Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Attitudes
Attitudes
Uploaded by
Şterbeţ RuxandraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attitudes
Attitudes
Uploaded by
Şterbeţ RuxandraCopyright:
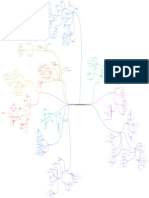
more resistent to change
more persistent
more information processing
more likely to guide behavior
strong attitude
weak attitude
vary in degree
accessibility extremity importance certainty
concept
subliminal
evaluative conditioning
priming
LINK
mere exposure effect
A-ffective
energy saving Zajonc
strength of attitude
mood influences evaluation attitudinal ambivalence
high accessibility
need for closure
people differ in past + anticipated future behavior
one-dimensional perspective "favorite" component
moderators fast decision object appraisal function
two-dimensional perspective highly predictive
self-perception theory
based on:
two-step model multiple component model B-ehavior
cognitive dissonance
achieve optimal outcome behavior with
habits linked to situational cues
evaluative implications
utilitarian function attitude objects differ
structure
reception few evidence McGuire minimize costs/punishments
all steps must cognitive object Implementation Intentions if...then..plans
affective object stereotypes
be completed C-ognitive
behavior retention yielding comprehension attention differ in object Fishbein, Ajzen
information processing model need-fulfillment by attitudes
willingness to invest more only salient beliefs
function content MJ pepsi car strengthens
help express values/self-image behavior
expectancy-value approach expectancy-value approach theory of reasoned action: Attitude Intention
decreases capacity to
distraction value-expressive function
generate own thoughts
positive vs negative
messags persuade if they evoke
predominantly favorable thoughts how people vary their behavior moderator subjective norm
self-monitoring
across social situations
strength
an overall evaluation of
a stimulus object beleifs about significant pulls through
inhibit persuasion positive thoughts cognitive response model other's views
formed about nearly everything
social adjustment function
Greenwald starting
distraction starts behavior
message help us identify with
liked others
match the message to the function Attitudes expression of attitude
attitudes change through theory of planned behavior: perceived behavioral control
detailed thought processes preparing
enhance persuasion negative thoughts
mediator ego-defensive function more up to date self-efficacy
measure theories of systematic processes
thought not argument considering
changes attitude
help protect our self-esteem
thought listing
own generated thoughts
unmotivated
models behavior change
Hovland-Yale model
Who? Dijkstra
e.g. stereotypes
source degree to which a attitude
rational actor predicts behavior biased perception
Says what?
To whom? highly accessible attitudes
message attitude-behavior relation behavior
low
audience no behavior
M otivation
approaches persuasion
behavior predictor high deliberate behavior
communication to change strength of attitude MODE model
beliefs/attitudes/behavior
when?
O pportunity
nonrational actor
domain of behavior how difficult it is to execute an DE terminants
action in order to express attitude
attitudinal and behavioral RIM model
measures must correspond in
role of person variables impulsive system
four key ways
reflective system
elicits behavior via automatic
associative links
elicits behavior via reasoned
measurement considering of available info.
action context time
target
too popular
implicit association test (IAT) by now
explicit if so high reliability
bipolar adjective scale semantic differential implicit
scale evaluative priming
often overlap
likert scale predict automatic Fazio
predict thoughtful
behavior behavior
problems
verbal unaware of nonverbal implicit biases
social desirability
attitude
You might also like
- Counseling TechniquesDocument369 pagesCounseling TechniquesŞterbeţ Ruxandra100% (3)
- Fear No More The Heat of The Sun: Gerald Finzi William ShakespeareDocument5 pagesFear No More The Heat of The Sun: Gerald Finzi William Shakespeareawrosdorff100% (2)
- Sicilienne: Allegretto Molto ModeratoDocument6 pagesSicilienne: Allegretto Molto ModeratoАлександр НиколаевNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument38 pagesAdjectivesFOM YESCH100% (2)
- Concertino For Alto Sax and PianoDocument7 pagesConcertino For Alto Sax and PianoCarmelo farandaNo ratings yet
- Deep Beauty - Understanding The Quantum World Through Mathematical InnovationsDocument488 pagesDeep Beauty - Understanding The Quantum World Through Mathematical InnovationsRobert Klinzmann100% (3)
- IHRMchapter 11Document11 pagesIHRMchapter 117_raghuNo ratings yet
- Module 19: Gender Roles and Differences: Student ObjectivesDocument9 pagesModule 19: Gender Roles and Differences: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Death and Co. Modern Classic Cocktails (Alphabetized) PDFDocument1 pageDeath and Co. Modern Classic Cocktails (Alphabetized) PDFJoshua Leiva MuñozNo ratings yet
- Module 20: Education: Schooling, Learning Difficulties and High IntelligenceDocument10 pagesModule 20: Education: Schooling, Learning Difficulties and High IntelligenceŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 18: Behavioral Problems: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pagesModule 18: Behavioral Problems: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Concertino: Pour Saxophone Alto Mi Et PianoDocument7 pagesConcertino: Pour Saxophone Alto Mi Et PianodeboraNo ratings yet
- Module 21: Health and Nutrition in A Child's DevelopmentDocument10 pagesModule 21: Health and Nutrition in A Child's DevelopmentŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- L5R 3e - 3rd Ed Char SheetDocument2 pagesL5R 3e - 3rd Ed Char SheetCarlos William LaresNo ratings yet
- Activity Based Teaching StrategiesDocument16 pagesActivity Based Teaching StrategiesGlennmar DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Concertino For Alto Sax and PianoDocument7 pagesConcertino For Alto Sax and PianoCarmelo farandaNo ratings yet
- Derrida Freud and The Scene of WritingDocument45 pagesDerrida Freud and The Scene of WritingPeter Liu100% (1)
- Grade 7 DLL W1Document3 pagesGrade 7 DLL W1Gina Artates100% (2)
- Purposive Comm Module 1 EditedDocument28 pagesPurposive Comm Module 1 EditedRafaela OngNo ratings yet
- Case IH Magnum Series 215,245,275,305 Tractors Electrical Schematic - 87588600Document4 pagesCase IH Magnum Series 215,245,275,305 Tractors Electrical Schematic - 87588600MilanNo ratings yet
- Celta Lesson Plan No 6 Danoff Dot Org PDFDocument10 pagesCelta Lesson Plan No 6 Danoff Dot Org PDFTatiana AlekseyetsevaNo ratings yet
- Class Lecture Slides Performance and Compensation ManagementDocument80 pagesClass Lecture Slides Performance and Compensation ManagementSaad Afridi100% (1)
- The SelfDocument1 pageThe SelfŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Services: Consulting SupportDocument16 pagesServices: Consulting SupportMohamed Ange NAPONo ratings yet
- Web Application SecurityDocument1 pageWeb Application SecurityEllisNo ratings yet
- Analisis 20aprilDocument1 pageAnalisis 20aprilDika ReyhanNo ratings yet
- 11 10 Layout1Document1 page11 10 Layout1Shah MuzzamilNo ratings yet
- Inside Ptmalloc2: Peng XuDocument27 pagesInside Ptmalloc2: Peng XuxkNo ratings yet
- Parenthood: General Dynamic Factors - Age - Gender - Ethnicity - Social Economic Status - Educational BackgroundDocument1 pageParenthood: General Dynamic Factors - Age - Gender - Ethnicity - Social Economic Status - Educational Backgroundjunebug3No ratings yet
- Nozawa Onsen Trail Map 0Document1 pageNozawa Onsen Trail Map 0hhjgjggNo ratings yet
- Ripple Effects of The Low Touch Economy: V2 - Latest Update April 16, 2020 Strong Link Weak LinkDocument1 pageRipple Effects of The Low Touch Economy: V2 - Latest Update April 16, 2020 Strong Link Weak LinkBlink Muttaneeya UjjinNo ratings yet
- ఆసరాDocument111 pagesఆసరాunnammadhava8No ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document37 pagesLecture 3goyij85837No ratings yet
- KRISHNA SHLOK RESIDENCY-ModelDocument1 pageKRISHNA SHLOK RESIDENCY-ModelgetlovefromgodNo ratings yet
- R 01 ModelDocument1 pageR 01 ModelRakesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Plano Replanteo San Mateo 2Document1 pagePlano Replanteo San Mateo 2Yerzi Arturo Arroyo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Advertising For Digital MediaDocument1 pageAdvertising For Digital Mediaaliarefnezhad2022No ratings yet
- Clase 4Document42 pagesClase 4Carlos ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Benja PlanDocument1 pageBenja Planmasumba patrickNo ratings yet
- Concertino For Alto Sax and PianoDocument7 pagesConcertino For Alto Sax and PianoCarmelo farandaNo ratings yet
- Concertino For Alto Sax and PianoDocument7 pagesConcertino For Alto Sax and PianoCarmelo farandaNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles: Angle: 2 Different Rays With Same EndpointDocument11 pages1.4 Measure and Classify Angles: Angle: 2 Different Rays With Same EndpointMrs. HedrickNo ratings yet
- Hungarian L 2 FirstDocument2 pagesHungarian L 2 Firstyaolin liuNo ratings yet
- Niwaha IvanDocument1 pageNiwaha IvanTwebazibwe EdsonNo ratings yet
- SubseaBoosting 2014 PosterDocument1 pageSubseaBoosting 2014 PosterL TNo ratings yet
- NRL MapDocument44 pagesNRL Mapসীমান্ত ছাড়িয়ে - Shemanto ChariyeNo ratings yet
- WW Ms ST 00 Mosque Minaret1631123643798Document7 pagesWW Ms ST 00 Mosque Minaret1631123643798孔庆龙No ratings yet
- STANDARD DRAWING FOR 1X1060mm Cross CulvertDocument3 pagesSTANDARD DRAWING FOR 1X1060mm Cross CulvertOKELLO OKOT PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Internet Orthodox ConnectionsDocument1 pageInternet Orthodox ConnectionsJohn AndrewNo ratings yet
- Serban Nichifor: The Infinite PassacagliaDocument8 pagesSerban Nichifor: The Infinite PassacagliaSerban NichiforNo ratings yet
- Theme&VariationsDocument13 pagesTheme&VariationsMikebat321No ratings yet
- Notes: Electrical KeyDocument1 pageNotes: Electrical KeyanzaniNo ratings yet
- PROY AM-Layout4Document1 pagePROY AM-Layout4Cangatron 14No ratings yet
- Funky ScoreDocument6 pagesFunky Scoreashenfall7No ratings yet
- Lopefy® (Norepinephrine) 1mg Per ML Concentrate For Solution For InfusionDocument1 pageLopefy® (Norepinephrine) 1mg Per ML Concentrate For Solution For InfusionTAJ PHARMA — A Health Care ProviderNo ratings yet
- The Schur Algorithm: Digtal Signal Processing (Et 4235)Document22 pagesThe Schur Algorithm: Digtal Signal Processing (Et 4235)KrishNo ratings yet
- Ilam and Iran, Volume 2Document3 pagesIlam and Iran, Volume 2Dariush DelaraNo ratings yet
- IL MARE CALMO DELLA SERA B Flat TrumpetDocument1 pageIL MARE CALMO DELLA SERA B Flat TrumpetMydoria BarrosNo ratings yet
- SDP 1Document1 pageSDP 1Zie FaithNo ratings yet
- A Couple's Duet Walkthrough (V0.10.0)Document1 pageA Couple's Duet Walkthrough (V0.10.0)BIG jekNo ratings yet
- SVVSVDocument1 pageSVVSVMunzurulKaderNo ratings yet
- Making It All WorkDocument1 pageMaking It All Workioan0% (2)
- Variations ScoreDocument2 pagesVariations ScorescwrightNo ratings yet
- Draft Structural Drawings-Lucky Mwanga 5BD House - BackupDocument7 pagesDraft Structural Drawings-Lucky Mwanga 5BD House - BackupFrex AumandoNo ratings yet
- 15 Ilm Jarh Wa TadilDocument19 pages15 Ilm Jarh Wa Tadilsabir latifNo ratings yet
- Since From My Dear H.purcellDocument3 pagesSince From My Dear H.purcellGGMNo ratings yet
- Phrasal Verbs ListDocument3 pagesPhrasal Verbs ListisadoraNo ratings yet
- 5382 Int 00 00 DR Me 320101 - P01Document1 page5382 Int 00 00 DR Me 320101 - P01Sanimouse MousesaniNo ratings yet
- Determine The Vertical and Horizontal Components of The VectorDocument17 pagesDetermine The Vertical and Horizontal Components of The Vectorpmorris1No ratings yet
- Alt Rokugon Map PosterDocument1 pageAlt Rokugon Map PosterTill Wer SonstNo ratings yet
- 赵曦 未找到的钥匙(合集抽选)Document13 pages赵曦 未找到的钥匙(合集抽选)wutianao753159No ratings yet
- Moriyama House in TokyoDocument1 pageMoriyama House in TokyoMariana Rodríguez GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Spanesta Brochure - 1-20Document10 pagesSpanesta Brochure - 1-20parnikabhatnagar04No ratings yet
- The Utah Marriage HandbookDocument52 pagesThe Utah Marriage HandbookŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Connect: Engaging in A Positive Social Network of SupportDocument8 pagesConnect: Engaging in A Positive Social Network of SupportŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Using Nurturing, Caring, and Affectionate Behaviors: What Care Looks LikeDocument6 pagesUsing Nurturing, Caring, and Affectionate Behaviors: What Care Looks LikeŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Share: Developing and Maintaining A Couple IdentityDocument8 pagesShare: Developing and Maintaining A Couple IdentityŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Parenting Styles+ Locus of Control Vs BullyingDocument18 pagesParenting Styles+ Locus of Control Vs BullyingŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Care For Self: Maintaining Physical, Sexual, Emotional, and Spiritual WellnessDocument8 pagesCare For Self: Maintaining Physical, Sexual, Emotional, and Spiritual WellnessŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Nermem 04 KnowDocument8 pagesNermem 04 KnowŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 14: Attachment and Relationship Building: Student ObjectivesDocument8 pagesModule 14: Attachment and Relationship Building: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 15: The Role of Separation in Child DevelopmentDocument10 pagesModule 15: The Role of Separation in Child DevelopmentŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 17: Self-Esteem and Confidence: Student ObjectivesDocument9 pagesModule 17: Self-Esteem and Confidence: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 13: Intellectual Development: Student ObjectivesDocument9 pagesModule 13: Intellectual Development: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 16: Language and Communication: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pagesModule 16: Language and Communication: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 11: Social Development: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pages11: Social Development: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 22: Developing Into Adulthood: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pagesModule 22: Developing Into Adulthood: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 10: Physical Development: Student ObjectivesDocument9 pages10: Physical Development: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 09: The Nature/Nurture Debate: Student ObjectivesDocument8 pages09: The Nature/Nurture Debate: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 02: Child Development Research and Theories: Student ObjectivesDocument7 pagesModule 02: Child Development Research and Theories: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 08: Genetics: Student ObjectivesDocument9 pagesModule 08: Genetics: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Child Psychology Worksheet Module 17Document6 pagesChild Psychology Worksheet Module 17Şterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 12: Emotional Development: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pages12: Emotional Development: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 07: Cognitive Development and The Teenage Years: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pages07: Cognitive Development and The Teenage Years: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 03: An Overview of Cognitive Development: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pagesModule 03: An Overview of Cognitive Development: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 06: Cognitive Development in The Middle Years: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pages06: Cognitive Development in The Middle Years: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 04: Cognitive Development in The First Year: Student ObjectivesDocument8 pages04: Cognitive Development in The First Year: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 05: Cognitive Development in The Toddler and Preschool YearsDocument9 pages05: Cognitive Development in The Toddler and Preschool YearsŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Critical LiteracyDocument5 pagesModule 8 Critical LiteracyJandee BarrientosNo ratings yet
- SOI Coaching Guide PDFDocument26 pagesSOI Coaching Guide PDFnhemsgmNo ratings yet
- Nike AdDocument4 pagesNike AdАйна АйтбаеваNo ratings yet
- Tos Lac Session MinutesDocument3 pagesTos Lac Session MinutesLevi Mae PacatangNo ratings yet
- TETENGLISHDocument24 pagesTETENGLISHMaheswara BisaloNo ratings yet
- Comparison - Contrast Essay 2Document2 pagesComparison - Contrast Essay 2susi lawatiNo ratings yet
- Case Study HaldiramDocument20 pagesCase Study HaldiramKajal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Indicative Verb Endings TableDocument2 pagesIndicative Verb Endings TableKateNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis With Surveys Final PDFDocument22 pagesData Analysis With Surveys Final PDFLamri BeyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Imperative SentenceDocument3 pagesSyllabus: Imperative SentenceDewantiNo ratings yet
- Ba219 Week 1-5Document24 pagesBa219 Week 1-5Flor, Ma. Sophia - 2101No ratings yet
- Who Decides What Art MeansDocument1 pageWho Decides What Art MeansJuliaNo ratings yet
- Discussion Phrases GuideDocument2 pagesDiscussion Phrases GuideRoderick Balce100% (1)
- Infancy and Toddlerhood FinalDocument4 pagesInfancy and Toddlerhood Finalapi-447499660No ratings yet
- Final Lesson Sce320Document10 pagesFinal Lesson Sce320marlenacolsherNo ratings yet
- Assessment Focus of Project-Based LearningDocument1 pageAssessment Focus of Project-Based LearningEddie Mamusog Awit100% (1)
- SDENG3J Assignment 1Document13 pagesSDENG3J Assignment 1Jonèl MareeNo ratings yet
- Doctex 1Document2 pagesDoctex 1nwahlian5270No ratings yet
- Year 7 English Portfolio AboveDocument31 pagesYear 7 English Portfolio AboveRomeo AvilesNo ratings yet
- Sylvia Plath in The Eyes of Modern TherapyDocument11 pagesSylvia Plath in The Eyes of Modern TherapyMike ZillNo ratings yet
- Administrative Leadership and Its ApplicationDocument49 pagesAdministrative Leadership and Its ApplicationRamirez RJNo ratings yet