Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AgileCheatSheet Updated
AgileCheatSheet Updated
Uploaded by
Lee SpadiniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AgileCheatSheet Updated
AgileCheatSheet Updated
Uploaded by
Lee SpadiniCopyright:
Available Formats
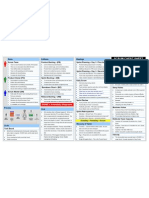
Roles Artifacts Meetings AGILE CHEAT SHEET *
Scrum Team Product Backlog - (PB) Sprint Planning - Day 1 / First Half Estimating
Scrum teams are self organizing. Maintained by the Product Owner. Product backlog prepared prior to meeting. User Stories
Team is cross-functional and consists of 5-9 List can contain bugs, and non-functional items. First half - Team selects items committing to complete.
people. Product Owner responsible for prioritizing. Additional discussion of PB occurs during actual High level definition of user requirements
There are no set project roles within the team. Items can be added by anyone at anytime. Sprint. that serves as a starting point for discussion.
Team defines tasks and assignments. Each item should have a business value assigned. Building blocks that can be assigned priorities,
Usually Dev : QA ratio is 3:1. Team develops the List of all desired product features. Sprint Planning - Day 1 / Second Half estimates, completion status.
product as per sprint backlog. Product backlog can be organized as a prioritized list Large user stories (Epics) that take longer than a
Occurs after half done - PO available for questions. sprint to build are broken into smaller user stories.
Ensures team works on highest valued features. of user stories in order of “high-risk, high-value”, “low- Team solely responsible for deciding how to build.
risk, high-value”, “low-risk, low-value”. User stories are NOT dependent on other stories.
Tasks created / assigned - Sprint Backlog produced. Story Template: As a <User>, I want <function>
Product Owner - (PO) Daily Scrum So that <desired result>
Sprint Backlog - (SB) Story Example: As a user, I want to print a recipe
Accountable for product success.
Held every day during a Sprint. so that I can cook it.
Defines all product features. To-do list (also known as Backlog item) for the Sprint.
Lasts 15 minutes.
Responsible for prioritizing product features. Created by the Scrum Team.
Team members report to each other not to Scrum Story Points
Maintains the Product Backlog. Product Owner has defined as highest priority.
Master. Story points indicate relative degree of difficulty
Ensures team works on highest valued features.
Answers 3 questions during meeting.
One full time product owner for every scrum team. Burndown Chart - (BC) and they follow the Fibonacci series because it
“What have you done since last daily scrum?” represents a set of numbers that we can intuitively
Chart showing how much work remaining in a Sprint. “What will you do before the next daily scrum?” distinguish between them as different magnitudes.
“What obstacles are impeding your work?”
Scrum Master - (SM) Calculated in hours remaining. Example: ”Send to a Friend” Story Points = 2
Maintained by the Scrum Master daily. Opportunity for team members to synchronize their “Shopping Cart” Story Points = 8
Holds daily 15 minutes team meeting.(Daily Scrum) Maintain seperate account of work remaining out of the work. “Advanced Search” Story Points = 13
Removes road blocks. “Original RB” and “New Features” added during the Having daily scrum over a conference call in
Facilitates planning and estimation. release. distributed teams is not advisable. Business Value
Maintains the Sprint Burndown Chart. Distributed teams are advised to break in multiple
Each User Story in the Product Backlog should have
Conducts Sprint Retrospective at the end of every Release Backlog - (RB) colocated teams.
a corresponding business value assigned.
Sprint.
Typically assign (L, M, H) Low, Medium, High.
Maintains team spirit. Same as the Product Backlog. May involve one or Sprint Review PO prioritizes Backlog items by the highest value.
Typically one scrum master can handle two scrum more sprints dependent on determined Release date.
User Stories can be classified as “Must have”,
teams. Team presents “done” code to PO and stakeholders.
“Should have”, “Could Have”, “Good to have”.
“DONE”= Potentially Shippable! Functionality not “done” is not shown.
TDD = Refactoring + TFD Feedback generated - RB may be reprioritized. Planning Poker
FAQ Scrum Master sets next Sprint Review.
Refactor code 3a Testing via xUnit Framework Cards bearing Fibonacci numbers
[tests unbroken] are distributed to all team members. Stories are
Who decides when a Release happens? At the end Sprint Retrospective
of any given Sprint the PO can initiate a Release. discussed and team members place cards, face
3b Refactor
Refactorcode
code
[Test(s)
[tests broken] Who is responsible for managing the teams? The Attendees - SM, PO and Team. down, containing their estimation for each story.
All Tests One or more Questions - What went well and what can be Cards are opened and the highest and the lowest
Pass teams are responsible for managing themselves.
Tests fail bidder debate to support their estimate.
What is the length of a task? Tasks should take no improved?
2 Fix Functional code
4
longer than 16 hours. If longer, then the task should be SM helps team in discovery - does not provide It is repeated till team converges on the estimate.
Can’t think
broken down further. answers.
of any 1 Write a test Velocity
more Who manages obstacles? Primary responsibility is
tests on the Scrum Master. However, teams must learn to
Visibility + Flexibility = Scrum The rate (Story Points per Sprint) at which team
resolve their own issues. If not able, then escalate to converts items to “DONE”.
Kanban After a few iterations velocity, becomes stable
SM.
XP Practices What are two of the biggest challenges in Scrum? Applies to any process that has sequence of steps. and predictable.
Teams not self-managing, Scrum Master managing, WIP-Limit - maximum WIP allowed at any step is
XP - Extreme Programming. Testing and Automation
not facilitating. fixed. WIP-Limit can be quantified in Story Points.
TDD - Test Driven Development, Routine Refactoring.
How to add new User Stories to SB in the middle of Typical steps - Requirement clarification, Manual QA and Dev are co-located, and in 1:3 ratio,
BDD - Behaviour Driven Development.
sprint? It is not advisable. Sprint should be short development, integration, testing, deployment, UAT. for new products. Automation QA team is separate.
TFD - Test First Development.
enough to allow new user stories to wait till the next Add or move resources to wherever the bottleneck is Continuous testing using automation for early defect
CI - Continuous Integration.
sprint starts. In exceptional cases, a new user story observed. Of course, the bottleneck may keep detection.
CD - Continuous Deployment.
can be added by removing one or more stories to moving. Automation lags by a sprint to allow recent test
UAT - User Acceptance Testing.
keep the total of story points constant. Works well for ongoing support/maintenance work. cases to stabilize.
SYNERZIP
* Inspired by ScrumLogic
www.synerzip.com
You might also like
- Scrum MasterDocument19 pagesScrum MasterDaniel Martinez100% (2)
- Scrum Cheat SheetDocument1 pageScrum Cheat Sheetsoupn2100% (100)
- User Stories Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pagesUser Stories Quick Reference GuideDmitry Sharkov100% (6)
- ScrumMaster Training BookDocument125 pagesScrumMaster Training Bookinkafan100% (10)
- Scrum Master Interview QuestionsDocument93 pagesScrum Master Interview QuestionsTanmoy Das100% (11)
- Roles& Meetings& Artifacts& Glossary&: Scrum&Cheat&Sheet&Document1 pageRoles& Meetings& Artifacts& Glossary&: Scrum&Cheat&Sheet&alfador_yx100% (1)
- Scrum Master Practitioner's GuideDocument11 pagesScrum Master Practitioner's GuideVasilis100% (1)
- Ebook V2.Becoming A Scrum MasterDocument38 pagesEbook V2.Becoming A Scrum MasterGabriela VenegasNo ratings yet
- Top 40 Agile Scrum Interview QuestionsDocument17 pagesTop 40 Agile Scrum Interview QuestionsSendil Kumar0% (1)
- Scrum Certification: All In One, The Ultimate Guide To Prepare For Scrum Exams And Get Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsFrom EverandScrum Certification: All In One, The Ultimate Guide To Prepare For Scrum Exams And Get Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Professional - Scrum - Master - NotesDocument10 pagesProfessional - Scrum - Master - NotesJM100% (3)
- Professional Scrum Master I - EXAM NOTESDocument45 pagesProfessional Scrum Master I - EXAM NOTESMamoon20100% (2)
- ScrumCheatSheet PDFDocument1 pageScrumCheatSheet PDFEdu OliverNo ratings yet
- Certified Scrum Master Exam Questions 2018 1Document5 pagesCertified Scrum Master Exam Questions 2018 1Sam50% (2)
- Scrum E Book 1Document58 pagesScrum E Book 1sungray100% (4)
- Your Complete Guide To Agile Scrum and KanbanDocument117 pagesYour Complete Guide To Agile Scrum and KanbanMiftahul Rizki Purwonegoro75% (4)
- Scrum Master Interview QuestionsDocument55 pagesScrum Master Interview Questionsshivaramreddy6950% (2)
- Scrum Master Certification Exam Sample Questions PDF 2019 1Document3 pagesScrum Master Certification Exam Sample Questions PDF 2019 1DIEGODLRNo ratings yet
- Agile Scrum Cheat SheetDocument1 pageAgile Scrum Cheat Sheetashisamk180% (5)
- Agile Coach Interview Questions and Answers - Tech Agilist PDFDocument12 pagesAgile Coach Interview Questions and Answers - Tech Agilist PDFSamarveer SinghNo ratings yet
- 2008-03-15 Mike Cohn - Agile Estimation and PlanningDocument36 pages2008-03-15 Mike Cohn - Agile Estimation and PlanningSam Yiu100% (5)
- Thinking in Java, 2 Edition, Bruce Eckel, President,: Release 11Document1,156 pagesThinking in Java, 2 Edition, Bruce Eckel, President,: Release 11ramakrishna79% (24)
- XML TutorialDocument80 pagesXML TutorialchisimdiriNo ratings yet
- Scaled Agile Draft Exam MockupDocument13 pagesScaled Agile Draft Exam MockupRob Gielen64% (11)
- Certified Scrum Master Question Dumps 2 - Tutorials For ExamsDocument7 pagesCertified Scrum Master Question Dumps 2 - Tutorials For ExamsGokul Krish100% (1)
- So You Want To Be A Scrum MasterDocument96 pagesSo You Want To Be A Scrum Masterroxr100% (1)
- Hands-On - SoftwareEnggDocument8 pagesHands-On - SoftwareEnggGeniushardware service75% (4)
- Agile Ba Cheat Sheet: Second EditionDocument1 pageAgile Ba Cheat Sheet: Second EditionLee SpadiniNo ratings yet
- Pocket guide to the Professional Scrum Master Certification (PSM 1)From EverandPocket guide to the Professional Scrum Master Certification (PSM 1)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- OSWA (Offensive Security Web Attacks) - Study Overview PT.1 PDFDocument399 pagesOSWA (Offensive Security Web Attacks) - Study Overview PT.1 PDFJames BondNo ratings yet
- PSM 1 PDFDocument71 pagesPSM 1 PDFA Gentlemen100% (1)
- Agile Training - User Stories and BacklogDocument12 pagesAgile Training - User Stories and BacklogKevin 'Boomer' Engelkamp100% (9)
- Compiler Compilers ToolDocument12 pagesCompiler Compilers ToolBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Professional Scrum Master Exam Questions PDF 2019 3Document3 pagesProfessional Scrum Master Exam Questions PDF 2019 3DIEGODLR60% (5)
- Scrum in 5 MinutesDocument16 pagesScrum in 5 MinutesOnlyMahesh96% (51)
- Scrum Cheat SheetDocument1 pageScrum Cheat Sheetmohitmcm100% (3)
- Scrum Master HandbookDocument11 pagesScrum Master HandbookPradeep PapannaNo ratings yet
- February 2010: Scrum: Developed and Sustained by Ken Schwaber and Jeff SutherlandDocument21 pagesFebruary 2010: Scrum: Developed and Sustained by Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherlandscrumdotorg100% (2)
- Scrum Cheat SheetDocument1 pageScrum Cheat SheethohingdayNo ratings yet
- Agile and Scrum Tip Sheet From Vitality Chicago Inc April 2020Document1 pageAgile and Scrum Tip Sheet From Vitality Chicago Inc April 2020Lee SpadiniNo ratings yet
- SAFe 4 Release Train Engineer ExamDocument12 pagesSAFe 4 Release Train Engineer Examspamme48% (25)
- Scrum: Understanding Scrum at a Deeper Level and Mastering Agile Project ManagementFrom EverandScrum: Understanding Scrum at a Deeper Level and Mastering Agile Project ManagementRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- PSM Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPSM Cheat SheetShare KhannaNo ratings yet
- Agile Estimating 2.0 Cheat SheetDocument1 pageAgile Estimating 2.0 Cheat SheetPeter SaddingtonNo ratings yet
- The Agile Pocket Guide: A Quick Start to Making Your Business Agile Using Scrum and BeyondFrom EverandThe Agile Pocket Guide: A Quick Start to Making Your Business Agile Using Scrum and BeyondRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Get SAFe Now: A Lightning Introduction to the Most Popular Scaling Framework on AgileFrom EverandGet SAFe Now: A Lightning Introduction to the Most Popular Scaling Framework on AgileRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- The Scrum Guide Unfolds: Agile Software Development, #2From EverandThe Scrum Guide Unfolds: Agile Software Development, #2Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Scrum Checklist AllDocument1 pageScrum Checklist AllM. Arifur Rahman100% (8)
- Agile Software Development ScrumDocument50 pagesAgile Software Development ScrumKevin Yudistira100% (2)
- Scrum Guide - Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesScrum Guide - Cheat SheetGonzalo Gonzalez75% (4)
- Safe Product Owner/Product Manager (4.6) : DescriptionDocument2 pagesSafe Product Owner/Product Manager (4.6) : DescriptionArvind SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Scrum Reference CardDocument6 pagesScrum Reference Cardrajisgood100% (1)
- Scrum Narrative and PSM Exam GuideFrom EverandScrum Narrative and PSM Exam GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- SAFe RTE 5.0 Flashcards - QuizletDocument2 pagesSAFe RTE 5.0 Flashcards - QuizletIero tr0% (1)
- Agile and Scrum Glossary - SCRUMstudyDocument17 pagesAgile and Scrum Glossary - SCRUMstudyRomarMroNo ratings yet
- Certified Scrum Master Random NotesDocument4 pagesCertified Scrum Master Random NotesamagazineNo ratings yet
- Agile Frameworks and PracticesDocument3 pagesAgile Frameworks and PracticesMary Charisse SandroNo ratings yet
- Master Data Approach PS 2015 06 OldDocument16 pagesMaster Data Approach PS 2015 06 OldLee SpadiniNo ratings yet
- Financial Management in An Agile World: by Beth Lassiter, Michael Noel, and Chris HessDocument6 pagesFinancial Management in An Agile World: by Beth Lassiter, Michael Noel, and Chris HessLee SpadiniNo ratings yet
- Agile Portfolio Management (Agilepfm) - For The Agile-Mature OrganisationDocument2 pagesAgile Portfolio Management (Agilepfm) - For The Agile-Mature OrganisationLee SpadiniNo ratings yet
- Action Item List: Last Updated: 7-Nov-17Document2 pagesAction Item List: Last Updated: 7-Nov-17Lee SpadiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Java Programming: Week 3Document30 pagesIntroduction To Java Programming: Week 3Shabana TahirNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument14 pagesPythonChinna EdigaNo ratings yet
- CV - Lam Thanh NhatDocument3 pagesCV - Lam Thanh NhatnqkhaidlNo ratings yet
- WEKADocument15 pagesWEKAIván AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Casino Number Guessing Game in CDocument9 pagesCasino Number Guessing Game in CA- SNo ratings yet
- Resume. Updated SanjanaDocument4 pagesResume. Updated SanjanaSanjana P Sanjana PNo ratings yet
- Cloudera Data Analyst Training PDFDocument2 pagesCloudera Data Analyst Training PDFjimmyNo ratings yet
- Aca Unit5Document13 pagesAca Unit5karunakarNo ratings yet
- Preface 1 Data Handling in Files: VIII 1Document179 pagesPreface 1 Data Handling in Files: VIII 1Hamza AtifNo ratings yet
- Expresscache x64 118Document2 pagesExpresscache x64 118Animatronic sonoroNo ratings yet
- Swe2005 Software-Testing Eth 1.0 47 Swe2005Document2 pagesSwe2005 Software-Testing Eth 1.0 47 Swe2005EswariNo ratings yet
- Python ResponderDocument37 pagesPython Responderadhi_narenNo ratings yet
- Dsa Cycle SheetDocument3 pagesDsa Cycle SheetPunit KumarNo ratings yet
- Integrazione Ariba MDGDocument66 pagesIntegrazione Ariba MDGGiuseppeComparettiNo ratings yet
- Simulado 7Document12 pagesSimulado 7Danillo AraujoNo ratings yet
- Argtable2 AdvancedDocument10 pagesArgtable2 AdvancedZombertoNo ratings yet
- Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT) - Library of Java Package - Contains 25 Packages With Hundreds of Classes - Used For GUI - Import Java - Awt.Document52 pagesAbstract Window Toolkit (AWT) - Library of Java Package - Contains 25 Packages With Hundreds of Classes - Used For GUI - Import Java - Awt.Indu SudhaNo ratings yet
- OAF CodeDocument18 pagesOAF CodeAsish PandaNo ratings yet
- A Mechanism For Converting A Relational Database Into An Object-Oriented Model: An AIS ApplicationDocument14 pagesA Mechanism For Converting A Relational Database Into An Object-Oriented Model: An AIS Applicationncbzkr zkrncbNo ratings yet
- Akshay's ResumeDocument6 pagesAkshay's ResumeVinod GodeNo ratings yet
- 1 - Siemens Open Library - Library Overview and Architecture V1.4Document19 pages1 - Siemens Open Library - Library Overview and Architecture V1.4RafaelNo ratings yet
- Add A Calculated Field To A TableDocument60 pagesAdd A Calculated Field To A TableAlage TekaNo ratings yet
- EECS112L Cadence Tutorial PDFDocument7 pagesEECS112L Cadence Tutorial PDFj1706205No ratings yet
- How To Optimize SQL Server Query Performance - Statistics, Joins and Index TuningDocument25 pagesHow To Optimize SQL Server Query Performance - Statistics, Joins and Index TuningMarcos TiagoNo ratings yet
- SharePoint Development Standards2Document10 pagesSharePoint Development Standards2Murali KrishanNo ratings yet