Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Contamination Transport & Fate
Uploaded by
Lingeswarran NumbikannuCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Contamination Transport & Fate
Uploaded by
Lingeswarran NumbikannuCopyright:
Available Formats
LINGESWARRAN
NUMBIKANNU
CONTAMINATION MKA191007
TRANSPORT AND FATE
CONTAMINATION FATE CONTAMINATION TRANSPORT
RADIOACTIVE DECAY
Introduction
BIODEGRADATION
Contaminant OXIDATION
Impurities/foreign compound presence in a body VOLATILIZATION
of natural environment that jeopardize the quality PHOTOLYSIS
of the element. Contaminant can either be inert HYDROLYSIS
or harmful to the environment depending on the
concentration of the element in the nature or
organism. Once reached a certain threshold,
contaminant are consider as pollutants that
causes severe effect.
Type : Organic & Inorganic Contaminant
Source : Biological (organic waste/biproducts)
Human activity (effluence & chemicals)
Phase Flow Liquid Contaminants (Groundwater)
Nonaqueous phase liquids are typically classified
as either light nonaqueous phase liquids
(LNAPLs) which have densities less than that of
water, or dense nonaqueous phase liquids
(DNAPLs) which have densities greater than that Fate of Contaminants in the Environment
of water.
Processes Governing the Environmental Fate of Chemicals
as well as an Indication of Specific Interactions Taking Place
at the Top Soil.
TRANSPORT SEVERITY
Transport of solute follows flow direction in a huge
ADVECTION 10 mass of fluid body.
Transport of solute that allows mixing and routing due
DISPERSION 9 to high velocity flow in a fluid body.
Transportation of solute that follows the concentration
DIFFUSION 8 gradient of the fluid body.
You might also like
- Mkaj 1093 - Unsaturated Soil Mechanics Project SEMESTER II, SESSION 2020/2021Document3 pagesMkaj 1093 - Unsaturated Soil Mechanics Project SEMESTER II, SESSION 2020/2021Lingeswarran Numbikannu0% (1)
- Lateral Earth PressureDocument15 pagesLateral Earth PressureLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- Machine Foundations On PilesDocument14 pagesMachine Foundations On PilesLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- Brace CutDocument12 pagesBrace CutLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationDocument31 pagesDynamic Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- Test MKAJ 1033Document2 pagesTest MKAJ 1033Lingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- AP - Jensen's PresentationDocument21 pagesAP - Jensen's PresentationLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- AJNTS Shengjin 10.9.2012Document11 pagesAJNTS Shengjin 10.9.2012Lingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- Remediation of Nitrobenzene Contaminated Soil by Combining Surfactant Enhanced Soil Washing and Effluent Oxidation With PersulfateDocument14 pagesRemediation of Nitrobenzene Contaminated Soil by Combining Surfactant Enhanced Soil Washing and Effluent Oxidation With PersulfateLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- Soil Washing For Metal Removal: A Review of Physical/chemical Technologies and Field ApplicationsDocument31 pagesSoil Washing For Metal Removal: A Review of Physical/chemical Technologies and Field ApplicationsLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- Soil Flushing of Cresols Contaminated Soil: Application of Nonionic and Ionic Surfactants Under Different PH and ConcentrationsDocument6 pagesSoil Flushing of Cresols Contaminated Soil: Application of Nonionic and Ionic Surfactants Under Different PH and ConcentrationsLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Azeotropic Distillation of Toluene With MethanolDocument16 pagesAzeotropic Distillation of Toluene With MethanolNurtasha AtikahNo ratings yet
- Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology: Sheela Chandra, Kazim Askari, Madhumita KumariDocument6 pagesJournal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology: Sheela Chandra, Kazim Askari, Madhumita KumariyasinNo ratings yet
- ASTM A352 18aDocument7 pagesASTM A352 18aKelly BatesNo ratings yet
- Base Oil Manufacturing Hydroprocessing (Amy Claxton, ICIS)Document36 pagesBase Oil Manufacturing Hydroprocessing (Amy Claxton, ICIS)die_1No ratings yet
- ANSWERS For ACT 8910111213 and Coverage of Lab ExamDocument8 pagesANSWERS For ACT 8910111213 and Coverage of Lab ExamPearlregine Cianne MirandaNo ratings yet
- Coal GenesisDocument29 pagesCoal GenesisIván Cáceres AnguloNo ratings yet
- BACTERIA CULTURE PRES Rev1Document28 pagesBACTERIA CULTURE PRES Rev1Jendie BayanNo ratings yet
- .Chapter 3Document21 pages.Chapter 3Santhosh VelanNo ratings yet
- SEM Picture of The Multi-Layer Structure of A 0.05 Micron MembraneDocument12 pagesSEM Picture of The Multi-Layer Structure of A 0.05 Micron MembraneRuben SerraNo ratings yet
- (CR (Acac) 3) ....Document14 pages(CR (Acac) 3) ....qamaralmahseriNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1876107012000107 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S1876107012000107 MainBUREAU VERITAS BLOQUESNo ratings yet
- Drimax 1234 MSDSDocument8 pagesDrimax 1234 MSDSSivakumar SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Gas Products Brochure - EnglishDocument7 pagesGas Products Brochure - EnglishNathalia DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Term 1 Week 1 - 2021Document4 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Term 1 Week 1 - 2021Lucky Jr MonobeNo ratings yet
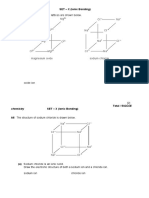
- O MG C Na: A7 The Structures of Two Ionic Lattices Are Shown BelowDocument33 pagesO MG C Na: A7 The Structures of Two Ionic Lattices Are Shown BelowFatema Khatun0% (1)
- Hilton Pharma Assignment DONEDocument8 pagesHilton Pharma Assignment DONEFakhrunnisa khanNo ratings yet
- There Are Three Main Groups of Resin:: Polyester ResinsDocument1 pageThere Are Three Main Groups of Resin:: Polyester ResinsmukeshNo ratings yet
- Soil, Soil Pollution & PesticidesDocument4 pagesSoil, Soil Pollution & PesticidesSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- In-W610 (Merit LMC 6 - Er70s-6) - 1Document2 pagesIn-W610 (Merit LMC 6 - Er70s-6) - 1Pratik LadNo ratings yet
- And Welding in Manufacturing: TIG MIGDocument27 pagesAnd Welding in Manufacturing: TIG MIGHope ThemNo ratings yet
- Chapter-16 Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument9 pagesChapter-16 Chemistry in Everyday LifeDeva RajNo ratings yet
- F500 Operation+instruction V1.0 - 201601 EN PDFDocument17 pagesF500 Operation+instruction V1.0 - 201601 EN PDFDonovan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Acumer Serie 3100 (HT) PDFDocument7 pagesAcumer Serie 3100 (HT) PDFAlfonso Dominguez Gonzalez100% (1)
- Chemistry - Mole Concept and Redox Reaction - Complete ModuleDocument101 pagesChemistry - Mole Concept and Redox Reaction - Complete Moduleruchir angraNo ratings yet
- sHOTPATCH 10 v3 PDFDocument2 pagessHOTPATCH 10 v3 PDFAnkita Baban GavadeNo ratings yet
- Fco PTMMC Gar 42-40Document5 pagesFco PTMMC Gar 42-40mahendrarakasiwi631No ratings yet
- Kesesuaian KesepkatanDocument12 pagesKesesuaian Kesepkatanfarmasi pikNo ratings yet
- Length Change of Concrete Due To Alkali-Carbonate Rock ReactionDocument4 pagesLength Change of Concrete Due To Alkali-Carbonate Rock ReactionJesús Luis Arce GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Man 4820 3601 LC Vanquish UHPLC Man48203601 ENDocument144 pagesMan 4820 3601 LC Vanquish UHPLC Man48203601 ENcraigorio616No ratings yet
- 12th Grade Chemical Kinetics WorhshhetDocument1 page12th Grade Chemical Kinetics WorhshhetAmen RaipurNo ratings yet