that we have the best-fit parameters for the model, we can plot the model predictions for the
vapor-liquid equilibrium.
Use Equations (3), (4), (5), (6), (7), and (8) and plot the model predictions for the vapor-liquid
equilibrium as in Figure (1).
Comment
Step 13 of 16
In Figure (1), treat the model as solid lines and the experimental data (on the same plots) as
symbols.
For the model values, use the following equations:
Calculate the activity coefficient of component 1 .
…… (9)
Here, Margules parameter is respectively.
Calculate the activity coefficient of component 2 .
…… (10)
Comment
Step 14 of 16
Write the formula to calculate the pressure .
…… (11)
Write the formula to calculate vapor mole fraction of component 1 or ethanol .
…… (12)
Comment
Step 15 of 16
Determine the model values of the excess molar Gibbs free energy.
…… (13)
Here, Margules parameters are .
Use Equations (9), (10), (11), (12), and (13) and plot the excess molar Gibbs free energy values
and activity coefficients as in Figure (2).
Comment
Step 16 of 16
In Figure (2), treat the model as solid lines and the experimental data (on the same plots) as
symbols.
Comment
Was this solution helpful? 6 0
Recommended solutions for you in Chapter 11
Chapter 11, Solution 5E Chapter 11, Problem 29P
The mole fraction of In a process analysis
component-(1) in liquid application, you are
mixture is 0.20. The working with the di-n-
vapor pressure of propyl ether (1) and 2-
component-(1) is 10 kPa propanol (2) system at
and that for... 25°C. Youthink...
See solution See solution
See more problems in subjects you study
COMPANY LEGAL & POLICIES CHEGG PRODUCTS AND SERVICES CHEGG NETWORK CUSTOMER SERVICE
About Chegg Advertising Choices Cheap Textbooks Online Tutoring EasyBib Customer Service
Become a Tutor Cookie Notice Chegg Coupon Sell Textbooks Internships.com Give Us Feedback
Chegg For Good General Policies Chegg Play Solutions Manual Studyblue Help with Chegg Tutors
College Marketing Intellectual Property Rights Chegg Study Help Study 101 Thinkful Help with eTextbooks
Corporate Development Terms of Use College Textbooks Textbook Rental Help to use EasyBib Plus
Investor Relations Chegg Tutors Terms of Service eTextbooks Used Textbooks Manage Chegg Study
Jobs Global Privacy Policy Chegg Math Solver Digital Access Codes Subscription
Join Our Affiliate Program DO NOT SELL MY INFO Mobile Apps Chegg Money Return Your Books
Media Center Honor Code Textbook Return Policy
Site Map
© 2003-2020 Chegg Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Wills & Trusts Outline UpdatedDocument26 pagesWills & Trusts Outline Updatedbrar001100% (1)
- Student Guide FC 120 FC Basics LDocument66 pagesStudent Guide FC 120 FC Basics LVishal MulikNo ratings yet
- Solved - If The Salmon River Temperature in Problem 7-33 Decreas...Document2 pagesSolved - If The Salmon River Temperature in Problem 7-33 Decreas...mabmi17No ratings yet
- Solved - A Mixture 25 Mol N Pentane 45 Mol N Hexane and 3... PDFDocument6 pagesSolved - A Mixture 25 Mol N Pentane 45 Mol N Hexane and 3... PDFYasmin KayeNo ratings yet
- CS-605 Data - Analytics - Lab Complete Manual (2) - 1672730238Document56 pagesCS-605 Data - Analytics - Lab Complete Manual (2) - 1672730238ullukanuNo ratings yet
- Solved The Maximum and Minimum Dry Unit Weights of A Sand Were...Document1 pageSolved The Maximum and Minimum Dry Unit Weights of A Sand Were...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - The Following Is A Set of VLE Data For The System Aceto...Document10 pagesSolved - The Following Is A Set of VLE Data For The System Aceto...Ehtisham ZiaNo ratings yet
- Project On BudgetingDocument75 pagesProject On BudgetingManeha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sandeep Aws - Devops ResumeDocument5 pagesSandeep Aws - Devops Resumesandeep ch100% (2)
- For The Radial Power System Shown in Figure 1.17, ...Document6 pagesFor The Radial Power System Shown in Figure 1.17, ...Ayush Gupta 4-Year B.Tech. Electrical Engineering100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI EditionDocument1 pageFundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI EditionNoman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI EditionDocument1 pageFundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, SI EditionNoman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Pregunta 6. Tarea 3Document3 pagesPregunta 6. Tarea 3Josebeth UlateNo ratings yet
- Solved - Chapter 10 Problem 28P Solution - Classical Mechanics 0th EditionDocument6 pagesSolved - Chapter 10 Problem 28P Solution - Classical Mechanics 0th EditionRyuNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis and Design, SI EditionDocument5 pagesPower System Analysis and Design, SI EditionAkimeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: (7th Edition)Document5 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: (7th Edition)Alia TasNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals and Applications: (3rd Edition)Document8 pagesFluid Mechanics Fundamentals and Applications: (3rd Edition)W DDNo ratings yet
- Solved - A Stage Extraction Process Is Depicted in Fig. P9.13. I...Document3 pagesSolved - A Stage Extraction Process Is Depicted in Fig. P9.13. I...Galuh Saputra 5No ratings yet
- Solved - Three Groups of Students From The Geotechnical EngineerDocument5 pagesSolved - Three Groups of Students From The Geotechnical Engineerabdullahiomar2020100% (1)
- Solved A Hot Water Stream at 80°C Enters A Mixing Chamber With CheggDocument3 pagesSolved A Hot Water Stream at 80°C Enters A Mixing Chamber With Cheggsalim.22en1No ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.41. Given q2 3800 LBFT, x1 18 ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.41. Given q2 3800 LBFT, x1 18 ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering: (5th Edition)Document4 pagesFoundations of Materials Science and Engineering: (5th Edition)IdridNo ratings yet
- Solved - Steam at 6000 Kpa and 500°C Enters A Steady-Flow Turbin...Document2 pagesSolved - Steam at 6000 Kpa and 500°C Enters A Steady-Flow Turbin...Irfan Nazir NoriNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: (7th Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics: (7th Edition)Hassanein HeidarNo ratings yet
- A Liquid Delivery SystemDocument3 pagesA Liquid Delivery SystemEhtisham ZiaNo ratings yet
- Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design: (9th Edition)Document3 pagesShigley's Mechanical Engineering Design: (9th Edition)mahdi najehNo ratings yet
- TSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 36P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionDocument1 pageTSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 36P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionxomuxNo ratings yet
- Solved Solve Problem 8.10 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Document1 pageSolved Solve Problem 8.10 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- TSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 34P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionDocument1 pageTSolved - Chapter 9 Problem 34P Solution - Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials 2nd EditionxomuxNo ratings yet
- Solved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Document1 pageSolved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) Electrostatic Precipit... PDFDocument3 pagesSolved - Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) Electrostatic Precipit... PDFAdeel ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Solved - Chapter 8 Problem 31P Solution - MATLAB 4th EditionDocument2 pagesSolved - Chapter 8 Problem 31P Solution - MATLAB 4th EditionSalahuddin D. EdolNo ratings yet
- Local Media2138585013869044277Document3 pagesLocal Media2138585013869044277panger moooNo ratings yet
- Question: Exercise (Test Your Understanding) A Beam of Yellow Light WithDocument3 pagesQuestion: Exercise (Test Your Understanding) A Beam of Yellow Light WithMuhammad SatrioNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: (7th Edition)Document4 pagesFluid Mechanics: (7th Edition)Asfand Yar QureshiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Vibrations With Applications: (5th Edition)Document2 pagesTheory of Vibrations With Applications: (5th Edition)Bayu ToxNo ratings yet
- Solved - Chapter 3 Problem 69RE Solution - Probability and Statistics For Engineers and Scientists 9th EditionDocument3 pagesSolved - Chapter 3 Problem 69RE Solution - Probability and Statistics For Engineers and Scientists 9th EditionJaleel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Solved - Chapter 10 Problem 14P Solution - Classical Mechanics 0th EditionDocument3 pagesSolved - Chapter 10 Problem 14P Solution - Classical Mechanics 0th EditionRyuNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To The Cross Section of The Earth Dam Shown in Fi...Document1 pageSolved Refer To The Cross Section of The Earth Dam Shown in Fi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - During A Plant Visit, It Was Noticed That A 12-M-Long S...Document1 pageSolved - During A Plant Visit, It Was Noticed That A 12-M-Long S...Shaiful IzzatNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Problem 8.4. Using The Flow Net Drawn, Calcula...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Problem 8.4. Using The Flow Net Drawn, Calcula...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- (Thermodynamics) Refrigerant-134a Is To Be Cooled ...Document2 pages(Thermodynamics) Refrigerant-134a Is To Be Cooled ...Logendran A/l MurgayaNo ratings yet
- Question: Water (Temperature 68F) Is Pumped From A Reservoir To A StoragDocument1 pageQuestion: Water (Temperature 68F) Is Pumped From A Reservoir To A StoragNiell Anakeen dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Solved A Pervious Soil Layer Is Sandwiched Between Two Impervi...Document1 pageSolved A Pervious Soil Layer Is Sandwiched Between Two Impervi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Loose Leaf For Mechanics of Materials: (7th Edition)Document5 pagesLoose Leaf For Mechanics of Materials: (7th Edition)TonkaNo ratings yet
- Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering: (7th Edition)Document7 pagesUnit Operations of Chemical Engineering: (7th Edition)Mega Shows100% (1)
- Solved - A Cumulatively Compounded DC Generator Is Operating Pro..Document3 pagesSolved - A Cumulatively Compounded DC Generator Is Operating Pro..ebraheemadelkopatiNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.46. A Flexible Circular Area of Radi...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.46. A Flexible Circular Area of Radi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Fluid Mechanics: (11th Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Fluid Mechanics: (11th Edition)كرار عبدالحسين قاسمNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering: (7th Edition)Document3 pagesUnit Operations of Chemical Engineering: (7th Edition)HennessysNo ratings yet
- Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering: (7th Edition)Document5 pagesUnit Operations of Chemical Engineering: (7th Edition)HennessysNo ratings yet
- Question: (A) A System Undergoes A Process Between Two Xed States RDocument2 pagesQuestion: (A) A System Undergoes A Process Between Two Xed States RIrfan Nazir NoriNo ratings yet
- Solved Estimate The Hydraulic Conductivity of A Saturated Clay...Document1 pageSolved Estimate The Hydraulic Conductivity of A Saturated Clay...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - A Prototype Automobile Is Designed To Travel at 65 km2Fh Cheggcom PDFDocument3 pagesSolved - A Prototype Automobile Is Designed To Travel at 65 km2Fh Cheggcom PDFNabihah AzanNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.49. For The Linearly Increasing Vert...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.49. For The Linearly Increasing Vert...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Calculus of A Single Variable: (11th Edition)Document1 pageCalculus of A Single Variable: (11th Edition)Noman MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Electric Machinery: (7th Edition)Document2 pagesElectric Machinery: (7th Edition)Luis AndradeNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 7.25. During An Auger Hole Test To Dete...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 7.25. During An Auger Hole Test To Dete...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Question: Pr.1 (45 Points) Boiling of Saturated Water at 137.78 C Occurs oDocument3 pagesQuestion: Pr.1 (45 Points) Boiling of Saturated Water at 137.78 C Occurs owaqasNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.43. A Strip Load of Q 1450 lbft2 ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.43. A Strip Load of Q 1450 lbft2 ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Physics: (7th Edition)Document4 pagesPhysics: (7th Edition)Malik NaeemNo ratings yet
- Solved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An AluDocument3 pagesSolved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An AluTafseer-e-QuranNo ratings yet
- Solved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An Alu-I... PDFDocument3 pagesSolved - The State of Plane Stress Shown Is Expected in An Alu-I... PDFTafseer-e-QuranNo ratings yet
- Measure Theory Notes Anwar KhanDocument171 pagesMeasure Theory Notes Anwar KhanMegan SNo ratings yet
- Innerwear Industry Pitch PresentationDocument19 pagesInnerwear Industry Pitch PresentationRupeshKumarNo ratings yet
- BUCOOL Business PlanzzzDocument11 pagesBUCOOL Business PlanzzzRachelle100% (1)
- 03 Ot-1Document15 pages03 Ot-1umang.parmar112597No ratings yet
- Tata Communications Annual Report 2014Document172 pagesTata Communications Annual Report 2014varaprasad_ganjiNo ratings yet
- Group 6: Irvan Nurhidayat (19322018) Vivi Rinawati (19322022) Sanazila Zakkaha (19322065) Nisrina Aziza (19322069)Document20 pagesGroup 6: Irvan Nurhidayat (19322018) Vivi Rinawati (19322022) Sanazila Zakkaha (19322065) Nisrina Aziza (19322069)Nisrina AzizaNo ratings yet
- Value Creation Through Project Risk ManagementDocument19 pagesValue Creation Through Project Risk ManagementMatt SlowikowskiNo ratings yet
- Ejectment JurisprudenceDocument17 pagesEjectment Jurisprudenceeds billNo ratings yet
- The Behavioral Ecology of The Komodo Monitor by Walter AuffenbergDocument10 pagesThe Behavioral Ecology of The Komodo Monitor by Walter Auffenbergqwertyuiop asdfghjklNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Curve FittingDocument19 pagesChapter 5 Curve FittingNiguse GeteNo ratings yet
- IBSSA 2008aDocument42 pagesIBSSA 2008asrdjan013No ratings yet
- EDEMDocument23 pagesEDEMRuben Purca100% (1)
- Review of Challenges Faced by Nursing Students During StudyingDocument2 pagesReview of Challenges Faced by Nursing Students During Studying4A - Rosemari EscarchaNo ratings yet
- Welding Journal 1959 8Document142 pagesWelding Journal 1959 8AlexeyNo ratings yet
- Preservative Challenge TestDocument8 pagesPreservative Challenge TestBernardo100% (1)
- Fuels and Fuel Handling Systems, For Steam GeneratorsDocument15 pagesFuels and Fuel Handling Systems, For Steam Generatorssam willNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated Circuit: Dual Operational AmplifierDocument5 pagesLinear Integrated Circuit: Dual Operational AmplifierBruno NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Budget Proposal Shirt PrintingDocument5 pagesBudget Proposal Shirt PrintingFatima MangadangNo ratings yet
- IsmailDocument25 pagesIsmailMubarak BegumNo ratings yet
- Minor ProjectDocument12 pagesMinor ProjectNikitaNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Fourth CircuitDocument2 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Fourth CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- McCrory Guilty Plea 2.25.15 TranscriptDocument66 pagesMcCrory Guilty Plea 2.25.15 Transcriptthe kingfishNo ratings yet
- Metro Jobs Clearance Form BlankDocument1 pageMetro Jobs Clearance Form BlankTj Daquigan100% (1)
- Metrics For Responsible Property Investing: Developing and Maintaining A High Performance PortfolioDocument43 pagesMetrics For Responsible Property Investing: Developing and Maintaining A High Performance PortfolioLisa Michelle GalleyNo ratings yet
- Prog 512. Assighnment Two PDFDocument5 pagesProg 512. Assighnment Two PDFTafex Wamabo Maphosa0% (4)