Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Protein Purification
Uploaded by
Black Widow0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesOriginal Title
protein_purification
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesProtein Purification
Uploaded by
Black WidowCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
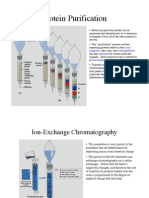
Protein Purification
Gel filtration / Mass Exclusion chromatography: separate by size
Porous resins are added into column
Molecules that are too big to enter the pores travel quickly through the column
Smaller molecules that enter the pores travel slowly through the column, since they have a longer
path to travel
Ion-exchange chromatography: separate by charge
Charged resins are added into column
Cation-exchange column to select for positively charged proteins
o Negatively charged groups on resins attract positively charged proteins and slows down
their movement through the column
Anion-exchange column to select for negatively charged proteins
o Positively charged groups on resins attract negatively charged proteins and slows down their
movement through the column
Wash column with increasing salt concentrations to elute protein
Affinity chromatography: separate by affinity to a particular ligand (substrate)
Resin with a particular ligand attached are added into the column
Proteins that have an affinity to the ligand bind to them, and thus stay in the column; other proteins
simply travel through the column and come out first
Wash column to disrupt the binding between the ligand and attached proteins and elute protein
o Do so by adding salt, changing pH, changing solvent, adding free ligand, adding compounds
that bind more strongly to the ligand, or more…
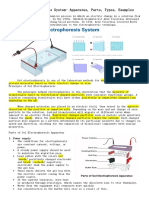
Protein Electrophoresis
Native PAGE: separate by size of native conformation
PAGE = PolyAcrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
Polyacrylamide/bisacrylamide (crosslinker) form a “web-like” net
An electric field is placed across the gel; negatively charged proteins move to positive pole, and vice
versa
Smaller-sized, more tightly packed molecules are able to travel through the gel more quickly than
larger-sized molecules
“Native” because protein is in original, undisrupted conformation
Agarose can be used in place of PAGE (although the resolution decreases)
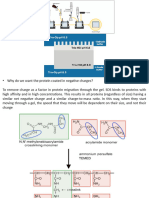
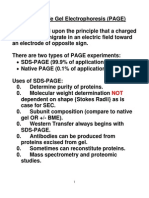
SDS-PAGE: separate by size of denatured conformation (molecular weight)
Similar to above, expect SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) is added
SDS is a detergent that denatures and negatively coats the protein at a constant ratio of 1 SDS/2 AA;
thus, proteins have a charge proportional to their size
β-mercaptoethanol is also added to reduce S-S bonds
Distance protein travels is proportional to log of molecular weight
Isoelectric focusing (IEF): separate by pI
A protein’s pI is the pH at which the protein has no net charge.
At a pH > pI, the protein has a negative charge
At a pH < pI, the protein has a positive charge
A pH gradient is made in the gel with ampholytes, a mixture of polyanionic and polycationic
molecuels
Proteins move in the gradient until its pI = pH
2D gel electrophoresis: separate by pI and molecular weight
IEF gel is run first
SDS-PAGE gel is run on second dimension
Images from Lodish textbook
You might also like
- Pdf45 9 Secrets To Obtaining Personal WealthDocument8 pagesPdf45 9 Secrets To Obtaining Personal WealthBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- Sample Interview Questions For Planning EngineersDocument16 pagesSample Interview Questions For Planning EngineersPooja PawarNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Molecular BiologyDocument41 pagesTechniques in Molecular BiologymneilgNo ratings yet
- Electrophoreti C Methods: Igaa SeptiariDocument22 pagesElectrophoreti C Methods: Igaa SeptiariGung Ari100% (1)
- Scrum Handbook: Scrum Training Institute PressDocument66 pagesScrum Handbook: Scrum Training Institute PressFranky RiveroNo ratings yet
- pdf14 Ultimate Guide To AssetsDocument24 pagespdf14 Ultimate Guide To AssetsBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- Sds PageDocument36 pagesSds PageDivya DharshiniNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Ky Thua Protein-Môn hóa sinh họcDocument83 pagesCH 5 Ky Thua Protein-Môn hóa sinh họcNam NguyenHoangNo ratings yet
- Downstream ProcessingDocument33 pagesDownstream ProcessingSampath Yadav GaddamNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Nastran In-CAD PDFDocument43 pagesAutodesk Nastran In-CAD PDFFernando0% (1)
- 04-Gel ElectrophoresisDocument24 pages04-Gel ElectrophoresisBen Abella100% (1)
- 02 Protein IsolationDocument14 pages02 Protein IsolationAntonio Calleja IINo ratings yet
- Principle and Protocol of Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) - Creative Biomart BlogDocument10 pagesPrinciple and Protocol of Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) - Creative Biomart BlogSatyam SoniNo ratings yet
- ElectrophoresisDocument15 pagesElectrophoresisVimal KishoreNo ratings yet
- Protein Identification: Size Charge Sequence ShapeDocument34 pagesProtein Identification: Size Charge Sequence ShapeAndreea SpiridonNo ratings yet
- Sds-Page Method Summary&ADocument3 pagesSds-Page Method Summary&AQuan ThieuNo ratings yet
- Gel Electrophoresis of ProteinsDocument4 pagesGel Electrophoresis of ProteinsRommel BauzaNo ratings yet
- SDS-PAGE & Western BlottingDocument19 pagesSDS-PAGE & Western BlottingSadia ShafiqeNo ratings yet
- CHEM 160 Module 3 Resource 5Document7 pagesCHEM 160 Module 3 Resource 5meyaNo ratings yet
- Appendix: Applications and TroubleshootingDocument4 pagesAppendix: Applications and TroubleshootingSky ImranNo ratings yet
- 9-10 Protein & Analisis ProteinDocument52 pages9-10 Protein & Analisis ProteinM. Irfan FebriansyahNo ratings yet
- Elphor Chrom AnswersDocument3 pagesElphor Chrom AnswersAnonymous b14ATJtNo ratings yet
- Sds Page TheoryDocument2 pagesSds Page TheoryvickykrishNo ratings yet
- WB and IPPDocument34 pagesWB and IPPShawon RahmanNo ratings yet
- Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis: ProcedureDocument8 pagesPolyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis: Procedureshailesh nikumbhaNo ratings yet
- Sample Preparation (Document3 pagesSample Preparation (John LexxNo ratings yet
- Protein PurificationDocument10 pagesProtein PurificationMichaella CabanaNo ratings yet
- Protein Extraction and QuantificationDocument6 pagesProtein Extraction and QuantificationWNo ratings yet
- Methods of Enzyme PurificationDocument24 pagesMethods of Enzyme PurificationVILEOLAGOLDNo ratings yet
- PageDocument19 pagesPagePhoebeliza Jane BroñolaNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Lecture SlidesDocument83 pagesCH 5 Lecture SlidesUyên Trần NhưNo ratings yet
- Protein PurificationDocument7 pagesProtein PurificationArchana BorahNo ratings yet
- Protein Characterization by Electrophoresis: Solidum, Andrew - , Chan, Catherine TDocument3 pagesProtein Characterization by Electrophoresis: Solidum, Andrew - , Chan, Catherine Tcoffeecity100% (2)
- Agerose Gel ElectrophoresisDocument6 pagesAgerose Gel ElectrophoresisAnura BandaraNo ratings yet
- ElectrophoresisDocument2 pagesElectrophoresisdr.a.k.gupta6924No ratings yet
- Basis For Separation: Immobilized PH Gradient (IPG) and IEF RunDocument2 pagesBasis For Separation: Immobilized PH Gradient (IPG) and IEF RunAli Azam KhanNo ratings yet
- Biochem Chapter 5 Notes. Protein PurificationDocument14 pagesBiochem Chapter 5 Notes. Protein PurificationOANo ratings yet
- Proteins & Proteins Purification TechniquesDocument54 pagesProteins & Proteins Purification Techniquesnurul farhanahNo ratings yet
- Purification and Characterization of ProteinsDocument13 pagesPurification and Characterization of ProteinsErika BarretoNo ratings yet
- Protein Purification: Ionic Properties Hydrophobicity Affinities FractionationDocument11 pagesProtein Purification: Ionic Properties Hydrophobicity Affinities FractionationNas KataNo ratings yet
- BCH 706 Lec 6 CHR Type Ion Exchange - 7591Document40 pagesBCH 706 Lec 6 CHR Type Ion Exchange - 7591zshanali6236No ratings yet
- MCAT Lab TechniquesDocument18 pagesMCAT Lab TechniquesJames Huynh100% (1)
- Techniques To Separate Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument38 pagesTechniques To Separate Amino Acids and ProteinsDawlat SalamaNo ratings yet
- Purification of ProteinsDocument24 pagesPurification of ProteinsDhansukh PatelNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry CH 3Document3 pagesBiochemistry CH 3Ann Ross FernandezNo ratings yet
- CHROMATOGRAPHY2Document33 pagesCHROMATOGRAPHY2Nurfatihah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Term Paper of Genetic EngineeringDocument20 pagesTerm Paper of Genetic EngineeringManju BhattiNo ratings yet
- Protein Characterization/Purification: Dr. Kevin AhernDocument34 pagesProtein Characterization/Purification: Dr. Kevin AhernkelpachurpaNo ratings yet
- Elektroforesis SDS PAGE SusiDocument32 pagesElektroforesis SDS PAGE SusiBhaga VadNo ratings yet
- SDS - Page, Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate - Polyacrylamide Gel ElectrophoresisDocument4 pagesSDS - Page, Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate - Polyacrylamide Gel ElectrophoresisJOSHUA CINCONo ratings yet
- Electrophoresis 2023Document16 pagesElectrophoresis 20238rmy44w9g6No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Topic 4. Ion Exchange, Affinity - Theory, Instrumentation and Applications.Document25 pagesUnit 4 Topic 4. Ion Exchange, Affinity - Theory, Instrumentation and Applications.ashra sindhikkaaNo ratings yet
- Sds PageDocument11 pagesSds PageBantita Treepong100% (1)
- Biochemistry LN06-2Document9 pagesBiochemistry LN06-2Rahaf Al-muhtasebNo ratings yet
- SDS PageDocument10 pagesSDS PageMeera SainiNo ratings yet
- Pollock 2007Document11 pagesPollock 2007Carolina TabascoNo ratings yet
- Native PageDocument1 pageNative Pagebeatrice cho ming xuanNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument36 pagesBiochemistryBrylle Espares LumberioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectrophoresisDocument52 pagesIntroduction To ElectrophoresisMegha AnandNo ratings yet
- Serum Protein Electrophoresis & Their Clinical ImportanceDocument44 pagesSerum Protein Electrophoresis & Their Clinical ImportanceDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Gel ElectroiphoresisDocument22 pagesGel ElectroiphoresisAqsa MazharNo ratings yet
- Dibt NotesDocument5 pagesDibt Notesiamkalash.vdNo ratings yet
- Western BlottingDocument20 pagesWestern BlottingmartinoNo ratings yet
- Crude Extract: Proteins Can Be Separated and PurifiedDocument9 pagesCrude Extract: Proteins Can Be Separated and PurifiedTanjina AkterNo ratings yet
- 22 JulyDocument44 pages22 JulyBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- Expt 33&34 ReqDocument11 pagesExpt 33&34 ReqBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- Classroom Contact Programme: Pre-Medical: Nurture Course (Phase: I)Document24 pagesClassroom Contact Programme: Pre-Medical: Nurture Course (Phase: I)Black WidowNo ratings yet
- Stats Bayes PracticeDocument2 pagesStats Bayes PracticeBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- BacteriaDocument2 pagesBacteriaBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- Classroom Contact Programme: Pre-Medical: Nurture Course (Phase: I & Ii)Document45 pagesClassroom Contact Programme: Pre-Medical: Nurture Course (Phase: I & Ii)Black WidowNo ratings yet
- Derek Bendall (1930-2014) : Photosynthesis Research May 2015Document5 pagesDerek Bendall (1930-2014) : Photosynthesis Research May 2015Black WidowNo ratings yet
- BPMME-2020 First AnnouncementDocument4 pagesBPMME-2020 First AnnouncementBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- Catalyst: Science QuizDocument111 pagesCatalyst: Science QuizBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- G Phase: Phase Describes A Cellular State Outside of The Replicative CellDocument9 pagesG Phase: Phase Describes A Cellular State Outside of The Replicative CellBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- Conic - Geometry (Theory) PDFDocument41 pagesConic - Geometry (Theory) PDFBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- Alg - Topo - Notes (Theory) PDFDocument91 pagesAlg - Topo - Notes (Theory) PDFBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- Utilization of A New Paint For Better Cooling of The Surrounding Offices in Metal IndustriesDocument1 pageUtilization of A New Paint For Better Cooling of The Surrounding Offices in Metal IndustriesBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- Revised - AIATS Schedule For Class XI Studying (2020-21)Document1 pageRevised - AIATS Schedule For Class XI Studying (2020-21)Black WidowNo ratings yet
- Gmail - ICICI BANK I PROCESS HIRING FOR BACKEND - OPERATION PDFDocument2 pagesGmail - ICICI BANK I PROCESS HIRING FOR BACKEND - OPERATION PDFDeepankar ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- ATS2017 ProspectusDocument13 pagesATS2017 ProspectusGiri WakshanNo ratings yet
- Cpar ReviewerDocument6 pagesCpar ReviewerHana YeppeodaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument33 pagesProjectPiyush PatelNo ratings yet
- FDD Spindle Motor Driver: BA6477FSDocument12 pagesFDD Spindle Motor Driver: BA6477FSismyorulmazNo ratings yet
- Bin Adam Group of CompaniesDocument8 pagesBin Adam Group of CompaniesSheema AhmadNo ratings yet
- English 2nd Quarter Week 7 Connotation DenotationDocument28 pagesEnglish 2nd Quarter Week 7 Connotation DenotationEdward Estrella GuceNo ratings yet
- Report-Smaw Group 12,13,14Document115 pagesReport-Smaw Group 12,13,14Yingying MimayNo ratings yet
- Atom SDDocument5 pagesAtom SDatomsa shiferaNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument6 pagesPronounsHải Dương LêNo ratings yet
- Learning TheoryDocument7 pagesLearning Theoryapi-568999633No ratings yet
- Watch One Piece English SubDub Online Free On Zoro - ToDocument1 pageWatch One Piece English SubDub Online Free On Zoro - ToSadeusuNo ratings yet
- 6 Uec ProgramDocument21 pages6 Uec Programsubramanyam62No ratings yet
- Design and Optimization of A Medium Altitude Long Endurance UAV Wingbox StructureDocument8 pagesDesign and Optimization of A Medium Altitude Long Endurance UAV Wingbox StructureamirNo ratings yet
- ISO-3046-4-2009 (Gobernador de Velocidad)Document8 pagesISO-3046-4-2009 (Gobernador de Velocidad)David GastelumNo ratings yet
- Junos ErrorsDocument2 pagesJunos ErrorsrashidsharafatNo ratings yet
- Chunking Chunking Chunking: Stator Service IssuesDocument1 pageChunking Chunking Chunking: Stator Service IssuesGina Vanessa Quintero CruzNo ratings yet
- Bustax Midtem Quiz 1 Answer Key Problem SolvingDocument2 pagesBustax Midtem Quiz 1 Answer Key Problem Solvingralph anthony macahiligNo ratings yet
- Case Study To Find Tank Bulging, Radial Growth and Tank Settlement Using API 650Document15 pagesCase Study To Find Tank Bulging, Radial Growth and Tank Settlement Using API 650Jafer SayedNo ratings yet
- Risha Hannah I. NazarethDocument4 pagesRisha Hannah I. NazarethAlpaccino IslesNo ratings yet
- Beamng DxdiagDocument22 pagesBeamng Dxdiagsilvioluismoraes1No ratings yet
- Assignment-For-Final of-Supply-Chain - Management of Courses PSC 545 & 565 PDFDocument18 pagesAssignment-For-Final of-Supply-Chain - Management of Courses PSC 545 & 565 PDFRAKIB HOWLADERNo ratings yet
- Example of Flight PMDG MD 11 PDFDocument2 pagesExample of Flight PMDG MD 11 PDFVivekNo ratings yet
- Channel & Lomolino 2000 Ranges and ExtinctionDocument3 pagesChannel & Lomolino 2000 Ranges and ExtinctionKellyta RodriguezNo ratings yet
- MiddleWare Technology - Lab Manual JWFILESDocument171 pagesMiddleWare Technology - Lab Manual JWFILESSangeetha BajanthriNo ratings yet
- Rab Sikda Optima 2016Document20 pagesRab Sikda Optima 2016Julius Chatry UniwalyNo ratings yet
- How To Be A Better StudentDocument2 pagesHow To Be A Better Studentct fatima100% (1)