Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Django
Django
Uploaded by
PRIYANSH TRIPATHI0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views2 pagesDjango
Django
Uploaded by
PRIYANSH TRIPATHICopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
-In order to start with Django you need to have python installed.
-Now in windows powershell write pip install django.
-In order to check it we can write
python -m django --version
-Make a directory DJANGO TUTORIAL
-To start project type django-admin startproject text
-So now we have Django TUTORIAL/text->text,manage.py
-Now the text contain _init_.py,settings.py,url.py,wsgi.py,manage.py
-manage.py is a command line utility create databases for migrations
hence it is used to launch server,manage database,create tables in db
settings.py is all settings of your project.
_init_.py is a blank file it tells it is a python package
url.py is a file containing all the url.It basically tells where to go
when a basic url is entered in django
wsgi.py is to deploy file on server
-Now in order to run a dummy server type "python manage.py runserver"
Once the server is running we can copy the address shown as
"http://127.0.0.1:8000/" in web browser and run it.
-Now here text is a project which is a collection of many apps.Suppose
you created a project named e-commerce website no in this you can have
many apps namely shop,pay,return etc.
-Now in order to create a app type "python manage.py startapp utilities"
-A utilities folder will appear whic contain:
migrations->_init_.py,admin.py,models.py,tests.py,views.py
Here migration carries the information abt db change
_init_ is a blank file and it tells python that it can be imported
views.py is a most imp file and contain all the functions responsible
for displaying all the views.
-->Now in text make urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path,include
urlpatterns=[
path('admin/',admin.site.url),
path('utilities/',include('utilities.url))
]
"http://127.0.0.1:8000/utilities"
-Now we are in urls.py of utilities
from django.url import path
from . import views
urlpatterns =[
path('',views.index,name='index')
]
-Now since there is no index we will create one in views.py so open
views.py and write
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.http import HttpResponse
def index(requests):
return HttpsResponse('We are at index function we created')
-Now run "python manage.py makemigrations"
-Go to utilities->models.py models are python classes having information
abt how your db is structured,which tables are containing your db and how
you want django to store your data.
-Now run "manage.py migrate" Every time you make some chages you have to
come here again
-If you want to manage some media go to setting.py and write
MEDIA_ROOT=os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'media')
MEDIA_URL='/media/'
->Lets again go to views and create more views
def index(request):
return HttpRequest('''
<b>This is a bold tag</b>
''')
-Here abve cannot be done again and again so inorder to skip it go to app
folder and create two directories named "static" "template".
Also create a "utility" directory in static and template as we might
have some conflicting files of different apps.
static-->"utilities"
templates-->"utilities"-->"index.html"
---->Write any webpage code in "index.html"
-Now again goes to views.py
def index(request):
return render(request,'utilities/index.html')
From nowonwards page will load successfully.
You might also like
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Whare Ra - Pentagram RitualDocument20 pagesWhare Ra - Pentagram RitualJanWill100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Fundamentals of Java - CPINTLDocument466 pagesFundamentals of Java - CPINTLtruth seekerNo ratings yet
- L - 14experence Connected Components WorkbenchDocument90 pagesL - 14experence Connected Components WorkbenchRosy CruzNo ratings yet
- FEM Senthil PDFDocument436 pagesFEM Senthil PDFAbdul Nazèêr67% (9)
- Old Age Management SynopsisDocument3 pagesOld Age Management Synopsisvivek vangalNo ratings yet
- I AnnexureDocument4 pagesI AnnexureRiSHI KeSH GawaINo ratings yet
- 01 How To Request LaMPSS AccessDocument2 pages01 How To Request LaMPSS AccessslimaniNo ratings yet
- Report 1277718Document81 pagesReport 1277718Ranjan KumarNo ratings yet
- Readme Text For Cracking Gta V PCDocument2 pagesReadme Text For Cracking Gta V PCChinmay NaikNo ratings yet
- Multilevel Water Level Control & Monitoring of Multiple TanksDocument7 pagesMultilevel Water Level Control & Monitoring of Multiple TanksAkalas U. JohnNo ratings yet
- WDS DeploymentGuide PDFDocument197 pagesWDS DeploymentGuide PDFeleazar_lostNo ratings yet
- A 1 Software User ManualDocument107 pagesA 1 Software User ManualasdasNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Crop MonitoringDocument6 pagesAgricultural Crop MonitoringRaju top 1234No ratings yet
- Chap 2 - Sensor Node Hardware and Network ArchitectureDocument41 pagesChap 2 - Sensor Node Hardware and Network Architecturesmruti jaiswal100% (1)
- Freddie Beckley: Professional Summary Radio & PodcastsDocument1 pageFreddie Beckley: Professional Summary Radio & PodcastsFreddie BeckleyNo ratings yet
- Zainab Al Lawati CV PDFDocument2 pagesZainab Al Lawati CV PDFIvan WrightNo ratings yet
- PassLeader - Ccde.400 007.Dumps.320.Q&AsDocument109 pagesPassLeader - Ccde.400 007.Dumps.320.Q&Aslyyq99No ratings yet
- Data Communication QBANKDocument3 pagesData Communication QBANKاكاديميه فاروس العلميهNo ratings yet
- CBS v. HeldmanDocument15 pagesCBS v. HeldmanTHROnlineNo ratings yet
- CCNA 3 v503 v60 Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100 FullDocument14 pagesCCNA 3 v503 v60 Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100 FullSándor PetrócziNo ratings yet
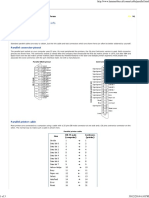
- Parallel Cable Pinout and Port InformationDocument3 pagesParallel Cable Pinout and Port InformationKailashNo ratings yet
- Mil PDF 89020B PDFDocument45 pagesMil PDF 89020B PDFade suhendar sutisnaNo ratings yet
- Sap HR Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument16 pagesSap HR Frequently Asked QuestionsbujjiummadiNo ratings yet
- DL Performance Evaluation of A Combined Cell in LTE Network - v2.0Document6 pagesDL Performance Evaluation of A Combined Cell in LTE Network - v2.0Kwangrok ChangNo ratings yet
- Integration Into Networks: 4.1 Network ParametersDocument2 pagesIntegration Into Networks: 4.1 Network ParametersMihai PopescuNo ratings yet
- DCN NotesDocument131 pagesDCN NotesGuzhal HariNo ratings yet
- Vsphere TutorialsDocument9 pagesVsphere TutorialsArnav VaidNo ratings yet
- What Is IPDocument70 pagesWhat Is IPElaine Tan-DiazNo ratings yet
- Jab Tum Us Link Se File Download Karlo Ge Tau Aise Ek File Waha Download HojaegeDocument10 pagesJab Tum Us Link Se File Download Karlo Ge Tau Aise Ek File Waha Download Hojaegearslansiddiqui7281No ratings yet
- Michelin Guide Taipei 2018 Press ReleaseDocument2 pagesMichelin Guide Taipei 2018 Press ReleaseMonica BurtonNo ratings yet