Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marshall Defined An Equilibrium Price As One at Which The
Uploaded by
trilocksp SinghOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marshall Defined An Equilibrium Price As One at Which The
Uploaded by
trilocksp SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Solved: Marshall defined an equilibrium price as one at
which the
Marshall defined an equilibrium price as one at which the
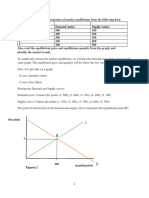
Marshall defined an equilibrium price as one at which the quantity demanded equals the
quantity supplied.
a. Using the data provided in problem 1.1, show that P = 3 is the equilibrium price in the orange
juice market.
b. Using these data, explain why P = 2 and P = 4 are not equilibrium prices.
c. Graph your results and show that the supply demand equilibrium resembles that shown in
Figure.
d. Suppose the demand for orange juice were to increase so that people want to buy 300 million
more gallons at every price. How would that change the data in problem 1.1? How would it shift
the demand curve you drew in part c?
e. What is the new equilibrium price in the orange juice market, given this increase in demand?
Show this new equilibrium in your supply demand graph.
f. Suppose now that a freeze in Florida reduces orange juice supply by 300 million gallons at
every price listed in problem 1.1. How would this shift in supply affect the data in problem 1.1?
How would it affect the algebraic supply curve calculated in that problem?
g. Given this new supply relationship together with the demand relationship shown in problem
1.1, what is the equilibrium price in this market?
h. Explain why P = 3 is no longer an equilibrium in the orange juice market. How would the
participants in this market know P = 3 is no longer an equilibrium?
i. Graph your results for this supplyshift.
Marshall defined an equilibrium price as one at which the
ANSWER
https://solvedquest.com/marshall-defined-an-equilibrium-price-as-one-at-which-the/
Reach out to freelance2040@yahoo.com for enquiry.
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
You might also like
- Money Master The GameDocument48 pagesMoney Master The GameSimon and Schuster72% (18)
- Solution Manual For Microeconomics 5th Edition by David BesankoDocument26 pagesSolution Manual For Microeconomics 5th Edition by David BesankomohsinwazirNo ratings yet
- Capstone Research Paper - Ferrari 2015 Initial Public OfferingDocument9 pagesCapstone Research Paper - Ferrari 2015 Initial Public OfferingJames A. Whitten0% (1)
- PNBDocument73 pagesPNBTushat GoelNo ratings yet
- Translate-BSG Quiz 1Document2 pagesTranslate-BSG Quiz 1franky mNo ratings yet
- ABC of StockDocument174 pagesABC of StockumaatntpcNo ratings yet
- Benchmarking as a Long-Term Strategy: A Case Study of Xerox CorporationDocument14 pagesBenchmarking as a Long-Term Strategy: A Case Study of Xerox CorporationJenny BascunaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Problems and Sustainability Chapter SummaryDocument41 pagesEnvironmental Problems and Sustainability Chapter SummaryTim Weaver75% (4)
- GRC PWC IntegritydrivenperformanceDocument52 pagesGRC PWC IntegritydrivenperformanceDeepak YakkundiNo ratings yet
- Microeco HW Answers Ch. 3, 4Document7 pagesMicroeco HW Answers Ch. 3, 4pheeyona100% (3)
- An Empirical Study of Price-Volume Relation: Contemporaneous Correlation and Dynamics Between Price Volatility and Trading Volume in the Hong Kong Stock Market.From EverandAn Empirical Study of Price-Volume Relation: Contemporaneous Correlation and Dynamics Between Price Volatility and Trading Volume in the Hong Kong Stock Market.No ratings yet
- Market EquilibriumDocument38 pagesMarket EquilibriumAbhi KumNo ratings yet
- Exercises Lecture 2Document13 pagesExercises Lecture 2Bus. Man - 2008-2011100% (1)
- Saad Karimi (Assignment 3)Document4 pagesSaad Karimi (Assignment 3)pakistanNo ratings yet
- ECON2000: INTERMEDIATE MICROECONOMICS I TUTORIAL SHEET 1Document6 pagesECON2000: INTERMEDIATE MICROECONOMICS I TUTORIAL SHEET 1Sarah SeunarineNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Pengantar EkonomiDocument3 pagesLatihan Soal Pengantar Ekonomihilmisifa100% (1)
- 1 The Following Relations Describe Demand and Supply QDocument3 pages1 The Following Relations Describe Demand and Supply Qtrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- FIN 6204 Managerial Economics Chapter 2 TutorialDocument6 pagesFIN 6204 Managerial Economics Chapter 2 TutorialTabassum AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Micro Economics by MankiwDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Micro Economics by MankiwRahulNo ratings yet
- Ch13. Price Determination (QB)Document4 pagesCh13. Price Determination (QB)Aaryan JainNo ratings yet
- AAEA Journal Article Examines Farm-Retail Price SpreadDocument12 pagesAAEA Journal Article Examines Farm-Retail Price SpreadFirdaussy YustiningsihNo ratings yet
- Please Read The Instructions Carefully Before Answering The Questions. Do Not Start Until You Are Told To Do SoDocument2 pagesPlease Read The Instructions Carefully Before Answering The Questions. Do Not Start Until You Are Told To Do SoLe Dieu Hang (K16HL)No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 AnswersDocument4 pagesChapter 4 AnswersMahekParmarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - MARKET EQUILIBRIUMDocument6 pagesLesson 10 - MARKET EQUILIBRIUMSheenah Almoite BalberonáNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 13 Suggested SolutionsDocument7 pagesTutorial 13 Suggested SolutionsHitesh MaharajNo ratings yet
- Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium: Hapter ObjectivesDocument34 pagesDemand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium: Hapter ObjectivesHussein YassineNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics With Land Reform and Taxation: Market Equilibrium Price and QuantityDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Economics With Land Reform and Taxation: Market Equilibrium Price and QuantityHealthyYOU100% (3)
- Week 4 - Attempt 3Document4 pagesWeek 4 - Attempt 3paulw22No ratings yet
- Microeconomics Principles and Applications 6Th Edition Hall Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument46 pagesMicroeconomics Principles and Applications 6Th Edition Hall Test Bank Full Chapter PDFlonnie.lotts387100% (12)
- Microeconomics Principles and Applications 6th Edition Hall Test Bank 1Document36 pagesMicroeconomics Principles and Applications 6th Edition Hall Test Bank 1douglascampbellwfztbmyndr100% (20)
- Economics Question & AnswerDocument5 pagesEconomics Question & AnswerumeshNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1-10 QuestionsDocument4 pagesExercise 1-10 QuestionsChuong HuyNo ratings yet
- L6Document6 pagesL6Maria RoaNo ratings yet
- L11'25Document3 pagesL11'25locomotivetrackNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 2 For Mid - Term ExamDocument3 pagesPractice Questions 2 For Mid - Term ExamMukhrizIzrafAzmanAzizNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand: Theory: Working With Numbers and GraphsDocument3 pagesSupply and Demand: Theory: Working With Numbers and Graphsrashmindri50% (4)
- Managerial Eco Final 3,4,5,8Document13 pagesManagerial Eco Final 3,4,5,8rawan ANo ratings yet
- AE LM 2ND QUARTER FINAL BalcitaDocument6 pagesAE LM 2ND QUARTER FINAL BalcitaRhystle Ann BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Bam 040Document3 pagesBam 040Maria Belen GagarNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 SP13 AnswersDocument5 pagesExam 1 SP13 AnswerskevinNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics For Today 8Th Edition Tucker Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesMicroeconomics For Today 8Th Edition Tucker Test Bank Full Chapter PDFlonnie.lotts387100% (11)
- Chap 5Document20 pagesChap 5wasisiNo ratings yet
- Master Supply and DemandDocument15 pagesMaster Supply and DemandMarivicEchavezBulaoNo ratings yet
- MARKET ANALYSISDocument8 pagesMARKET ANALYSISRuby CocalNo ratings yet
- CH2 CH5 Ä Æ È ÇDocument23 pagesCH2 CH5 Ä Æ È Çsherry.yang1010No ratings yet
- The Law of Demand and Supply 3.1FEDocument15 pagesThe Law of Demand and Supply 3.1FEJenn TajanlangitNo ratings yet
- Elasticity 1Document28 pagesElasticity 1Samiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Ch04 SolutionsDocument8 pagesCh04 SolutionsMuhammadNo ratings yet
- ME Quiz-1 SolutionDocument4 pagesME Quiz-1 SolutionVinay GahlotNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1-10 QuestionsDocument5 pagesExercise 1-10 QuestionsTam NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ecns 300 MT 3 Answers to 1-4Document2 pagesEcns 300 MT 3 Answers to 1-4ttrn219No ratings yet
- STD Xi - Eco QPDocument6 pagesSTD Xi - Eco QPlokimanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Equilibrium PriceDocument4 pagesDetermination of Equilibrium PricePranshu MishraNo ratings yet
- UoP Los Baños Economics Paper on Elasticity ConceptsDocument2 pagesUoP Los Baños Economics Paper on Elasticity ConceptsKenzie AlmajedaNo ratings yet
- Mid term Wan Muhammad Danial AmranDocument10 pagesMid term Wan Muhammad Danial Amranw.m.danialNo ratings yet
- Economics AssignmentDocument6 pagesEconomics Assignmentkibreabsello4No ratings yet
- Lecture Note #4Document5 pagesLecture Note #4Lea AndreleiNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1Document5 pagesAssessment 1nishant.a23xNo ratings yet
- An Assertion Is Made in The Lemons Discussion in ThisDocument2 pagesAn Assertion Is Made in The Lemons Discussion in Thistrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - SchemeDocument5 pagesTutorial 4 - SchemeTeo ShengNo ratings yet
- BlobDocument3 pagesBlobJolyna E. AduanaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Consumer Behavior Marianne CastroDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Consumer Behavior Marianne CastroGear Arellano IINo ratings yet
- Elasticities Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesElasticities Practice Problemsbalachmalik60% (5)
- Microeconomics tutorial questionsDocument2 pagesMicroeconomics tutorial questions吴国豪No ratings yet
- Elasticity and Equilibrium MCQDocument4 pagesElasticity and Equilibrium MCQpaulw22No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Multiple Choice QuestionsFATNIN HAZIQAH SABTUYAHNo ratings yet
- Econ Principles Homework on Supply and Demand AnalysisDocument9 pagesEcon Principles Homework on Supply and Demand AnalysisJames GiangrandeNo ratings yet
- Probset 1Document10 pagesProbset 1Phat Minh HuynhNo ratings yet
- Giovanni Construction Company Uses The Job Order Cost System inDocument2 pagesGiovanni Construction Company Uses The Job Order Cost System intrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Fred S Frames Mass Produces and Wholesales Wooden Picture FramesDocument1 pageFred S Frames Mass Produces and Wholesales Wooden Picture Framestrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Government Competition Leviathan and Benevolence Suppose Governments Can Spend TaxpayerDocument2 pagesGovernment Competition Leviathan and Benevolence Suppose Governments Can Spend Taxpayertrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Gazarra Company Is A Very Profitable Small Business It HasDocument1 pageGazarra Company Is A Very Profitable Small Business It Hastrilocksp Singh0% (1)
- Global Company Ethical Challenges in June 2009 The GovernmentDocument2 pagesGlobal Company Ethical Challenges in June 2009 The Governmenttrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Game Guys Is A Retail Store Selling Video GamesDocument1 pageGame Guys Is A Retail Store Selling Video Gamestrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- General Guideline Transfer Pricing The Shamrock Company ManufaDocument1 pageGeneral Guideline Transfer Pricing The Shamrock Company Manufatrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Governments Often Impose Costs On Businesses in Direct Relation ToDocument1 pageGovernments Often Impose Costs On Businesses in Direct Relation Totrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- General Ledger Relationships Under and Over AllocationDocument1 pageGeneral Ledger Relationships Under and Over Allocationtrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- General Guideline Transfer Pricing The Slate Company ManufacturDocument1 pageGeneral Guideline Transfer Pricing The Slate Company Manufacturtrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Goal Incongruence and Roi Bleefi Corporation Manufactures FurniDocument1 pageGoal Incongruence and Roi Bleefi Corporation Manufactures Furnitrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Flexible Budget and Sales Volume Variances Marron Inc ProduceDocument1 pageFlexible Budget and Sales Volume Variances Marron Inc Producetrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- George Marcus A Recent College Graduate Has Been Hired byDocument1 pageGeorge Marcus A Recent College Graduate Has Been Hired bytrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- General Equilibrium Effects of A Property Tax in Chapter 19Document2 pagesGeneral Equilibrium Effects of A Property Tax in Chapter 19trilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Gamboa Incorporated Is A Relatively New U S Based Retailer of SpecialtyDocument1 pageGamboa Incorporated Is A Relatively New U S Based Retailer of Specialtytrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- For Each of The Following Transactions Determine The Contribution ToDocument1 pageFor Each of The Following Transactions Determine The Contribution Totrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Goal Congruence Problems With Cost Plus Transfer Pricing MethodsDocument1 pageGoal Congruence Problems With Cost Plus Transfer Pricing Methodstrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Fifteen Workers Are Assigned To A Group Project The ProductionDocument1 pageFifteen Workers Are Assigned To A Group Project The Productiontrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Fishing in The Commons in The Text We Introduced TheDocument2 pagesFishing in The Commons in The Text We Introduced Thetrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Framing The Options Praying While Smoking and Fighting Pandemics byDocument1 pageFraming The Options Praying While Smoking and Fighting Pandemics bytrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Figures 1 2 and 1 6 Rely On Data From 2010 andDocument1 pageFigures 1 2 and 1 6 Rely On Data From 2010 andtrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Flexible Budget Variances Review of Chapters David James Is ADocument1 pageFlexible Budget Variances Review of Chapters David James Is Atrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Follete Inc Operates at Capacity and Makes Plastic Combs andDocument2 pagesFollete Inc Operates at Capacity and Makes Plastic Combs andtrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Following The Example in The Text Consider Two Hiv PreventionDocument1 pageFollowing The Example in The Text Consider Two Hiv Preventiontrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Financing A Strategic Investment Under Quantity Competition Suppose You OwnDocument2 pagesFinancing A Strategic Investment Under Quantity Competition Suppose You Owntrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Following Are Transactions and Events of The General Fund ofDocument2 pagesFollowing Are Transactions and Events of The General Fund oftrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Financial and Nonfinancial Performance Measures Goal CongruenceDocument1 pageFinancial and Nonfinancial Performance Measures Goal Congruencetrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Financial Budgets Cash Outflows Country Club Road NurseriesDocument1 pageFinancial Budgets Cash Outflows Country Club Road Nurseriestrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Figures A B and C Are Taken From A PaperDocument1 pageFigures A B and C Are Taken From A Papertrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- First and Second Best Rawlsian Income Redistribution Most Governments Raise TaxDocument2 pagesFirst and Second Best Rawlsian Income Redistribution Most Governments Raise Taxtrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Industry Analysis - BankingDocument33 pagesIndustry Analysis - BankingANUSHKANo ratings yet
- Presentation On Internship Program Done at The Enq: Subhankar BhattacharjeeDocument28 pagesPresentation On Internship Program Done at The Enq: Subhankar BhattacharjeeSubhankar BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- GST Question Bank Nov 22Document750 pagesGST Question Bank Nov 22mercydavizNo ratings yet
- Marketing Project On SuzukiDocument96 pagesMarketing Project On SuzukiAsh LayNo ratings yet
- BoK - BPI AO - Final Customer Risk Profiling (CRP) FormatDocument3 pagesBoK - BPI AO - Final Customer Risk Profiling (CRP) FormatMuhammad Yaseen LakhaNo ratings yet
- F6zwe 2016 Jun Q PDFDocument11 pagesF6zwe 2016 Jun Q PDFGamuchirai KarisinjeNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Factors Affecting Termination of Construction Contracts in Gaza StripDocument122 pagesInvestigation of Factors Affecting Termination of Construction Contracts in Gaza Stripsuranjan deyNo ratings yet
- Gurpreet Gill: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesGurpreet Gill: ObjectiveJustin EverettNo ratings yet
- Zero Base BudgetingDocument15 pagesZero Base BudgetingSumitasNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Financial Reporting Financial Statement Analysis and Valuation 8th EditionDocument23 pagesTest Bank For Financial Reporting Financial Statement Analysis and Valuation 8th Editionbriansmithmwgrebcstd100% (25)
- Step: 1Document24 pagesStep: 1LajukNo ratings yet
- Calculate LTV ratio and monthly amortizationDocument4 pagesCalculate LTV ratio and monthly amortizationMichelle GozonNo ratings yet
- Joint Venture Between Tata and ZaraDocument4 pagesJoint Venture Between Tata and ZaraShrishti Agarwal100% (1)
- ProdmixDocument10 pagesProdmixLuisAlfonsoFernándezMorenoNo ratings yet
- Ra 11058 OshlawDocument17 pagesRa 11058 OshlawArt CorbeNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Steel Industry - December 2019 PDFDocument19 pagesBangladesh Steel Industry - December 2019 PDFMahmudul Hasan SajibNo ratings yet
- MO QuestionDocument2 pagesMO Questionlingly justNo ratings yet
- Coca-Cola Hellenic 2011 Annual Report (IFRS FinancialsDocument86 pagesCoca-Cola Hellenic 2011 Annual Report (IFRS FinancialskhankhanmNo ratings yet
- Dsr April 2024Document10 pagesDsr April 2024vapatel767No ratings yet
- 1.1.1 Political StabilityDocument3 pages1.1.1 Political StabilityCuong VUongNo ratings yet
- Report and Recommendation of The PresidentDocument18 pagesReport and Recommendation of The PresidentTú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Term Paper (Business Mathematics)Document34 pagesTerm Paper (Business Mathematics)Omar Faruk100% (1)