Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Materia Medica: Ip Discussion
Uploaded by
anmol sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views7 pagesOriginal Title
Ajp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views7 pagesMateria Medica: Ip Discussion
Uploaded by
anmol sharmaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
MATERIA MEDICA
IP DISCUSSION
Ujrpuria Janta Annaram
Roll no. :- 51
2nd BHMS
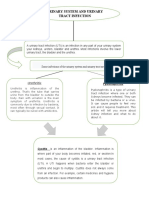
URINARY TRACT INFECATION (UTI) :-
Definition :-
Uti’s are common infection that
happen when bacteria offen from the
skin or rectum, enter the urethra
&infect the urinary tract.
It is invasion of the urothelium that
results in an inflammatory response.
The infection can affect several parts
of the urinary tract , but the most
common type is a bladder infection
(cystitis).
Bacteria especially E.coli –are the
most common cause of UTI.
Symptoms include needing to pee
often pain while peeing &pain in side or
lower back.
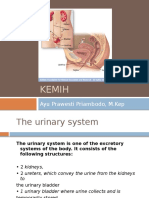
Anatomy :-
A urinary tract infection is an infection in any part of the
urinary system.
The urinary system includes the kidney , ureters , bladder &
urethra.
Most infections involve the lower urinary tract – the bladder
&the urethra.
Women are at greater risk of developing UTI than man.
Women’s urethra (tube from the bladder to where the urine
comes out of the body) is shorter then a man. Bacteria can
reach the bladder more easily in women.
Anatomy of urinary tract :-
The body takes nutrients from food & converts them to
energy.
After the body has taken the food components that it needs ,
waste products are left behind in the bowel & in the blood.
Though it is not extensively studied ,differences in
pelvic anatomy may predispose UTI.
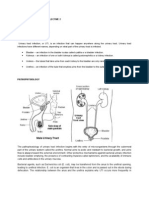
Physiology :-
Urinary tract infections are caused by bacterium
that invade the urinary epithelium calls causing
irritation & inflammation of these calls.
The infection can start in the urethra & can progress
it’s way up to the bladder , ureters or kidney.
Physiology of urinary tract :-
Micturition primarily functions in the excretion of
metabolic products & toxic wastes.
The urinary tract also serves as a storage vessel of the
waste filtered from the kidneys.
Urine stored in the bladder is released from the bladder
through the urethra upon a complex network of
neurological function.
THANK YOU ALL
You might also like
- Female Urinary Tract Infections in Clinical PracticeFrom EverandFemale Urinary Tract Infections in Clinical PracticeBob YangNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument10 pagesUrinary Tract Infectionjaah diazNo ratings yet
- Cystitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition Treatment And Urinary DiseasesFrom EverandCystitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition Treatment And Urinary DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Modern Review of Dysuria: Causes, Symptoms and ManagementDocument19 pagesModern Review of Dysuria: Causes, Symptoms and ManagementKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ein Uti Kelompok 4Document21 pagesEin Uti Kelompok 4Eni MuslihahNo ratings yet
- RLE Urinary Tract InfectionDocument13 pagesRLE Urinary Tract InfectionAliza AlyyNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Urinary Tract Infections (UTIsDocument4 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Urinary Tract Infections (UTIsVandie MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Theoretical background Urinary Tract infectionDocument7 pagesTheoretical background Urinary Tract infectiondenebrench23No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Document6 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (UTI)Anonymous iG0DCOfNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY #3 Urinary System (Urninary Tract Infection or UTI)Document5 pagesCASE STUDY #3 Urinary System (Urninary Tract Infection or UTI)Lerma PagcaliwanganNo ratings yet
- What Is A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Urinary Tract InfectionStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- What Is A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Urinary Tract InfectionYmelda ComediamNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan UTIDocument5 pagesLesson Plan UTITopeshwar TpkNo ratings yet
- Infection Urinary Tract Urine Bladder KidneyDocument18 pagesInfection Urinary Tract Urine Bladder KidneygdquijanoNo ratings yet
- Seminar On: Urinary Tract Infections and NephritisDocument34 pagesSeminar On: Urinary Tract Infections and NephritisGargi MPNo ratings yet
- Assalamualaikum Warahmatullahi WabarakatuhDocument11 pagesAssalamualaikum Warahmatullahi WabarakatuhAngga bayuNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection (Maramag Eunice Laman Jenny Pearl)Document16 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (Maramag Eunice Laman Jenny Pearl)Carlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- MO Penyebab ISK April 2019Document34 pagesMO Penyebab ISK April 2019murdaaripinNo ratings yet
- JETIR1808875Document8 pagesJETIR1808875UsmleNo ratings yet
- Recurrent UTI Patient Education: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument4 pagesRecurrent UTI Patient Education: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentZaveri Hemant GirishkumarNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Urinary Tract InfectionDocument10 pagesCase Study - Urinary Tract InfectionJiffy198867% (3)
- A Case Study On UtiDocument10 pagesA Case Study On UtiMark Tristan AsuncionNo ratings yet
- UTIDocument6 pagesUTIAyessa Marie BarbosaNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System: Causes and Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIsDocument61 pagesThe Urinary System: Causes and Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIsDezttie IdEss NdessNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Urinary Tract Infections (UTIsDocument4 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Urinary Tract Infections (UTIsGencris Medrano Giray RNNo ratings yet
- Asiya Project 1Document32 pagesAsiya Project 1eimadNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument14 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionSilva RahmaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection in AdultsDocument8 pagesUrinary Tract Infection in AdultsFeenyxNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIIDocument2 pagesChapter IIIalifNo ratings yet
- Understanding Urinary Tract Infections and the Urinary SystemDocument1 pageUnderstanding Urinary Tract Infections and the Urinary SystemAlejandro PazNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument17 pagesUrinary Tract Infectionss.khan9211rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- A Urinary Tract InfectiondiffertialDocument1 pageA Urinary Tract InfectiondiffertialAlappatt John JuniorNo ratings yet
- Brown Aesthetic Group Project PresentationDocument11 pagesBrown Aesthetic Group Project PresentationAddah, Dhenaraiza H.No ratings yet
- Case Study UTIDocument43 pagesCase Study UTINicole Quinsayas100% (1)
- Function of The Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesFunction of The Urinary SystemniknokaNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Uti in Benin PDFDocument54 pagesPrevalence of Uti in Benin PDFcamiladovalle95No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionDRANo ratings yet
- Females, Being A Biologic Factor, Are More Prone To UTI Due To The Proximity PathoDocument2 pagesFemales, Being A Biologic Factor, Are More Prone To UTI Due To The Proximity PathoGenica MaylemNo ratings yet
- Bab Ii IskDocument18 pagesBab Ii Isksherenridca100% (1)
- Elective 2 ReportDocument7 pagesElective 2 ReportJem TellainNo ratings yet
- Renal DisDocument166 pagesRenal DisCharles MutaiNo ratings yet
- What Is A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Urinary Tract InfectionVanessa MendezNo ratings yet
- Female Urinary System: Types of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument6 pagesFemale Urinary System: Types of Urinary Tract InfectionCarmela BedanoNo ratings yet
- vt59.2708-21368446078 - 3195905547377425 - 5588203228225134062 - n.pdfColorful-Aesthetic-Retro-Group-Project - 3Document12 pagesvt59.2708-21368446078 - 3195905547377425 - 5588203228225134062 - n.pdfColorful-Aesthetic-Retro-Group-Project - 3LwhynnNo ratings yet
- UoP Assignment: Cystitis - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and ImpactDocument7 pagesUoP Assignment: Cystitis - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and ImpactCali GureNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection: Point Wise Lecture Along With Consisted Table, Image and Schematic DiagramsDocument15 pagesUrinary Tract Infection: Point Wise Lecture Along With Consisted Table, Image and Schematic DiagramsVipinNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection UTI and Dementia FactsheetDocument10 pagesUrinary Tract Infection UTI and Dementia FactsheettoobaziNo ratings yet
- UTI PresentationDocument19 pagesUTI PresentationRegina EstherNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument5 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsEben Leonel Albano MaiopueNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument22 pagesUrinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentNoor AliNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Uti in BeninDocument49 pagesPrevalence of Uti in Benincamiladovalle95No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument7 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionNader Smadi100% (7)
- UTI in AdultsDocument4 pagesUTI in Adultsjoan_padilla2000No ratings yet
- Uti PathoDocument15 pagesUti PathoEden Astred ObilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan UTIDocument15 pagesLesson Plan UTIS GNo ratings yet
- Coli Bacterial Strains That Usually Inhabit The ColonDocument4 pagesColi Bacterial Strains That Usually Inhabit The Colonemman122392No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections: December 2016Document12 pagesUrinary Tract Infections: December 2016Suraj PatilNo ratings yet
- UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)Document9 pagesUTI (Urinary Tract Infection)Carson BirthNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Back GroundDocument43 pages1.1. Back GroundalifNo ratings yet
- Bab I Pendahuluan A. Latar BelakangDocument23 pagesBab I Pendahuluan A. Latar BelakangKevin PinartoNo ratings yet