Professional Documents
Culture Documents
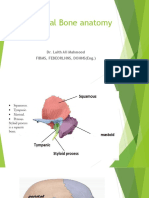
spine of Henle: Suprameatal / Macewen Triangle
Uploaded by
adham bani younesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
spine of Henle: Suprameatal / Macewen Triangle
Uploaded by
adham bani younesCopyright:
Available Formats
Suprameatal / Macewen
triangle
suprameatal crest ( temporal line of the squamous part of the temporal bone)
backward continuation of the posterior root of the zygoma
ridge of bone forming the upper edge of the bony meatus
corresponds to the floor of the middle cranial fossa
suprameatal spine/spine of Henle:
upper and posterior edge of the meatus which is formed by a thin, small shell or edge of
bone running from the suprameatal crest downward and backward to the posterior wall of
EUC
suprameatal fossa:
triangular in shape depression Behind the suprameatal spine and between it and the
posterior portion of the suprameatal crest
suprameatal triangle of Macewen :
Located post superior to the EUC
1. upper border: suprameatal crest
2. anterior border: suprameatal spine
3. Posterior border: tengent drawn from the post margin of the opening of the external canal (the
ridge of bone, running from the posterior portion of the crest to the lower portion of the spine).
Superficial (surface) landmark of the mastoid antrum through which the antrum may be reached.
The mastoid antrum is 1.5 cm deep to this land mark
In children McEwen's triangle is marked by small perforations through which pass the small blood
vessels ( cribrosa area)
So the following structures are surface landmark for mastoid antrum in mastoidectomy:
1. Temporal line
2. Suprameatal spine
3. Cribrosa area
Tegmen mastoid:
thin plate covering the mastoid
This plate in infant is microscopically cribriform there for otitis media is actually subperiosteal
infection
ال تنسونا من صالح دعائكم
اللهم اغفر لي و لوالدي و للمؤمنين و المؤمنات
دياال المارديني.د
You might also like
- Temporal Bone AnatomyDocument39 pagesTemporal Bone AnatomymizmuzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Ear PDFDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Ear PDFDeshini Balasubramaniam83% (6)
- Anatomy of The EarDocument10 pagesAnatomy of The EarJP SouaidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Temporal and Infratemporal FossaDocument8 pagesLecture 8 Temporal and Infratemporal Fossanatheer ayedNo ratings yet
- Applied AnatomyDocument14 pagesApplied AnatomySumit PrinjaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The SkullDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The SkullYeraldin EspañaNo ratings yet
- Middle Ear Anatomy and Physiology of HearingDocument58 pagesMiddle Ear Anatomy and Physiology of HearingGokul Krishnan VadakkeveeduNo ratings yet
- SMAS: The Superficial Musculoaponeurotic System Is A Fibromuscular Fascial ExtensionDocument4 pagesSMAS: The Superficial Musculoaponeurotic System Is A Fibromuscular Fascial Extensionblackurlz4111No ratings yet
- 17 TMJ (Done)Document2 pages17 TMJ (Done)osamaeNo ratings yet
- Middle EarDocument21 pagesMiddle Earadham bani younes100% (1)
- Middle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Document17 pagesMiddle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Dr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- Temporal BoneDocument104 pagesTemporal Bonekatnev100% (1)
- Temporal Bone RadioantomyDocument43 pagesTemporal Bone RadioantomyRavindra MuzaldaNo ratings yet
- The Human EarDocument6 pagesThe Human EarWild GrassNo ratings yet
- 25 Middle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Document17 pages25 Middle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)osamaeNo ratings yet
- SEQ Head - NeckDocument6 pagesSEQ Head - NeckAruni piyuminiNo ratings yet
- GRDA Infratemporal FossaDocument10 pagesGRDA Infratemporal FossaKingNo ratings yet
- DR Flings NotesDocument8 pagesDR Flings NotesSutanu SarkarNo ratings yet
- TMJ 2.0Document13 pagesTMJ 2.0Janvi RwtNo ratings yet
- The Development of The Middle Ear Spaces and Their Surgical SignificanceDocument15 pagesThe Development of The Middle Ear Spaces and Their Surgical SignificanceDrTarek Mahmoud Abo Kammer100% (2)
- Topographic AnatomyDocument1 pageTopographic AnatomyklxNo ratings yet
- Gross B 2.20. Superficial Structures and Posterior Triangle of The NeckDocument6 pagesGross B 2.20. Superficial Structures and Posterior Triangle of The NeckShaira Aquino VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Fossa Notes - HelpfulDocument4 pagesCranial Fossa Notes - HelpfulKo HakuNo ratings yet
- Temporal BoneDocument20 pagesTemporal BoneHuynh NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Foramen Magnum: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.DDocument39 pagesThe Foramen Magnum: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.Dbodeadumitru9261100% (1)
- 28 Temporal Bone (Done)Document7 pages28 Temporal Bone (Done)Ayah HyasatNo ratings yet
- Intricacies of Middle Ear and MastoidDocument44 pagesIntricacies of Middle Ear and MastoidMohit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Pap 0102Document14 pagesPap 0102Bogdan PraščevićNo ratings yet
- Muscles of MasticationDocument82 pagesMuscles of MasticationTanu ShreyaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Arteries and Veins of The Head and Neck Temporomandibular JointsDocument92 pagesGroup 1 Arteries and Veins of The Head and Neck Temporomandibular JointsGuo YageNo ratings yet
- 06 Lec 11 12 Anatomy First YearDocument13 pages06 Lec 11 12 Anatomy First YearS:M:ENo ratings yet
- Bones and Cartilages of The Head and NeckDocument27 pagesBones and Cartilages of The Head and Neckyachiru121100% (1)
- Secti On: Osteology of Head and NeckDocument102 pagesSecti On: Osteology of Head and NeckMarie GdlNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 Anatomy First StageDocument36 pagesLec 6 Anatomy First Stagespo9equtabaNo ratings yet
- Adhi Wardana 405120042: Blok PenginderaanDocument51 pagesAdhi Wardana 405120042: Blok PenginderaanErwin DiprajaNo ratings yet
- Paranasal Sinus (Repaired) EntDocument48 pagesParanasal Sinus (Repaired) EntDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- Middle Cranial FossaDocument5 pagesMiddle Cranial Fossaalexandra663No ratings yet
- TEMPORAL AND INFRATEMPORAL FOSSAE Lecture-1Document62 pagesTEMPORAL AND INFRATEMPORAL FOSSAE Lecture-1Prashant Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Chapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressDocument12 pagesChapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressWudieNo ratings yet
- Middle EarDocument16 pagesMiddle EarproshishNo ratings yet
- The Body (Corpus Mandibulæ) .-The Body Is Curved Somewhat Like ADocument10 pagesThe Body (Corpus Mandibulæ) .-The Body Is Curved Somewhat Like AGurveer ToorNo ratings yet
- The Ear: Head & Neck Unit - مسعسلا ليلج رديح .دDocument20 pagesThe Ear: Head & Neck Unit - مسعسلا ليلج رديح .دStevanovic StojaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Infratemporal Fossa, TMJDocument46 pagesAnatomy of The Infratemporal Fossa, TMJBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Tentorial IncisuraDocument23 pagesTentorial Incisurabodeadumitru9261100% (1)
- Introduction To Cranial CavityDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Cranial CavityexoNo ratings yet
- Upper Extremity, MEMBRUM Superius: LayersDocument31 pagesUpper Extremity, MEMBRUM Superius: LayersSyafiq KhalilNo ratings yet
- Temporalis Masseter Medial Pterygoid Lateral Pterygoid Muscles Temporal Fossa Infratemporal Fossa Mandible Temporomandibular JointDocument5 pagesTemporalis Masseter Medial Pterygoid Lateral Pterygoid Muscles Temporal Fossa Infratemporal Fossa Mandible Temporomandibular JointpmNo ratings yet
- The Infratemporal FossaDocument5 pagesThe Infratemporal FossaxxyumeNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Anatomy: A. Arsalan, MD M. Martin MD, DMD October 4-5, 2017Document53 pagesHead and Neck Anatomy: A. Arsalan, MD M. Martin MD, DMD October 4-5, 2017aaamirrrNo ratings yet
- Anterior and Posterior Petrosectomy Seminar 13 Jan 2021 DR Abhinav 2Document76 pagesAnterior and Posterior Petrosectomy Seminar 13 Jan 2021 DR Abhinav 2Tamajyoti GhoshNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy Related To Skull Base SurgeryDocument24 pagesSurgical Anatomy Related To Skull Base Surgeryeldoc13No ratings yet
- Muscles of MasticationDocument27 pagesMuscles of MasticationNanditha Swaroop100% (2)
- Aprimaion Angulo PontocerebelosoDocument64 pagesAprimaion Angulo PontocerebelosoLuis Carlos Avellaneda CurchoNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Terkini Bedah OmskDocument31 pagesTatalaksana Terkini Bedah OmskLimeysahni NazhoeNo ratings yet
- Blank-2023-09-16 22-28-41Document6 pagesBlank-2023-09-16 22-28-41adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Surgical AnatomyDocument44 pagesSurgical AnatomyVishalKumarNo ratings yet
- Temporalis Muscle Flap-1Document5 pagesTemporalis Muscle Flap-1Truong NguyenNo ratings yet
- A New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasFrom EverandA New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasNo ratings yet
- ظ Untitled20Document4 pagesظ Untitled20adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Emergency Room Record: Chief Complaint: HistoryDocument1 pageEmergency Room Record: Chief Complaint: Historyadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Clin 20181Document4 pagesClin 20181adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Ent Residency ProgramJMOHDocument30 pagesSyllabus of Ent Residency ProgramJMOHadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Ent Residency ProgramJMOHDocument30 pagesSyllabus of Ent Residency ProgramJMOHadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Aspiration: Definition: The Passage of Secretions Beyond The V.CDocument5 pagesAspiration: Definition: The Passage of Secretions Beyond The V.Cadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Larynx CasesDocument25 pagesLarynx Casesadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Ear Notes - ExtractDocument50 pagesEar Notes - Extractadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- WelcomeDocument5 pagesWelcomeCatNo ratings yet
- Laryngology NotesDocument296 pagesLaryngology Notesadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-01-15 at 22.19.21Document74 pagesScreenshot 2022-01-15 at 22.19.21adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Benign: Inverted PapillomaDocument2 pagesBenign: Inverted Papillomaadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Mast Cells in Inflammatory Aural Polyps: Drago Slav A R. Djericj, M.D., PH.DDocument4 pagesMast Cells in Inflammatory Aural Polyps: Drago Slav A R. Djericj, M.D., PH.Dadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Atelectatic vs. Adhesive OMDocument2 pagesAtelectatic vs. Adhesive OMadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Management of Alkaline Button Battery Foreign BodyDocument4 pagesManagement of Alkaline Button Battery Foreign Bodyadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- NAC - Allergic Rhinitis Treatments Chart - 2020Document1 pageNAC - Allergic Rhinitis Treatments Chart - 2020adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Management of Alkaline Button Battery Foreign BodyDocument4 pagesManagement of Alkaline Button Battery Foreign Bodyadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Dialogue With The ENT Residents - Tuning Fork TestsDocument6 pagesDialogue With The ENT Residents - Tuning Fork Testsadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy-CI Updated 8-7-14Document3 pagesTracheostomy-CI Updated 8-7-14adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Benign Lesion of The LarynxDocument17 pagesBenign Lesion of The Larynxadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choices Questions For ENT ResidentsDocument5 pagesMultiple Choices Questions For ENT Residentsadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Respiratory Reviews: Andreas P Eger, Ernst EberDocument9 pagesPaediatric Respiratory Reviews: Andreas P Eger, Ernst Eberadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- 1289 FullDocument12 pages1289 Fulladham bani younesNo ratings yet
- A. First Pharyngeal ArchDocument3 pagesA. First Pharyngeal Archadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- ENT MCQs Basic 13Qs.Document5 pagesENT MCQs Basic 13Qs.adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- A. Paresthesia of The CheckDocument4 pagesA. Paresthesia of The Checkadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Second and Third Year Ent McqsDocument6 pagesSecond and Third Year Ent Mcqsadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Second and Third Year Ent McqsDocument6 pagesSecond and Third Year Ent Mcqsadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- KhaledDocument9 pagesKhaledadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- MCQ EidoonDocument4 pagesMCQ Eidoonadham bani younesNo ratings yet