Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Physical Distribution?
What Is Physical Distribution?
Uploaded by
Aiza S. Maca-umbos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesPhysical distribution is the marketing function that facilitates the movement of goods from manufacturers to end users. Physical distribution managers ensure these activities are carried out efficiently. The objectives of physical distribution are to contribute to overall profitability by reducing costs without sacrificing customer service quality. This provides opportunities to improve customer service, reduce distribution costs, create time and place utilities, stabilize prices, influence channels, and control shipping costs. Key elements of efficient physical distribution include inventory planning and control, transportation via various modes, warehousing in private or public facilities, and order processing which involves order placement, internal processing, preparation, and shipment.
Original Description:
Distribution Management
Original Title
MARKETING21 REPORT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPhysical distribution is the marketing function that facilitates the movement of goods from manufacturers to end users. Physical distribution managers ensure these activities are carried out efficiently. The objectives of physical distribution are to contribute to overall profitability by reducing costs without sacrificing customer service quality. This provides opportunities to improve customer service, reduce distribution costs, create time and place utilities, stabilize prices, influence channels, and control shipping costs. Key elements of efficient physical distribution include inventory planning and control, transportation via various modes, warehousing in private or public facilities, and order processing which involves order placement, internal processing, preparation, and shipment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesWhat Is Physical Distribution?
What Is Physical Distribution?
Uploaded by
Aiza S. Maca-umbosPhysical distribution is the marketing function that facilitates the movement of goods from manufacturers to end users. Physical distribution managers ensure these activities are carried out efficiently. The objectives of physical distribution are to contribute to overall profitability by reducing costs without sacrificing customer service quality. This provides opportunities to improve customer service, reduce distribution costs, create time and place utilities, stabilize prices, influence channels, and control shipping costs. Key elements of efficient physical distribution include inventory planning and control, transportation via various modes, warehousing in private or public facilities, and order processing which involves order placement, internal processing, preparation, and shipment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Chapter 9
Physical Distribution
What is Physical Distribution?
Physical distribution is that marketing function which facilitates the movement of
goods from the manufacturer to the location of the ultimate users.
The Physical Distribution Managers are the people assigned to ensure that
physical distribution activities are carried out.
The Objectives of Physical Distribution
Every activity in the organization must be made to contribute to the overall
profitability of the firm. These include activities concerning physical
distribution. Since physical distribution is not directly concerned with the
generation of income through actual selling, it can contribute to profitability
by reducing costs. This may be achieved through the efficient management
of its functions.
The reduction of costs, however, must be made without sacrificing the
quality of service to customers, at least those that will affect profitability or
the attainment of other worthwhile objectives.
When physical distribution activities are well managed, it provides
opportunities for the firm to compete effectively
These opportunities are as follows
Improve Customer Service
Reduce Distribution Costs
Create Time and Place Utilities
Stabilize Prices
Influence Channel Decisions
Control Shipping Costs
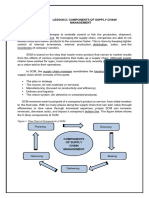
Elements of an Efficient Physical Distribution
Physical distribution is efficient if its assigned objective is achieved at the least
cost. It is possible if the following elements are properly managed:
1. Inventory Planning and Control
2. Transportation
The shipping of products to customers is one of the most important activities in
physical distribution. As products must be delivered at specific dates and at the
quality required, care must be taken in deciding what form of transportation to
adapt.
Railroads
Trucks
Water vessels
Pipelines
Airplanes
3. Warehousing
Warehousing is an important component of physical distribution: Due to some
reasons, most products are not delivered to the customers right after they come
out of the production line. Nevertheless, they must be kept in good condition
until they are finally delivered to buyers. The places where they are kept are
called warehouses and the activity done is called warehousing.
Types of Warehousing
Private Warehousing
Public Warehousing
4. Order Processing
Order processing refers to receiving, recording, filling, and assembling orders for
shipment. The steps undertaken from the time the customer makes an order up to
the time the ordered goods are delivered is called the "order cycle."
The Major Components of the Order Cycle. Four major components consist the order
cycle. These are as follows:
1. Order Placement
2. Internal Order Processing
3. Order Preparation
4. Order Shipment
PREPARED BY: MACA-UMBOS, AIZA
S.
You might also like
- The Protestant Work Ethic (Weber)Document349 pagesThe Protestant Work Ethic (Weber)Isabel Chew50% (2)
- Managerial Economics 11 Edition: by Mark HirscheyDocument13 pagesManagerial Economics 11 Edition: by Mark Hirscheyrandom17341No ratings yet
- Dbs PurchasingDocument67 pagesDbs PurchasingBenjamin Adelwini BugriNo ratings yet
- Business StrategiesDocument24 pagesBusiness StrategiesJohn Patrick Lazaro AndresNo ratings yet
- Nature of MarketingDocument30 pagesNature of MarketingTanvi Desai0% (1)
- Oligopoly and Game TheoryDocument50 pagesOligopoly and Game TheoryPeter MastersNo ratings yet
- Logistics ManagementDocument16 pagesLogistics ManagementsmtbnmNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Logistics ManagementDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Logistics ManagementFaisal Tanwar100% (1)
- Capturing Surplus: Solutions To Review QuestionsDocument23 pagesCapturing Surplus: Solutions To Review QuestionsAmeya Sakpal100% (1)
- Payroll SlipDocument3 pagesPayroll SlipAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- Managing Fulfillment Operations: DistributionDocument34 pagesManaging Fulfillment Operations: DistributionMaroa Al HabsiNo ratings yet
- RFBT-07-01a Law On Obligations Notes With MCQs Practice SetDocument110 pagesRFBT-07-01a Law On Obligations Notes With MCQs Practice SetAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- Документ Microsoft WordDocument9 pagesДокумент Microsoft WordcvenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Components of Distribution Management (B)Document16 pagesChapter 2 Components of Distribution Management (B)muhdfirdausNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document28 pagesChapter 9Hychell Mae Ramos DerepasNo ratings yet
- 1 ERP Business ProcessesDocument8 pages1 ERP Business ProcessessoniaNo ratings yet
- Physical Distributi ONDocument29 pagesPhysical Distributi ONMintu Tom JoseNo ratings yet
- Logistics and SCMDocument11 pagesLogistics and SCMShahma SalamNo ratings yet
- Course: Logistics Management Session: Dec 2019: Question No.-1 AnswerDocument5 pagesCourse: Logistics Management Session: Dec 2019: Question No.-1 AnswerRakesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Course: Logistics Management Session: Dec 2019: Question No.-1 AnswerDocument5 pagesCourse: Logistics Management Session: Dec 2019: Question No.-1 AnswerRakesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Name: Kim A. Rebarbas Subject: MM 221 - Distribution ManagementDocument2 pagesName: Kim A. Rebarbas Subject: MM 221 - Distribution ManagementOdysseus AryataNo ratings yet
- Physical DisturbutionDocument16 pagesPhysical Disturbutionmanasa2022No ratings yet
- Physical Distribution: Marketing ManagementDocument6 pagesPhysical Distribution: Marketing ManagementShajina ShyjuNo ratings yet
- Channel Management: Physical DistributionDocument7 pagesChannel Management: Physical Distributionraymond gatuNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument7 pagesAssignmentlulu luvelyNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 WarehousingDocument7 pagesUnit 4 WarehousingLaimi MutikishaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Warehousing and Material HandlingDocument15 pagesTopic 7 - Warehousing and Material HandlingAngel29JNo ratings yet
- Answer 4Document3 pagesAnswer 4Shubham imtsNo ratings yet
- Logistics Management PJT GLS VS VRJDocument20 pagesLogistics Management PJT GLS VS VRJSHABNAMH HASANNo ratings yet
- Physical Distribution of LogisticsDocument20 pagesPhysical Distribution of LogisticsDrisya K DineshNo ratings yet
- Question 1: The Logistics Functions and Various Objectives of The LogisticsDocument10 pagesQuestion 1: The Logistics Functions and Various Objectives of The LogisticsVandita KhudiaNo ratings yet
- International Logistics ManagementDocument8 pagesInternational Logistics ManagementAby M DominicNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain OperationsDocument7 pagesSupply Chain OperationsAngel AtienzaNo ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument66 pagesInternational BusinessHarpal Singh MassanNo ratings yet
- Logistics AssignmentDocument22 pagesLogistics AssignmentKalp DoshiNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management - TQMDocument11 pagesSupply Chain Management - TQMsuriya kishoreNo ratings yet
- GU 01 Physical Distribution OverviewDocument4 pagesGU 01 Physical Distribution OverviewTanmayNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document9 pagesUnit 4Surendar ENo ratings yet
- SCM Q 3 FinishedDocument6 pagesSCM Q 3 FinishedMohammed Imtiaz ShayekNo ratings yet
- Place Sales ManagementDocument9 pagesPlace Sales ManagementSheena ShahnawazNo ratings yet
- Warehousing PDFDocument36 pagesWarehousing PDFsaleem100% (1)
- Inventory Cycle - UploadDocument2 pagesInventory Cycle - UploadSean AntiojoNo ratings yet
- Hrde3 - Logistics Management - Lecture 2Document5 pagesHrde3 - Logistics Management - Lecture 2Renier Palma CruzNo ratings yet
- Module 2.1Document7 pagesModule 2.1ParalogityNo ratings yet
- Materials Management Is Defined As "The Groupings of Management FunctionsDocument15 pagesMaterials Management Is Defined As "The Groupings of Management FunctionsAugusto Jr Rafael BasaNo ratings yet
- DPM 101 Logistics and Distribution ManagementDocument33 pagesDPM 101 Logistics and Distribution Managementkennedy wanderaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain & Logistics Management Questions AnswersDocument6 pagesSupply Chain & Logistics Management Questions AnswersAmrita PatilNo ratings yet
- Issd Warehouse ManagementDocument14 pagesIssd Warehouse ManagementJayakumar NJNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: Paper Assignment English: Critical Thinking and Writing Proficiency, TMI 1603 (IB)Document10 pagesSupply Chain Management: Paper Assignment English: Critical Thinking and Writing Proficiency, TMI 1603 (IB)srir_41No ratings yet
- Operation PlanDocument13 pagesOperation PlanJellian ۦۦNo ratings yet
- Bagas Anandaffa Firdaus - Quiz5 (PPIC)Document3 pagesBagas Anandaffa Firdaus - Quiz5 (PPIC)Lunatic WrestlingNo ratings yet
- Physical DistributionDocument2 pagesPhysical DistributionkapooranukaranNo ratings yet
- Physical Distribution SystemDocument20 pagesPhysical Distribution SystemSubha RudraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document4 pagesChapter 8xhknrksy7qNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document5 pagesChapter 13Mary Grace PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Physical Dist - MGMTDocument106 pagesPhysical Dist - MGMTaby nasserNo ratings yet
- Logistic Planning: Logistics Is Generally The Detailed Organization and ImplementationDocument7 pagesLogistic Planning: Logistics Is Generally The Detailed Organization and ImplementationHarshit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Let Us Know First What Is Facility Is All AboutDocument2 pagesLet Us Know First What Is Facility Is All AboutJulhayda FernandoNo ratings yet
- Pa Print PoDocument2 pagesPa Print PoGABRIELLE DE LEONNo ratings yet
- Distribution Managment PrelimDocument10 pagesDistribution Managment Prelimfrederick liponNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3harleycrispino.eduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 AssignmentDocument5 pagesChapter 6 AssignmentJo GreedyNo ratings yet
- Cindy Adelia - Tugas EbDocument3 pagesCindy Adelia - Tugas EbCindy AdeliaNo ratings yet
- Production and Operation ManagementDocument8 pagesProduction and Operation ManagementBavya RajNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Managing Operations LessonsDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Managing Operations LessonsMa. Nicka BediaNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations Management: Chapter: 05. Inventory ControlDocument5 pagesProduction and Operations Management: Chapter: 05. Inventory ControlSN AdnanNo ratings yet
- Logistic and Transportatio Hamza YounasDocument5 pagesLogistic and Transportatio Hamza YounasAhmar ChNo ratings yet
- The Four CaliphDocument4 pagesThe Four CaliphAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- HISTORY Defined, Briefly, As The Record of Mankind On Earth. It Deals With What Men Had Done To HisDocument18 pagesHISTORY Defined, Briefly, As The Record of Mankind On Earth. It Deals With What Men Had Done To HisAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- Understanding The History of The Muslims in The PhilippinesDocument151 pagesUnderstanding The History of The Muslims in The PhilippinesAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- PASSION Shoe Apparel Company'sDocument22 pagesPASSION Shoe Apparel Company'sAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 The Audit ProcessDocument16 pagesChapter 01 The Audit ProcessAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- Principle of ManagementDocument8 pagesPrinciple of ManagementAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- Principle of ManagementDocument8 pagesPrinciple of ManagementAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- Study Objectives Study ObjectivesDocument59 pagesStudy Objectives Study ObjectivesAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- Department of Accountancy: Investment in AssociateDocument2 pagesDepartment of Accountancy: Investment in AssociateAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- Department of Accountancy: Inventory EstimationDocument2 pagesDepartment of Accountancy: Inventory EstimationAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- Department of Accountancy: Investment in Equity SecuritiesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Accountancy: Investment in Equity SecuritiesAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- Application of Free FallDocument2 pagesApplication of Free FallAiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- Department of Accountancy: RC-Al Khwarizmi International College Marawi City, 9700Document3 pagesDepartment of Accountancy: RC-Al Khwarizmi International College Marawi City, 9700Aiza S. Maca-umbosNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Fuel Hedging and Airline Profitability PDFDocument24 pagesThe Relationship Between Fuel Hedging and Airline Profitability PDFBeatriz FernandesNo ratings yet
- Mountain of Monopoly ProblemsDocument8 pagesMountain of Monopoly ProblemsPatricia Borjas GomezNo ratings yet
- Defence Presentation 1Document19 pagesDefence Presentation 1Isaa JatuNo ratings yet
- Apoplexy Case Study - Preparation Document For InterviewDocument5 pagesApoplexy Case Study - Preparation Document For InterviewEugene GaraninNo ratings yet
- Assignment/ Tugasan: BDEK1103 Introductory Microeconomics Pengenalan Mikroekonomi January 2023 SemesterDocument11 pagesAssignment/ Tugasan: BDEK1103 Introductory Microeconomics Pengenalan Mikroekonomi January 2023 SemesterMalar StylesNo ratings yet
- RKSingla's BS XII Worksheet2Document10 pagesRKSingla's BS XII Worksheet2ANUJ SHARMANo ratings yet
- G2 Stem 1 Business Entrepreneurship 1Document49 pagesG2 Stem 1 Business Entrepreneurship 1kyle PraderaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Revitalisation of Adamjee Jute MillDocument16 pagesIndustrial Revitalisation of Adamjee Jute Millসূর্য্য রবি75% (4)
- Study Man EcoDocument6 pagesStudy Man EcoJoan Gayle BalisiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 (Duality Interpretation)Document11 pagesLecture 4 (Duality Interpretation)Deeksha SinghNo ratings yet
- 5SSMN933 Tutorial SolutionsDocument43 pages5SSMN933 Tutorial Solutionsexample3335273No ratings yet
- Quiz # 2Document2 pagesQuiz # 2Jomelnelyna100% (1)
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationMaryy DemiiNo ratings yet
- Tina Li Xiaomi - Final ThesisDocument62 pagesTina Li Xiaomi - Final ThesisEshvin KrishNo ratings yet
- Pervan 2020 Efficiency of Large Firms OperatingDocument9 pagesPervan 2020 Efficiency of Large Firms OperatingStiven Riveros GalindoNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Cost AccountingDocument12 pagesObjectives of Cost AccountingHANS & HANSLI PRODUCTIONNo ratings yet
- The Impacts of Emotional Intelligence On Work Life Balance An EmpiricalDocument309 pagesThe Impacts of Emotional Intelligence On Work Life Balance An EmpiricalRajlaxmi GargNo ratings yet
- Review of Literature of Fast Food IndustryDocument4 pagesReview of Literature of Fast Food Industryanjali1187No ratings yet
- Business Chapter 18Document321 pagesBusiness Chapter 18Samantha GohsyNo ratings yet
- Final Chapter 1of 1 SolDocument2 pagesFinal Chapter 1of 1 SolNur DinieNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2016 2017Document77 pagesAnnual Report 2016 2017Dream GoalNo ratings yet
- Consumer Handbook: Department of Consumer Affairs Government of IndiaDocument78 pagesConsumer Handbook: Department of Consumer Affairs Government of IndiakeshavsainiNo ratings yet
- A-1+Steak+Sauce Fall. 2015 Poop SheetDocument13 pagesA-1+Steak+Sauce Fall. 2015 Poop Sheettudor_cristea_platonNo ratings yet
- Price and Output Determination in Various Market StructureDocument48 pagesPrice and Output Determination in Various Market Structurenikki0% (1)