Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
Uploaded by
Stepyn Salvador0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pagesA urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria enters the urinary system through the urethra and infects the urethra, kidneys, or bladder. Normally urine does not contain bacteria, but it can enter the urinary tract from outside the body. UTIs are very common, affecting 1 in 5 women at some point in their lives. Women are more susceptible due to their anatomy. Older adults also have a higher risk of cystitis due to medical conditions affecting bladder emptying. Symptoms of a UTI include pain or burning with urination. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific type of UTI where bacteria infects the bladder.
Original Description:
uti
Original Title
What is a Urinary Tract Infection
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria enters the urinary system through the urethra and infects the urethra, kidneys, or bladder. Normally urine does not contain bacteria, but it can enter the urinary tract from outside the body. UTIs are very common, affecting 1 in 5 women at some point in their lives. Women are more susceptible due to their anatomy. Older adults also have a higher risk of cystitis due to medical conditions affecting bladder emptying. Symptoms of a UTI include pain or burning with urination. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific type of UTI where bacteria infects the bladder.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pagesWhat Is A Urinary Tract Infection
Uploaded by
Stepyn SalvadorA urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria enters the urinary system through the urethra and infects the urethra, kidneys, or bladder. Normally urine does not contain bacteria, but it can enter the urinary tract from outside the body. UTIs are very common, affecting 1 in 5 women at some point in their lives. Women are more susceptible due to their anatomy. Older adults also have a higher risk of cystitis due to medical conditions affecting bladder emptying. Symptoms of a UTI include pain or burning with urination. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific type of UTI where bacteria infects the bladder.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
What is a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection of the urinary
system. This type of infection can involve your urethra (a
condition called urethritis), kidneys (a condition
called pyelonephritis) or bladder, (a condition called cystitis).
Your urine typically doesn’t contain bacteria (germs). Urine is a
byproduct of our filtration system—the kidneys. When waste
products and excess water is removed from your blood by the
kidneys, urine is created. Normally, urine moves through your
urinary system without any contamination. However, bacteria
can get into the urinary system from outside of the body, causing
problems like infection and inflammation. This is a urinary tract
infection (UTI).
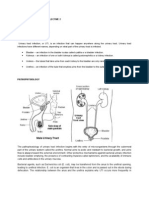
What is the urinary tract?
The urinary tract makes and stores urine, one of the body's liquid
waste products. The urinary tract includes the following parts:
Kidneys: These small organs are located on back of your
body, just above the hips. They are the filters of your body
— removing waste and water from your blood. This waste
becomes urine.
Ureters: The ureters are thin tubes that carry urine from the
kidneys to your bladder.
Bladder: A sac-like container, the bladder stores your urine
before it leaves the body.
Urethra: This tube carries the urine from your bladder to
the outside of the body.
How common are urinary tract infections (UTIs)?
Urinary tract infections are very common, occurring in 1 out of 5
women sometime in their lifetime. Though UTIs are common in
women, they can also happen to men, older adults and children.
One to 2% of children develop urinary tract infections. Each year,
8 million to 10 million visits to doctors are for urinary tract
infections.
Who gets urinary tract infections (UTIs)?
Anyone can get a urinary tract infection, but they are more
common in women. This is because the urethra (tube the carries
urine out of the body) in females is shorter and closer to the
anus, where E. coli bacteria are common. Older adults also are
at higher risk for developing cystitis. This increased risk may be
due to incomplete emptying of the bladder. There are several
medical conditions that can be related to this, including
an enlarged prostate or a bladder prolapse (a condition where
the bladder falls or slips out of its usual position).
If you get frequent urinary tract infections, your healthcare
provider may do tests to check for other health problems — such
as diabetes or an abnormal urinary system—that may be
contributing to your infections. People with frequent UTIs are
occasionally given low-dose antibiotics for a period of time to
prevent the infection from coming back. This cautious approach
to treating frequent UTIs is because your body can develop a
resistance to the antibiotic and you can get other types of
infections, such as C. diff colitis. This practice is used very
infrequently.
What’s the difference between a urinary tract infection (UTI) and
bladder infection (cystitis)?
A urinary tract infection is a more general type of infection. There
are many parts of your urinary tract. A UTI is a term for an
infection that takes place throughout the urinary tract. A bladder
infection, also called cystitis, is a specific infection. In this
infection, bacteria makes its way into the bladder and causes
inflammation.
Not all urinary tract infections become bladder infections.
Preventing the spread of the infection is one of the most
important reasons to treat a UTI quickly when you have
symptoms. The infection can spread not only to the bladder, but
also into your kidneys, which is a more complicated type of
infection than a UTI.
You might also like
- FNCP-Presence of Breeding or Resting Sites of Vectors of DiseasesDocument5 pagesFNCP-Presence of Breeding or Resting Sites of Vectors of DiseasesAlessa Marie BadonNo ratings yet
- What Is A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Urinary Tract InfectionYmelda ComediamNo ratings yet
- Infection Urinary Tract Urine Bladder KidneyDocument18 pagesInfection Urinary Tract Urine Bladder KidneygdquijanoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument17 pagesUrinary Tract Infectionss.khan9211rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Background Urinary Tract InfectionDocument7 pagesTheoretical Background Urinary Tract Infectiondenebrench23No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument10 pagesUrinary Tract Infectionjaah diazNo ratings yet
- Uti PathoDocument15 pagesUti PathoEden Astred ObilloNo ratings yet
- What Is A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Urinary Tract InfectionVanessa MendezNo ratings yet
- Coli Bacterial Strains That Usually Inhabit The ColonDocument4 pagesColi Bacterial Strains That Usually Inhabit The Colonemman122392No ratings yet
- UTI in AdultsDocument4 pagesUTI in Adultsjoan_padilla2000No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Document6 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (UTI)Anonymous iG0DCOfNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Uti Adawdiasdfkuhasdlukfhalkfjashdkljfahrguilahrluihadfkljnxj, CnalksefhauehDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Uti Adawdiasdfkuhasdlukfhalkfjashdkljfahrguilahrluihadfkljnxj, CnalksefhauehVandie MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Types of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesTypes of Urinary Tract InfectionGencris Medrano Giray RNNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection UTI and Dementia FactsheetDocument10 pagesUrinary Tract Infection UTI and Dementia FactsheettoobaziNo ratings yet
- Female Urinary System: Types of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument6 pagesFemale Urinary System: Types of Urinary Tract InfectionCarmela BedanoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument7 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionNader Smadi100% (7)
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) : A Guide For WomenDocument2 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (UTI) : A Guide For WomenBily ManNo ratings yet
- Urinary TractDocument4 pagesUrinary TractRoland APARECENo ratings yet
- Written Assignment 7 Hs2211Document7 pagesWritten Assignment 7 Hs2211Cali GureNo ratings yet
- Elective 2 ReportDocument7 pagesElective 2 ReportJem TellainNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionDRANo ratings yet
- RLE Urinary Tract InfectionDocument13 pagesRLE Urinary Tract InfectionAliza AlyyNo ratings yet
- UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)Document9 pagesUTI (Urinary Tract Infection)Carson BirthNo ratings yet
- UTIDocument6 pagesUTIAyessa Marie BarbosaNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System. The Urinary System Helps Maintain Proper Water and Salt Balance ThroughoutDocument4 pagesThe Urinary System. The Urinary System Helps Maintain Proper Water and Salt Balance ThroughoutArjay EspañolNo ratings yet
- What Is A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Urinary Tract InfectionLunaNo ratings yet
- Readings: Acute PyelonephritisDocument6 pagesReadings: Acute PyelonephritisMauriceNo ratings yet
- Article For Patient EducationDocument4 pagesArticle For Patient EducationZaveri Hemant GirishkumarNo ratings yet
- Function of The Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesFunction of The Urinary SystemniknokaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Document9 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (UTI)ogwal andrewictynetNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections in Teens and Adults: Topic OverviewDocument1 pageUrinary Tract Infections in Teens and Adults: Topic OverviewRaRa PRawitaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument2 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionAnonymous KillerNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument5 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsEben Leonel Albano MaiopueNo ratings yet
- What Causes A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument6 pagesWhat Causes A Urinary Tract InfectionStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY #3 Urinary System (Urninary Tract Infection or UTI)Document5 pagesCASE STUDY #3 Urinary System (Urninary Tract Infection or UTI)Lerma PagcaliwanganNo ratings yet
- Kidney InfectionDocument3 pagesKidney InfectionMaxpein Zin Dell Valle-MoonNo ratings yet
- Infeksi Saluran KemihDocument65 pagesInfeksi Saluran KemihHaziq AnuarNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection (Maramag Eunice Laman Jenny Pearl)Document16 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (Maramag Eunice Laman Jenny Pearl)Carlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- Renal InfectionDocument5 pagesRenal InfectionNaqash NobleNo ratings yet
- OverviewDocument3 pagesOverviewAlhaisa BejemilNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument13 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionAlexis PiocosNo ratings yet
- 5 Common Uts DiseasesDocument9 pages5 Common Uts DiseasesJeremiah NayosanNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection 1Document17 pagesUrinary Tract Infection 1Annie Lou AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Cases of Group 3 LC 1Document13 pagesCases of Group 3 LC 1abdul basithNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Uti in Benin PDFDocument54 pagesPrevalence of Uti in Benin PDFcamiladovalle95No ratings yet
- K - 9 Urinary Tract Infection (Ilmu Penyakit Dalam)Document24 pagesK - 9 Urinary Tract Infection (Ilmu Penyakit Dalam)Ruthra Devi NarayanasamyNo ratings yet
- Female Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesFemale Urinary SystemVikas SarkarNo ratings yet
- Case Study (Uti)Document6 pagesCase Study (Uti)Bible EvergardenNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Uti in BeninDocument49 pagesPrevalence of Uti in Benincamiladovalle95No ratings yet
- Cystitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition Treatment And Urinary DiseasesFrom EverandCystitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition Treatment And Urinary DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection (Uti) Definition:: TypesDocument2 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (Uti) Definition:: TypesAneela ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Uti Case StudyDocument7 pagesUti Case StudyStephNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine COPCDocument20 pagesFamily Medicine COPCrachellesliedeleonNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument18 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionDaphne ChendunNo ratings yet
- ProjDocument12 pagesProjرافعہ میر بٹNo ratings yet
- Materia Medica: Ip DiscussionDocument7 pagesMateria Medica: Ip Discussionanmol sharmaNo ratings yet
- Uti ReadingsDocument6 pagesUti ReadingskarenbelnasNo ratings yet
- What Is A UTI?: Urinary Tract Infection, Let's Talk About ItDocument1 pageWhat Is A UTI?: Urinary Tract Infection, Let's Talk About ItPrecious SorianoNo ratings yet
- vt59.2708-21368446078 - 3195905547377425 - 5588203228225134062 - n.pdfColorful-Aesthetic-Retro-Group-Project - 3Document12 pagesvt59.2708-21368446078 - 3195905547377425 - 5588203228225134062 - n.pdfColorful-Aesthetic-Retro-Group-Project - 3LwhynnNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On UtiDocument10 pagesA Case Study On UtiMark Tristan AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Excretory System Worksheet Made By: Zoha NabeelDocument6 pagesExcretory System Worksheet Made By: Zoha Nabeel정국JungkookNo ratings yet
- Lysolipids in The Vascular SystemDocument29 pagesLysolipids in The Vascular SystemStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Why People Use CBD OilDocument4 pagesWhy People Use CBD OilStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Nonpharmacological TreatmentDocument5 pagesNonpharmacological TreatmentStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- The 4 Phases of Cardiac RehabilitationDocument3 pagesThe 4 Phases of Cardiac RehabilitationStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- The Purpose of StentsDocument2 pagesThe Purpose of StentsStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Heart Bypass SurgeryDocument6 pagesHeart Bypass SurgeryStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- What Are GallstonesDocument15 pagesWhat Are GallstonesStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous Tissue CompositionDocument2 pagesSubcutaneous Tissue CompositionStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Prodromal Symptoms: FaintingDocument6 pagesProdromal Symptoms: FaintingStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Diseas1Document3 pagesCoronary Artery Diseas1Stepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Silent Heart AttackDocument3 pagesSilent Heart AttackStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- How Do Vaccines Work?: Immune SystemDocument4 pagesHow Do Vaccines Work?: Immune SystemStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- What Happens After The Cystoscopy ProcedureDocument2 pagesWhat Happens After The Cystoscopy ProcedureStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Calcium ScanDocument3 pagesCalcium ScanStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument4 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- What Is An UltrasoundDocument7 pagesWhat Is An UltrasoundStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Based XPSDocument2 pagesLaboratory Based XPSStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Lung Function TestsDocument3 pagesLung Function TestsStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- What Is A CystosDocument4 pagesWhat Is A CystosStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanical TreatmentDocument3 pagesQuantum Mechanical TreatmentStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- What Causes A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument6 pagesWhat Causes A Urinary Tract InfectionStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Low-Energy CID and High-Energy CID: EnergiesDocument2 pagesLow-Energy CID and High-Energy CID: EnergiesStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Bonds in PolymersDocument3 pagesHydrogen Bonds in PolymersStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- National Vitamin A Supplementation (VAS) Guidelines For Children U5 in PakistanDocument14 pagesNational Vitamin A Supplementation (VAS) Guidelines For Children U5 in PakistanMuhammad YousufNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Intestinal Obstruction in A Child With Massive AscariasisDocument4 pagesCase Report: Intestinal Obstruction in A Child With Massive AscariasisWella Vista EdwardNo ratings yet
- 12 Advantages and Disadvantages of Animal Testing On CosmeticsDocument3 pages12 Advantages and Disadvantages of Animal Testing On CosmeticsElo RubioNo ratings yet
- Proforma For Registration of Subject For Dissertation Dissertation ProposalDocument11 pagesProforma For Registration of Subject For Dissertation Dissertation Proposalkuruvagadda sagarNo ratings yet
- Public Health Act CHAPTER 15 17rDocument76 pagesPublic Health Act CHAPTER 15 17rmiti victorNo ratings yet
- Acog Practice Bulletin Summary: Prelabor Rupture of MembranesDocument5 pagesAcog Practice Bulletin Summary: Prelabor Rupture of Membranesasm obgin100% (1)
- FAESGraduateSchoolAtNIH2014 2015Document124 pagesFAESGraduateSchoolAtNIH2014 2015Anonymous hK9rR30No ratings yet
- Underlying Contributors To Childhood Stunting: What Evidence Exists On Nutrition-Sensitive Risk Factors?Document12 pagesUnderlying Contributors To Childhood Stunting: What Evidence Exists On Nutrition-Sensitive Risk Factors?Andi Fahira NurNo ratings yet
- Treatment and Prevention of Streptococcal Tonsillopharyngitis - UpToDateDocument14 pagesTreatment and Prevention of Streptococcal Tonsillopharyngitis - UpToDateJavier Manuel Escobedo CalderónNo ratings yet
- Nursing Role and Nursing Care During Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument21 pagesNursing Role and Nursing Care During Pregnancy Complicationsvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Study of Bloody Diarrhoea Among Children in Baghdad, IraqDocument9 pagesEpidemiological Study of Bloody Diarrhoea Among Children in Baghdad, IraqInternational Medical PublisherNo ratings yet
- Theories and Level of Disease Occurence FinalDocument108 pagesTheories and Level of Disease Occurence FinalruthNo ratings yet
- General Science Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 2Document6 pagesGeneral Science Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 2Ashwini KhareNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Current Guidelines of Five International Societies On Clostridium Difficile Infection ManagementDocument24 pagesA Comparison of Current Guidelines of Five International Societies On Clostridium Difficile Infection ManagementJulio S. UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Metcalf & Eddy Waste Water Treatment Plants 4th 2003 Part 4Document126 pagesMetcalf & Eddy Waste Water Treatment Plants 4th 2003 Part 4SourabhAdike86% (7)
- Syngineering Water MBR Vs SBR PDFDocument5 pagesSyngineering Water MBR Vs SBR PDFjaianit89No ratings yet
- ACR-Global Hand Washing Day 2021Document2 pagesACR-Global Hand Washing Day 2021Katy Chenee Napao Perez100% (1)
- Contoh SopDocument4 pagesContoh SopSiti Hawa NabillahNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument10 pagesMenstrual CycleintanNo ratings yet
- Human Diseases Including Communicable and Non - Communicable Diseases - Prevention and Remedies - 1st - ChapterDocument22 pagesHuman Diseases Including Communicable and Non - Communicable Diseases - Prevention and Remedies - 1st - ChapterVijaya Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Decolonizing International Health - India and Southeast Asia 1930-65 - Amrith (2006)Document276 pagesDecolonizing International Health - India and Southeast Asia 1930-65 - Amrith (2006)shahadat115No ratings yet
- NCP EndometriosisDocument1 pageNCP EndometriosisDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Promkes Naidoo (Indonesia)Document496 pagesPromkes Naidoo (Indonesia)plinzzyNo ratings yet
- POGI Preclampsia 2022Document52 pagesPOGI Preclampsia 2022SDM RSTINo ratings yet
- NWMP Data 2018Document56 pagesNWMP Data 2018Copper xNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers: Varicella (Chickenpox)Document3 pagesQuestions and Answers: Varicella (Chickenpox)MENU A/P MOHANNo ratings yet
- Cot 2 Health 6 - Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesCot 2 Health 6 - Lesson PlanAnna Clarissa TapallaNo ratings yet
- ENDOMETRITISDocument19 pagesENDOMETRITISannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Teaching Slide Set 2021: Global Initiative For Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (Gold)Document58 pagesTeaching Slide Set 2021: Global Initiative For Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (Gold)hendra ritongaNo ratings yet