Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bonds. Corporate Bonds Raise Funds For A Company Who Run Out of Cash To Develop New Products, Cover
Uploaded by
Mounicha AmbayecOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bonds. Corporate Bonds Raise Funds For A Company Who Run Out of Cash To Develop New Products, Cover
Uploaded by
Mounicha AmbayecCopyright:
Available Formats
Like governments, corporations also borrow money by issuing bonds.
These bonds are called corporate
bonds. Corporate bonds raise funds for a company who run out of cash to develop new products, cover
immediate expenses, and fund construction of new projects. In the context of U.S, corporate bonds are
typically sold at a paramount of $1000 and companies pay bondholders a predetermined amount of
interest payments usually on a semi-annual basis as mentioned in the video. In terms of interest payment,
corporate bonds do not share the same potential tax advantage as municipal or government bonds and do
not have the backing of the full faith and credit by the government. Moreover, corporate bonds are
typically seen as riskier securities, so they usually have higher interest rates to compensate for this
additional risk but to compensate for this disadvantage, corporate bonds generally offer higher yields than
government securities.
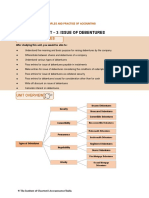
Perhaps one of the basics of corporate bonds that I also significantly learned was its two general types.
Below is a diagram that shows my understanding on the categories under corporate bonds and how each
works based from the video:
CORPORATE BONDS
Secured Bonds vs. Unsecured Bonds
are are
backed by some asset of value that the are not backed by any distinct physical
issuer can use as a security or collateral collateral but rather the credit of the issuer
and can be further claimed by thus they are given less priority in terms of
bondholders in case of default claims on assets than senior secured bonds
can be characterized as
some examples of
this type are
Debentures Subordinated
Mortgage Equipment Debentures
Collateral -are bonds which are
Trust
Bonds Trust Bonds Certificates unsecured by a -because of their
collateral. It is often lower precedence
-is a bond secured by -are secured bonds -the equipment in regarded as the other and subsequent
a mortgage on one or that are backed by this type of secured term for “unsecured credit risk, they may
more assets, typically the issuer’s bond serves as the bonds” itself offer higher yields
backed by real estate investment in other collateral and the
assets corporations titles of which are
held in trust until
debt has been repaid
to bondholders
You might also like
- Activity 3Document8 pagesActivity 3chibi.otaku.neesanNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Bonds and DebenturesDocument2 pagesDifference Between Bonds and DebenturesAhmed DanafNo ratings yet
- Doc-20231220-Wa0002. 20231220 232817 0000Document15 pagesDoc-20231220-Wa0002. 20231220 232817 0000Khushdeep Kaur KaurNo ratings yet
- Cream Neutral Minimalist Finance Basics Webinar Presentation 20231106 135405 0000Document13 pagesCream Neutral Minimalist Finance Basics Webinar Presentation 20231106 135405 0000gutierrezquilitmadelynNo ratings yet
- Debt FinancingDocument52 pagesDebt FinancingJean Ashley Napoles AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Attributes: Corporate Finance InstrumentDocument2 pagesAttributes: Corporate Finance InstrumentShayan ZafarNo ratings yet
- Company Acc Unit 3Document39 pagesCompany Acc Unit 3Megha DevanpalliNo ratings yet
- 67188bos54090 Cp10u3Document31 pages67188bos54090 Cp10u3Pawan TalrejaNo ratings yet
- Performance Guarantees - Traps and PitfallsDocument3 pagesPerformance Guarantees - Traps and PitfallsWilliam TongNo ratings yet
- Issue of Debentures: UNIT - 3Document31 pagesIssue of Debentures: UNIT - 3Hansika ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Security AssetsDocument45 pagesSecurity AssetsLalita BarveNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Issue of Debentures: Learning OutcomesDocument30 pagesUnit 3: Issue of Debentures: Learning Outcomesashish malhotraNo ratings yet
- A Case For Senior LoansDocument20 pagesA Case For Senior LoansstieberinspirujNo ratings yet
- What Are Corporate Bonds?: Investor BulletinDocument6 pagesWhat Are Corporate Bonds?: Investor BulletinSangeetha ChandramohanNo ratings yet
- What Are Corporate Bonds?: Investor BulletinDocument6 pagesWhat Are Corporate Bonds?: Investor Bulletinkishore13No ratings yet
- Definition of BondDocument1 pageDefinition of BondjayubaradNo ratings yet
- Quasi EquityDocument2 pagesQuasi EquitypratikNo ratings yet
- DebenturesDocument12 pagesDebenturesNamrata DasNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapsDocument4 pagesCredit Default Swapsza_gabyNo ratings yet
- Master in Business Finance: Praloy Majumder Icai Mumbai May 2010Document38 pagesMaster in Business Finance: Praloy Majumder Icai Mumbai May 2010praloy66No ratings yet
- SecuritisationDocument31 pagesSecuritisationAbhishek MalikNo ratings yet
- Sources of Finance 156Document10 pagesSources of Finance 156Radha ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- FM 4B Debt Financing Activity CMMDocument12 pagesFM 4B Debt Financing Activity CMMKim EspinaNo ratings yet
- Debentures ForamDocument10 pagesDebentures ForamForamNo ratings yet
- WK 7.2 - Bond FeaturesDocument21 pagesWK 7.2 - Bond Featureshfmansour.phdNo ratings yet
- Bonds & Debentures: Presented By-Group 3 Deepak Pandey Shagun Sarib Shahbaaz Simran Shivam Pandey Iti SrivastavaDocument10 pagesBonds & Debentures: Presented By-Group 3 Deepak Pandey Shagun Sarib Shahbaaz Simran Shivam Pandey Iti Srivastavasarib shahbazNo ratings yet
- Debentures: Sowmya.L 2018258034Document14 pagesDebentures: Sowmya.L 2018258034mba tourismNo ratings yet
- CL Topic 6Document11 pagesCL Topic 6magdawaks46No ratings yet
- Corporate Bonds: Mortgage Bonds Are Used To Finance A Specific Project. For Example, ADocument2 pagesCorporate Bonds: Mortgage Bonds Are Used To Finance A Specific Project. For Example, ADummy GoogleNo ratings yet
- Debenture Vs Shares-2Document19 pagesDebenture Vs Shares-2nemewep527No ratings yet
- Central University of South Bihar: Debenture, Its Kind and Issues of DebentureDocument17 pagesCentral University of South Bihar: Debenture, Its Kind and Issues of DebenturePriyaranjan Singh100% (1)
- "Debenture Trustee" - Position, Powers and Duties - It Is The LawDocument13 pages"Debenture Trustee" - Position, Powers and Duties - It Is The LawRohitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Note On Financial InstrumentsDocument5 pagesNote On Financial InstrumentsVismay GharatNo ratings yet
- Debentures and BondsDocument13 pagesDebentures and BondsLakhan KodiyatarNo ratings yet
- Debentures and BondDocument16 pagesDebentures and Bondbishal bothraNo ratings yet
- Ifs PresentationDocument21 pagesIfs Presentationvanitha_gangatkarNo ratings yet
- BondsDocument9 pagesBondsSheethal RamachandraNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 6Document6 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 6niks525No ratings yet
- Fixed Income Chapter7Document34 pagesFixed Income Chapter7Sourabh pathakNo ratings yet
- Debentures 20231220 232420 0000Document15 pagesDebentures 20231220 232420 0000Khushdeep Kaur KaurNo ratings yet
- SecuritizationDocument68 pagesSecuritizationPranav ViraNo ratings yet
- What Is A DebentureDocument11 pagesWhat Is A Debentureking gangsterNo ratings yet
- Tabulate The Different Type of Bonds and Identify Its Differences. Types of BondsDocument2 pagesTabulate The Different Type of Bonds and Identify Its Differences. Types of BondsgarbenNo ratings yet
- Securitization 130715232722 Phpapp01Document70 pagesSecuritization 130715232722 Phpapp01MRS.NAMRATA KISHNANI BSSSNo ratings yet
- Security Analysis and Portfolio Management: Valuation of BondsDocument28 pagesSecurity Analysis and Portfolio Management: Valuation of BondsFranklin ArnoldNo ratings yet
- 02 CorporationDocument8 pages02 CorporationEarl ENo ratings yet
- Group 4 Debt ManagementDocument31 pagesGroup 4 Debt ManagementVellaNo ratings yet
- Trust Guide: Features Uses Regulatory FrameworkDocument15 pagesTrust Guide: Features Uses Regulatory FrameworkSeun IdowuNo ratings yet
- Leac202 DebenturesDocument75 pagesLeac202 DebenturesMidhunidharNo ratings yet
- Credit Derivatives: CDS, CDO and CLO: SimplifiedDocument5 pagesCredit Derivatives: CDS, CDO and CLO: Simplifiedmani singhNo ratings yet
- DebenturesDocument3 pagesDebenturesAbhishek Raj100% (1)
- Chapter 14 Study GuideDocument7 pagesChapter 14 Study GuideStephanie RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Value of CollateralDocument1 pageValue of CollateralJude ConwayNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Financing: Debts: Financial Management Part IIDocument11 pagesLong-Term Financing: Debts: Financial Management Part IIKisha QuirozNo ratings yet
- Retail BankingDocument8 pagesRetail BankingClyncia PereiraNo ratings yet
- Bonds NotesDocument5 pagesBonds Notesjamie2rose4No ratings yet
- Asset Backing SecuririesDocument7 pagesAsset Backing Secuririesdisha2509No ratings yet
- Bonds Collateral Issuer Bondholders Debt: Debentures AreDocument2 pagesBonds Collateral Issuer Bondholders Debt: Debentures AreDeep DebnathNo ratings yet
- Pledge Vs Hypothecation Vs Lien Vs Mortgage Vs AssignmentDocument2 pagesPledge Vs Hypothecation Vs Lien Vs Mortgage Vs AssignmentLion Naresh PradhanNo ratings yet
- Safe Guarding Your Future: Financial Literacy How a Trusts Can Shield Your Assets & Reduce TaxesFrom EverandSafe Guarding Your Future: Financial Literacy How a Trusts Can Shield Your Assets & Reduce TaxesNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument2 pagesStatisticsMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- BuszDocument2 pagesBuszMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1Document2 pagesCase Problem 1Mounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Baking LawsDocument1 pageBaking LawsMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- RecommendationsDocument2 pagesRecommendationsMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Fact SheetDocument25 pagesFact SheetMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- AMBAYEC, Mounicha C.: 7km 30km/hr 7km 25km/hrDocument3 pagesAMBAYEC, Mounicha C.: 7km 30km/hr 7km 25km/hrMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- ScripDocument1 pageScripMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Beneficiality SpeechDocument2 pagesBeneficiality SpeechMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- FFFDocument57 pagesFFFMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- ES7 EssayDocument1 pageES7 EssayMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- HHHHHHHHDocument2 pagesHHHHHHHHMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Center?" or "Where Is The Best Location To Build An Ambulance Station?". Also, One of TheDocument2 pagesCenter?" or "Where Is The Best Location To Build An Ambulance Station?". Also, One of TheMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Reed 2 Biblical Exegesis Final Exam Online I. Multiple Choices (Answer With Letter Only)Document2 pagesReed 2 Biblical Exegesis Final Exam Online I. Multiple Choices (Answer With Letter Only)Ma. Kristine Laurice AmancioNo ratings yet
- Deportment: No. of Days Present in PracticesDocument2 pagesDeportment: No. of Days Present in PracticesMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.2: Luke 17:20-21Document3 pagesAssignment No.2: Luke 17:20-21Mounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Activity 1. Introduction and Overview of Financial Markets (Answers)Document2 pagesActivity 1. Introduction and Overview of Financial Markets (Answers)Mounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Given: EPS: PHP 2.75 Expected Growth: 25% P/E: 30 Times Earnings Solution: Next Year's EPSDocument3 pagesGiven: EPS: PHP 2.75 Expected Growth: 25% P/E: 30 Times Earnings Solution: Next Year's EPSMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- DDDDDDocument2 pagesDDDDDMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Finance Assignment SolvingDocument1 pageFinance Assignment SolvingMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Given: EPS: PHP 2.75 Expected Growth: 25% P/E: 30 Times Earnings Solution: Next Year's EPSDocument3 pagesGiven: EPS: PHP 2.75 Expected Growth: 25% P/E: 30 Times Earnings Solution: Next Year's EPSMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions: Non Depository DepositoryDocument3 pagesFinancial Institutions: Non Depository DepositoryMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Second, I Learned That Bonds Are Generally Perceived As Less Risky Alternative To Stocks and AreDocument2 pagesSecond, I Learned That Bonds Are Generally Perceived As Less Risky Alternative To Stocks and AreMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Pays To Keep Going Is The Most Relevant Write-Up On Our Topic About Business Ideas That AlmostDocument1 pagePays To Keep Going Is The Most Relevant Write-Up On Our Topic About Business Ideas That AlmostMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- GeDocument1 pageGeMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Kantian Critique ABDocument39 pagesKantian Critique ABMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- The Fulfillment of Being Able To Help Shape The Future of The World Whether It's A New Consumer Product, A ServiceDocument2 pagesThe Fulfillment of Being Able To Help Shape The Future of The World Whether It's A New Consumer Product, A ServiceMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Insights On Video 2: Financial InstrumentsDocument2 pagesInsights On Video 2: Financial InstrumentsMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Plaster Mold Making For Ceramic Industry: Name of InvestigatorDocument9 pagesPlaster Mold Making For Ceramic Industry: Name of InvestigatorMounicha AmbayecNo ratings yet
- Road NPV Irr AnalysisDocument403 pagesRoad NPV Irr AnalysisJay BadiyaniNo ratings yet
- 02.time Value of Money III and Risk and Return IDocument4 pages02.time Value of Money III and Risk and Return IMaithri Vidana Kariyakaranage100% (1)
- Overview of Financial System of BangladeshDocument18 pagesOverview of Financial System of BangladeshKazi Mahbubur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Script-Role Play-ProcurementDocument9 pagesScript-Role Play-ProcurementCruz Isaac Ken100% (3)
- NEGO (Hizon Notes)Document86 pagesNEGO (Hizon Notes)Bethany MangahasNo ratings yet
- Jim Chanos ImportantDocument40 pagesJim Chanos Importantkabhijit04No ratings yet
- Who Is On The Other Side?: Antti IlmanenDocument65 pagesWho Is On The Other Side?: Antti IlmanenaptenodyteNo ratings yet
- Stata Bankscope IMPORTANTDocument27 pagesStata Bankscope IMPORTANTSaad A W HussainNo ratings yet
- Economic Value AddedDocument25 pagesEconomic Value AddedDipen Ashokkumar KadamNo ratings yet
- FM - Valuation of Bond and StocksDocument10 pagesFM - Valuation of Bond and StocksMaxine SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Equity ValuationDocument33 pagesChapter 13 Equity Valuationsharktale2828No ratings yet
- Arvind Fashions IC ICICI Sec 19jun19Document23 pagesArvind Fashions IC ICICI Sec 19jun19chetankvoraNo ratings yet
- Mba Mba Batchno 158Document78 pagesMba Mba Batchno 158Moheed UddinNo ratings yet
- BehaviourDocument86 pagesBehaviouroscu0802100% (1)
- Master of Business Administration - Semister - 1 Mb0041 - Fianncial Management Accounting SET - 2Document10 pagesMaster of Business Administration - Semister - 1 Mb0041 - Fianncial Management Accounting SET - 2Asha JyothiNo ratings yet
- Carryover TransactionsDocument2 pagesCarryover Transactionsmindreadur3No ratings yet
- Research WorkDocument74 pagesResearch Workm.com22shiudkarsudarshanNo ratings yet
- St. Mary'S University Business Faculty Department of AccountingDocument56 pagesSt. Mary'S University Business Faculty Department of Accountingmustafe ABDULLAHINo ratings yet
- Conceptual FrameworkDocument23 pagesConceptual FrameworkKelvin MasekoNo ratings yet
- Adam Talmadge ResumeDocument1 pageAdam Talmadge ResumeSt. Bonaventure Students in Money ManagementNo ratings yet
- Nautica V YumulDocument3 pagesNautica V YumulPauline CarilloNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Employers ' Liability Insurance (A)Document1 pageCertificate of Employers ' Liability Insurance (A)Vincent JohnNo ratings yet
- Investing in Precious MetalsDocument37 pagesInvesting in Precious MetalsSomaSorrowNo ratings yet
- Road Map To Prosperity: Book ReviewDocument3 pagesRoad Map To Prosperity: Book ReviewRaghubalan DurairajuNo ratings yet
- AFAR QuizDocument18 pagesAFAR QuizHans Even Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Council's EmailsDocument366 pagesCouncil's EmailsMax LondbergNo ratings yet
- Chap 005 StudentsDocument24 pagesChap 005 StudentsAlex BenyayevNo ratings yet
- For Money Transfer Service Scheme (MTSS)Document2 pagesFor Money Transfer Service Scheme (MTSS)Parimi VeeraVenkata Krishna SarveswarraoNo ratings yet
- OO0519Document16 pagesOO0519Anonymous 9eadjPSJNgNo ratings yet
- Sanjay BakshiDocument38 pagesSanjay BakshimarsulexNo ratings yet