Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C-121 Ignition Analyzer
C-121 Ignition Analyzer
Uploaded by
arizonaflyer1_7329760 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views5 pagesC-121 Ignition Analyzer
Original Title
C-121_Ignition_Analyzer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentC-121 Ignition Analyzer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views5 pagesC-121 Ignition Analyzer
C-121 Ignition Analyzer
Uploaded by
arizonaflyer1_732976C-121 Ignition Analyzer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
1.0. 1€.121¢-2
¢. Remove pressure pot and bleed hose, and install
valve seal caps securely
5-119A. TROUBLE SHOOTING TORQUE PRES-
SURE ON THE GROUND. When low or erratic
torque pressures are indicated, a comparison check of
manifold pressure, rpm and torque pressure, between
two or more engines should be made to determine if
erratic torque pressure readings are caused by improper
functioning of the engine, or hy 4 faulty torquemeter
system. If it is determined that the torque system is at
fault, the trouble can be isolated by using the following
procedures:
a, Remove torquemeter gage connector (see figure
S+14A), located near teansmitier on front supercharger
Do not attempt to test the internal oil line
with torquemeter transmitter pad installed.
housing.
b. Plug internal oil line at torquemeter gage connes-
tion, using an engine plug or a ¥g NPT plug (see figure
5-14B). Be sure all connections are tight.
« Remove torquemeter oil external tube connector
(see figure 5-14C), located on engine nose section
approximately midway between left distributor and
front oil pump.
4, Install locally manufactured adapter (see figure
5-14D), When this adapter is installed and internal line
is plugged on front supercharger housing, it blocks off
passage to nose section and checks internal oil paseage
in engine.
¢ Pump oil from test unit (see gure 5-14E), into
line until pressure reads 200 psi. Close needle valve
(Gee figure 5-14F), Test for ewo minutes with an allow-
able drop of 5 psi per minute after closing needle valve.
If amount of leakage is beyond these limits, engine will
be removed.
£ Remove adapter (see figure 5-14D), and install
adapter (see figure 5-14G). When this adapter is
installed, it blocks off pressure to torquemeter gage
connector located on front supercharger housing.
& Atcach a direct reading gage with a suficient
length of hose to adapter (see figure 5~14H).
hh, Start and warm up engine to normal operating
temperatures, then check torque pressure readings on
Revised 15 March 1957
Section V
Paragraphs 5-119A to 5-123
test gage. If test gage readings are abnormal, trouble
is in torquemeter system in nose section.
5-120. TORQUEMETER CIRCUIT. (Refer to Section
X.) The circuit consists of an autosyn transmitter on a
shock-mounted panel on the right side of each power
plane accessory section. These transmitters are electric-
ally connected to the corresponding sections of dual
autosyn indicators mounted on the flight engineers
lower instrument panel. The system is energized by
2G.volt, d00-cycle ac, and the riruit of sach engine ie
protected by four 2ampere fuses on the lower MJB
panel at station 212.
5-121, TROUBLE SHOOTING TACHOMETER AND
SYNCHROSCOPE CIRCUIT. (Refer to Section X.)
‘The tachometer and syncheascope installation is 2 system
complete in itself and has no connection with either the
aigplane dec or 2-c electrical systems. Trouble shooting
therefore, consists of checking for continuity and proper
function of components.
Trouble Probable Cause Remedy
Non Open circuit
indication. sea
Connect the plug
Fay indicator
wh ofthe operative
or tachometer
benerator
Indication
restored, replace
erator I otf
Place indicator
(Check and tighten
all connections.
Crorecheck tach:
‘scope anc
ion. ‘Loose connector
‘terminal.
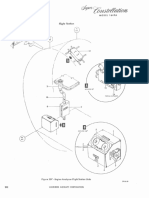
5-122, ENGINE ANALYZER.
5-123. DESCRIPTION. ‘Refer to Section X.) The
engine ignition analyzer will detect, locate, and identify
the malfunctions and imminent failures that may occur
dating engine operation. ‘The functions of the engine
are projected onto a cathode ray tube in the form of
voltage patterns taken from the magneto coils through
protective resistors.
567
Section V
Paragraphs 5-124 10 5-130
5-124. The following items comprise the engine ana-
lyzer system:
We. per
Airplane
‘Ample, tower Supply 7
Generator, Synchronizing 4
Indicotor, Engine Anelyter
Indicotor Hornets Attembhy 1
Slgnol Goin Transformer 1
Left side fight engineers
usiiry conte stond,
Switch, Condition Selector '
cvsiliry cone stond
Switch, Cyle Selector 1 tat side aight
Switch, 1 Att of selector site.
5-125. The condition switch selects a particular engine
and its ignition system for study. The cycle switch
initiates the sweep across the indicator at a particular
point in the crankshaft cycle, so that the ignition pattera
of a selected cylinder of a chosen engine will be the first
to appear at the left edge of the indicator, The power
supply amplifier contains special circuits for amplifying
the sweep across the indicator and for controlling its
length over a range of engine speeds from 1,000 to
3,000 rpm, and furnishes the proper voltages forall its
tubes and the cathode ray tube in the indicator.
5-126. As the pattern on the indicator is swept hori
ontally in synchronism with the engine, it is also
defected vertically by the changing voltage under obser-
vation. Horizontal movement of the pattera is controlled
by the electronic sweep generator in the amplifier unit,
The pattern starts at the left and eravels at constant
speed toward the right. The time of cravel is automat
cally adjusted regardless of engine speed to cover the
‘openings and closings of the distributor breaker points
for the fing of two consecutive cylinders in the order
of fring The three-phase generator om the auxiliary
tachometer drive synchronizes the sweep with engine
rotation. The voltage from the generator alternates in
step with the engine and is used co start the sweep at
the beginning of its movement across the tube of the
indicator. The sweep is initiated ac the instant before
firing of any desired cylinder chosen by che cycle selec-
tor switch. To display patterns of the ignition system,
the changing voltage at the magneto switch in the
primary cicuit is applied directly, without any change
for distortion, co the vertical deflection circuit of the
568
1.0. 1C-1216-2
indicator. This connection is made through resistors
mounted in a separate box near the magneto grounding
switch box. All common ignition malfunctions can be
readily detected by pattern comparison of a character-
istic normal pattern for the engine. In addition, such
malfunctions as bad injection pump, leading nozales,
ow compression, oil passing rings, broken distributor
brushes, breaker points burned, distributor out of tim.
ing, and engine synchronlzation can be detected.
5-127. IGNITION PATTERNS. Interpretation of the
various patterns presented on the analyzer scope requires
a knowledge of engines as well as an understanding of
what a certain eype pattern means. For an accurate inter.
pretation, the operator should be aware of all estab-
lished engine conditions. The exact size and shape of
the ignition patterns shown may vary due to the particu-
Jar characteristics of the individual engine and ignition
system on test.
5-128. GENERATOR. The generator is a 3-phase,
permanent-magner alternator attached to each engine's
auxiliary tachometer drive. The generator is driven at
onehalf crankshaft speed and serves as a reference
volage. This voltage is converted into single-phase
voliage by the cycle switch, This voltage triggers the
indicator sweep circuit enabling the display of repeti
tive ignition signal as a constant picture.
5-129, TIMING THE GENERATOR. There are two
methods used for timing the generator; by timing the
generator co the engine, and by timing the generator to
an ignition malfunction,
5-130. Timing genecator w ce engine is xs follows
4. Check that the piston of magneto timing cylinder
is on compression stroke and locate top dead center.
Rotate propeller at least 180 degrees opposite to normal
rotation and then rocate it in the direction of normal
rotation smoothly to take out all possible play in gears.
‘Stop crankshaft rotation at 0 degrees before top dead
center to be able to observe the firing in the engine
cylinder, in both the retard and advance position of the
ignition, on the indicator scope.
, Loosen clamp that secures generator cover to gen-
erator housing and remove screw from central hole in
cover. Insert timing pin into this hole and while main-
taining slight pressure on it, rotate generator cover,
court to rotor rotation, until timing pin slips into
groove on rotor. Lock generator cover in that position
with cover clamping ring. Generator is now synchro-
nized with crankshaft
Revised 1 January 1956
1.0. 16-1216-2
Check the phase rotation of generator in this
Disconnect a lead from any convenient spark plug
and tie ie to some engine part in such a manner that
the spark can not jump to ground,
Start engine, and with analyzer in operation, set
cycle switch 0 cylinder from which the spark plug lead
was removed. Index the knob with “R” if spark plug
lead is disconnected from front plug in cylinder or to
“L" if lead is disconnected Irom rear plug. Pattern of
sereen should indicace an open circuit for that plug.
Index cycle switch one step in direction of firing order
of cylinders (clockwise) and while doing so note direc-
tion of pattern shift. A shife off screen to the left
indicates correct phase rotation; a shift to the right
indicates incorrect rotation.
5-131. Timing generator to an ignition malfunction is
as follows:
Note
Before this method is used, the magneto must
be correctly timed, and there must be no mal-
functions in the ignition system.
a, Remove ignition lead from No. 10 cylinder front
spark plug. Cap lead with plastic protector (this will
give an open secondary pattern).
b. Loosen clamp an analyzer signal generator enough
to turn by hand, but tight enough not to move when
engine io running.
c. With engine running at or above 1800 rpm, set
selecor switch to RIGHT distributor. Set cycle switch
to No. 1 cylinder, pull button out for “SLOW SWEEP.”
Adjuse intensity control on power amplifier for
brightness
‘Adjust focus for picture clearness.
Adjust horizontal centering to obtain Y% inch at
each end of trace line,
Adjust horizontal length to obtain 2¥% inches of
trace line,
4. With engine running at about 2000 rpm, set cycle
switch to No. 10 cylinder "FAST SWEEP.” Rotate rear
housing of signal generator until malfunction pattera
(open secondary) appears on indicator at approximately
Fg inch from left
©. Rotate cycle switeh to 1No, 1 cylinder
signal generator timing.
11 compleve
Section V
Paragraphs 5-131 to 5-135
Note
Due to cam compensation, No. 10 cylinder is
used only as a reference and not as final timing.
jghten and lock-wire screw on signal generator
£
clamp.
5-132, CYCLE SWITCH. The cycle switch selects the
specific poine of a complete engine cycle at which the
horizontal time sweep across the cathode ray tube of
the indicator is ¢o be initiated. A push-pull knob, cen:
trally located oa the switch dial, changes the speed of
the sweep across che tube, In the normal (pushed-ia)
position, the sweep is fast, and in the pulled-out po:
tion, che slow sweep is in effect and all events occurring
through 720 degrees of crankshaft rotation are portrayed
during the time the beam traverses the ube. The fixed
sing of the switch is macked offi numerical desiguat
to correspond co the firing order of the engine. The
rotatable switch dial represents the four stcokes of the
four-stroke cycle internal combustion engine. One revo-
lution of the dial represents a full engine cycle or two
crankshaft revolutions. The nearest detent to alignment
of the rotatable dial with a cylinder designation which
does not splie a given pattern should be used.
5-133. CONDITION SWITCH. The condition switch
selects a specific engine for checking che left, right, of
both magnetos, or the speed synchronism between
engines. The function of the switch is primarily the
selection and orientation of the type of analysis desired,
5-134. POWER SUPPLY AMPLIFIER. The power
supply amplifier chassis contains all of the electronic
circuits ot the engine analyzer except the indicator. Mx
fnture tubes are used throughout. The power supply
requirements is 0.6 ampere, 115-volt, 400-cyele, single-
phase, and the circuits are protected by a one-ampere
fuse. Access to the fuse is on the face of the amplifier,
and is labeled “FUSE.” All tubes should be replaced
with new tubes after 1000 hours service time, To expose
the tubes for replacement, unserew the four cover screws
and lift the unit cover off. As the cover is removed, the
safety interlock switch breaks the power input circui
Replace the cover and reenergize the tubes for opera-
tion, Remove the cover, and with caution, touch all
fubes checking for their operation. A tube which feels
cold must be replaced. Most of the tubes are covered
with cylindrical metal shields which can be removed by
pressing them down slightly and turning counterclock-
wise,
5-135. INDICATOR. The indicator assembly is a hous-
ing which encloses a cathode ray tube with a 3inch,
‘green phosphorescent screen of medium persistence. It
fv
pr tine with ne distor-
ties a bigh innensicy
tion, and has a shore warm-up period.
569
Section V
Paragraphs 5-136 t0 5-138
5-136, ADJUSTMENT OF AMPLIFIER AND.
INDICATOR.
a, Turn on power to system, and allow amplifier and
indicator tube to warm up (approximately one minute)
b, Start engines and allow chem to warm up for
period required, depending on outside temperature.
‘After warmup, throttle engines to cruising speed
€. Adjust shafts marked “FOCUS” and “INTEN-
SITY” (0 obtain brilliance and focus of image desired.
4. Adjust shaft marked “LENGTH” to obtain a
horizontal sweep about 2% inches long. The push-pull
kknob on cycle switch must be in the pushed.in position
fe. Adjust shaft marked “H.CENTERING" so. that
the leading edge of sweep starts about Yyinch from
left edge of the indicator screen.
5-137. REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
OF UNITS.
a. Deenergize electrical ci
b. Remove electrical connectors and mounting screws
from each unit.
‘The amplifier is mounted with four snap slides.
€ Installation is reverse of removal. Use caution
when installing tube of indicator. To install generator,
set shaft of generator into the square hale of tachometer
drive shaft and mace generator pad to that of the tach-
ometer drive. Rotate the generator in 90-degree steps
as necessary, so that it is best positioned to accept the
cable from engine junction box. Secure generator with
‘nuts and lock-wire.
5-138, CHECK OF ENGINE ANALYZER
INSTALLATION.
a. Disconnect spark plug lead from front plug of
cylinder No. 10 for each engine,
b. Run engine at approximately 2000 spm; turn on
engine analyzer and allow at least one minute warmup
¢. Place condition switch in any position under
“IGNITION,” and push-pull knob on cycle switch in
pulled out position. On cycle switch, set index of dial
labeled “IGN” to any cylinder on fixed ring,
4. On amplifier power supply, adjust “FOCUS,”
“INTENSITY,” and “GAIN” controls as necessary.
Adjust "H-CENTERING” control so that leading edge
570
T.0.1€-1216-2
of sweep starts about 1 inch from left edge of indicator
sereen and using “LENGTH” control adjust sweep
length to about 2¥2 inches.
. Condition switch index to "2" under “SYN.”
g. Run engine No, 2 FASTER than No. 1. Pattern
shall shift horizontally to left
hh. Synchronize engine No. 1 and 2. Pattern shall
remain stationary.
i. Condition switch co "3" under “SYN,
j. Repeat steps € through h for No. 3 engi
k. Condition switch to "4" under "SYN."
1. Repeat steps f through h for No. 4 engine.
m. Condition switch: Place index of dial on “R” near
numeral “1,” beneath "IGNITION" on fixed ring.
tn, Cycle switch: Set index dial labeled “IGN” on
"10" on fixed ring. Push in push-pull knob.
©. Observe indicator. Ignition pattern of right mag-
‘eto of cylinders No. 10 and 3 for engine No. 1 should
be observed. At an engine speed of approximately 2000
1pm, pattern of No. 10 cylinder should appear first and
should be approximately 3% ich from left side of poine
‘where sweep starts. If pattern of cylinder No. 10 does
‘ot appeat, or is not in its correct position, a change
in timing of engine analyzer tachometer is indicated.
». Pull out push-pull knob on cycle switch. Ignition
pattern of left magneto of all cylinders should be
‘observed on indicator beginning with No. 10.
jine No. 1 to
q, Turn magneto switch for enj
Pattern on scope should disappear
. Return magneto ewitch for engine No. 1 to
“BOTH.” Push in push-pull knob on cycle switch,
s. Rotate index of condition switch to “L” near
‘umeral "1," under “IGNITION.” Ignition pattern of
right magneto of cylinder No. 10 and 3 of engine No. 1
should be observed on indicator.
© Pull out push-pull knob on cycle switch. Ignition
pattern of right magneto of all cylinders should be
observed on indicator.
4, Turn magneto switch for engine No. 1 to right
magneto. Pattern on indicator should disappear.
vy. Return magneto switch for engine No. 1 to
“BOTH.”
ww. Rotate index of condition switch t0
under “IGNITION.” Paccera shal
escentially the same as in steps p and t.
x. Push in push-pull knob,
1.0. 16-1216-2
Repeat steps m through x for engine No. 2, placing
Zaitien switch on "Le "Be and R” near ‘oumeral
ender “IGNITION.”
2. Repent steps m through x for engines No, 3 and 4
placing-condition switch on °C," "By" and “R” neat
Fometas "3" and "4" respectively
tn, Condition switch: Place index of dial on "R”
ovat numeral "t” beneath “IGNITION” on fixed rng.
4b. Cyle switch: Set index of dial labeled "IGN" on
“10” on fixed ring
fe. Pattern Shall indicate an open ploy oa No. 10
cylinder
ad. Turn cycle switch to “17.” Pattern shall shift t0
right.
fae, Repeat steps an chrough wi for engines No. 2,
sand 4
5-139. FUEL SYSTEM.
5-140. DESCRIPTION. (See figures 5-15 and 5-16.)
"The fuel system has six integral wing tanks and a
removable five-cell center section tank interconnected
so that each tank can feed any engine. Fuel transfer from
fone tank to another is not possible. Two tanks are
Tocated in each inner wing panel, and one in each cuter
wing panel. Those in the inner wing are identified as
No. 1 to No. 4 in consecutive order, No. 1 being the
outer tank in the left inner wing panel. The tank in the
left outer wing panel is identified as No. 2A, the tight
‘outer wing panel tank is No. 3A and the center section
tank is No. 5. The outer wing tanks extend to the
Teading edge, while the inner wing tanks extend only to
the wing front beam. Tanks No. 2 and No. 3 extend
trom wing station 87 co wing stativu 213 uf the lefe
and right wings respectively. Each is divided in wo
parts to provide space for the main landing gear wheel
well; the two sections of these tanks are interconnected
by tubes in the wheel wells. Tanks No. 1 and No. 4
extend from wing station 215 to wing station 450.5
Of the fefe anid sight wings scopectively. Tanke No, 24
and No. 3A extend from wing station 480.0 to wing
station 667.4 of the left and right wings respectively.
Center section tank No. 5 is located between wing sta-
tions 41.380 left and 41.580 right and extends from the
‘wing front beam to the wing rear beam.
5-141, The fuel vapor return lines from the fuel injec:
tion systems for engines No. 1 and No. 2 are routed
to No, 1 tank, and the lines from engines No. 3 and
No, 4 are routed to No. 4 tank. A check valve in each
‘vapor return line allows vapor flow to the tank only.
5.142, A thecal relief valve is incorporated in each
tocele to relieve excessive resure ue to Reve Aer
agin shutdown, or inthe event of 4 fe in 1002
fsa chermal cle valve installed in the right inet
ing, beeween the erosseed lie and No.4 fal tank
sero crack at 40 (C21) ps and eens 20 32 Ph
Section V
Paragraphs 5-139 t0 5-143
5-143, The following components are installed in the
fuel system:
Ne. per
eens Airplone
Amplifer, Fuel Gone
Fuel Gose 7 ower forward carpe
Fost Totizer '
Cente section fel nk
1
Cel, Center Section Fe! 4 Center section fue! tnk
Cock, Fel Filter rain 5 Fuel ters.
Cou, Fel Dump Valve Drain & “Fuel dump volves.
Feat Tank 2 Outboard section No.2 ond
Fier, Foe 5 Wheel walls ond one inthe
Inciater, Foe Few Ovel ,
{Engines No.1 2)
Indicotr, Foe Flow Dua ,
(Eogines No, 38 4)
Indiclr, Fuel Peete 1
(Engines No. 3&4)
Indicotr, Fuel Qvorty, 2 Fight
Inner Wing Outboard
vont. 2
inateument panel
1 Fight engineers middle
Inner wing dump chute.
Pomp, Engine Driven Fuel 4 Engine acessory cose.
Pump, Asvembly, Submerged Fl tanks.
Trontiter, Fost Flow 4 Engine nacelle,
Tronamite, Fel Prestore Engine noc
Transmiter, Tonk Unit 2 Tanks A ond 3A
Tromsniter, Tank Unit 2 Tonks Zhond 34,
‘utr Wing (Cents)
Transmit, Tonk Ui, 2 Tanks 7A ond 3A
‘Outer Wing fnboard)
Trontmiter, Tonk Tanks 1 ond 4
Inner Wing (Ouboore)
{ronmiter, Tonk Unit 2 Tanks 1 ond 4
lane Wing (Center)
‘ronimiter, Tonk Uni 2 Tonks 1 ond 4
Tamer Wing (nboerd)
Tronimiter, Tonk Uni, 2 Tonks Pond 3,
Taner Wing (Outboard)
571
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- T 6 Texan Flight Manual PDFDocument103 pagesT 6 Texan Flight Manual PDFarizonaflyer1_732976100% (3)
- Stromberg Float Carburetor For R-1340 Carb NAY9E1Document40 pagesStromberg Float Carburetor For R-1340 Carb NAY9E1arizonaflyer1_732976100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Engine Operating SupplementDocument7 pagesPratt & Whitney R-1340 Engine Operating Supplementarizonaflyer1_732976100% (1)
- Thrush S2R R-1340 Maintenence ManualDocument227 pagesThrush S2R R-1340 Maintenence Manualarizonaflyer1_732976100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Hamilton Standard Propeller Operation For R1340 Installations - BZ - v9Document4 pagesHamilton Standard Propeller Operation For R1340 Installations - BZ - v9arizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet
- R-1340 Radial Engine Pre-Oiling Procdure PDFDocument2 pagesR-1340 Radial Engine Pre-Oiling Procdure PDFarizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet
- Lockheed Super Constellation - Pocket Handbook PDFDocument209 pagesLockheed Super Constellation - Pocket Handbook PDFarizonaflyer1_732976100% (3)
- 777 Autoland Hydraulic Requirements Ver.5 2020 JCBDocument6 pages777 Autoland Hydraulic Requirements Ver.5 2020 JCBarizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet
- Beko k54270h k54305h SMDocument43 pagesBeko k54270h k54305h SMarizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet
- L1649 R3350 Ignition AnalyzerDocument4 pagesL1649 R3350 Ignition Analyzerarizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet
- 777 Hydraulic Fluid Transfer PreventionDocument1 page777 Hydraulic Fluid Transfer Preventionarizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet
- 777 Elev Flare CompensationDocument1 page777 Elev Flare Compensationarizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet
- 777F Air Conditioning Smoke or Fumes Odor v5Document4 pages777F Air Conditioning Smoke or Fumes Odor v5arizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet
- You Can't Fly Without Gouge PDFDocument6 pagesYou Can't Fly Without Gouge PDFarizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet
- Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Radial Engine HistoryDocument10 pagesPratt & Whitney R-1340 Radial Engine Historyarizonaflyer1_732976100% (2)
- Curtiss Wright Pre-Oiling Aircraft Radial EnginesDocument13 pagesCurtiss Wright Pre-Oiling Aircraft Radial Enginesarizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet
- The Complete Nav Gouge: "The Only One You Need"Document4 pagesThe Complete Nav Gouge: "The Only One You Need"arizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet
- Aero Q209Document32 pagesAero Q209Sinta SiraitNo ratings yet
- Pratt & Whitney R1340 StartingDocument3 pagesPratt & Whitney R1340 Startingarizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet
- Lockheed C-121c Maintenance Manual T.O. 1C-121C-2Document1,100 pagesLockheed C-121c Maintenance Manual T.O. 1C-121C-2arizonaflyer1_732976No ratings yet