Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Causes of Voice Disorder
Uploaded by
lnzzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Causes of Voice Disorder
Uploaded by
lnzzCopyright:
Available Formats
1/3
Causes of Voice Disorder
Most voice disorders and laryngeal pathologies will have contributions from more
than one etiologic factor and that there is considerable overlap among these three
groupings. For example, inappropriate vocal behaviors or excessive vocal demands
may generate organic pathology (e.g., polyps or nodules). Psychological trauma or
excessive emotional stress may accompany the onset of spasmodic dysphonia.
Any disturbances in the physiologic balance of vocal subsystems (Respiratory
system, phonation system, and resonance system) may lead to voice disturbances.
A) Functional misuse or abuse of the voice components
(Respiration, phonation, resonance, pitch, loudness, and
rate):
Vocal hyperfunction may be characterized by intermittent periods of laryngeal area
tension, as may occur when someone shouts or clears the throat (1).
1) Inappropriate respiration:
o Reduced respiratory support
2) Inappropriate phonation:
o Glottal attacks
o Glottal fry
o Breathy phonation
3) Inappropriate resonance:
4) Inappropriate pitch:
o Using too low pitch
o Using too high pitch
5) Inappropriate loudness
o Using too loud voice
o Using too soft voice
6) Functional causes (2):
1) Diplophonia
2) Falsetto
3) Vocal Fold thickening
4) Functional aphonia
5) Functional dysphonia
6) Muscle tension
7) Nodules
8) Phonation breaks
9) Pitch breaks
Dr.Hani Abdulsattar Shaker
Medical Speech & Swallowing Disorders
2/3
10) Polyps
11) Reinke's edema
12) Traumatic laryngitis
13) Ventricular dysphonia
B) Pathological causes:
1) Congenital:
o Laryngomalacia
o Laryngeal web
2) Trauma:
o Thermal and chemical burns
o Swallowing of sharp objects
o Gastroesophageal reflux
o Laryngeopharyngeal reflux
o Vocal abuse and misuse.
o Puberphonia/ Mutational Falsetto Persistence of high pitched voice
beyond the age at which voice change is expected to have occurred.
o Phonation and pitch breaks
3) Infections:
o Viral laryngitis
o Bacterial laryngitis
o TB
o Fungal laryngitis
4) Allergic laryngitis
5) Tumor
o Vocal nodules
o Vocal polyps
o Reinke's edema/ polypoid degeneration
o Vocal cord granulomas/ contact ulcer
o Vocal cord cyst
o Laryngeal papilloma
o Squamous cell cancer of the larynx
o Hemangioma
o Laryngeal adenoma
o Hyperkeratosis
o Leukoplakia
6) Neuromuscular:
o Vocal folds paralysis
o Spasmodic dysphonia
Dr.Hani Abdulsattar Shaker
Medical Speech & Swallowing Disorders
3/3
o Velopharyngeal weakness
o Paralysis and Ankylosis
o Spastic Dysarthria
o Ataxic Dysarthria
o Paradoxical Vocal Folds Motion (PVFM)
o Myasthenia Gravis
o Cerebrovascular accident
o Parkinson's disease
o Essential tremor
o Multiple Sclerosis
o Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
7) Endocrine:
o Hypothyroidism (myxedematous laryngitis)
o Sex hormone imbalance
o Pubertal changes
8) Drug effects:
9) Miscellaneous:
o Vocal cord atrophy
o Vocal cord scarring
o Muscle tension dysphonia
o Medications (Anti-histamine – Anti-depressant – Large Vitamine C
doses)
o Presbylaryngis (age-related voice changes)
o Subglottic and tracheal stenosis
o Zenker's diverticula
o Barrett's esophagus
o Sulcus vocalis
o Contact ulcers
C) Psychogenic Voice Disorders
Works Cited
1. Stemple, J.C., Glace, L. and Klaben, P.B. Survey of voice management. Clinical Voice
Pathology: Theory and Management. 3rd. San Diego : Singular Publishing Group, 2000, pp.
312-314.
2. Shipley, K.G. and McAfee, J.G. Assessment of Voice and Resonance. Assessment in
Speech-Language Pathology: A Resource Manual. 3rd. Clifton Park : Thomson Learning Inc,
2004.
Dr.Hani Abdulsattar Shaker
Medical Speech & Swallowing Disorders
You might also like
- 3 - The Resonance Tube Method in Voice Therapy PDFDocument7 pages3 - The Resonance Tube Method in Voice Therapy PDFFonoaudiologiaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Dysphonia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Dysphonia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Aging Voice: Presented by Anastasia Serbalik Presented To Rebecca L. Gould, MSC, CCC-SLPDocument32 pagesThe Aging Voice: Presented by Anastasia Serbalik Presented To Rebecca L. Gould, MSC, CCC-SLPAtri AmmuluNo ratings yet
- Voice Disorders: AIISH - ProjectDocument16 pagesVoice Disorders: AIISH - ProjectnepmistNo ratings yet
- Damaging Vocal TechniquesDocument20 pagesDamaging Vocal TechniquesDevi Suriani100% (1)
- Hoarseness-Causes and TreatmentsDocument33 pagesHoarseness-Causes and TreatmentsSatrio WisnugrohoNo ratings yet
- AAO-HNSF Primary Care Otolaryngology HandbookDocument121 pagesAAO-HNSF Primary Care Otolaryngology HandbookCary DeeNo ratings yet
- Voicedisordersinthe Elderly: Karen M. Kost,, Robert T. SataloffDocument13 pagesVoicedisordersinthe Elderly: Karen M. Kost,, Robert T. SataloffFernanda MerichesNo ratings yet
- Sample Blank AudiogramDocument1 pageSample Blank AudiogramPeter SalimNo ratings yet
- Occupational Noise Exposure: A Review of Its Effects, Epidemiology, and Impact With Recommendations For Reducing Its BurdenDocument28 pagesOccupational Noise Exposure: A Review of Its Effects, Epidemiology, and Impact With Recommendations For Reducing Its BurdenRizal KendariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication Sciences and Disorders (Weismer) - Rehabilita ShopDocument411 pagesIntroduction To Communication Sciences and Disorders (Weismer) - Rehabilita ShopRomian ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Thorax and Lungs SGDocument2 pagesThorax and Lungs SGDestinee Caple100% (1)
- DISARTRIADocument4 pagesDISARTRIACamy Alejandra Gonzales GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Vocal Polyps and NodulesDocument11 pagesVocal Polyps and NodulesAyu Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- ENT For Entrance Exams - S. Buchiraja PDFDocument442 pagesENT For Entrance Exams - S. Buchiraja PDFBharat G90% (20)
- Voice Disorder 2011 PDFDocument6 pagesVoice Disorder 2011 PDFfaidgustisyarifNo ratings yet
- The Aging Voice and Differentiating Diseases: Laurie KozlakowskiDocument19 pagesThe Aging Voice and Differentiating Diseases: Laurie KozlakowskiJaviera Cortés MoralesNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Infection in ChildrenDocument70 pagesAcute Respiratory Infection in Childrenmayadwintas100% (1)
- Voice DisordersDocument6 pagesVoice DisorderssulnaikNo ratings yet
- Neurogenic Disorders of The LarynxDocument37 pagesNeurogenic Disorders of The LarynxSyaffira SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Voice and Speech DisordersDocument2 pagesVoice and Speech DisordersVishal Gaurav100% (1)
- Ear DisordersDocument7 pagesEar DisordersGéorel John Colonia GoteraNo ratings yet
- ENT Exam-TZAR DOHNS Report 2011-860056v1-UbayasiriDocument2 pagesENT Exam-TZAR DOHNS Report 2011-860056v1-Ubayasirinob2011nob0% (1)
- Sulcus Vocalis Our Experience-DikonversiDocument5 pagesSulcus Vocalis Our Experience-DikonversiNuni SukindarNo ratings yet
- Obstruktive Sleep ApneaDocument29 pagesObstruktive Sleep ApneaEfri SyaifullahNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Macarambon, FDDocument5 pagesCase Study - Macarambon, FDUmar MacarambonNo ratings yet
- Clinicopathological Study of Change of Voice: ST THDocument10 pagesClinicopathological Study of Change of Voice: ST THAshokNo ratings yet
- Dysphonia: The Voice of Change: Phonation 63Document3 pagesDysphonia: The Voice of Change: Phonation 63Ali Arridha MolahellaNo ratings yet
- Mezze Dim I 2016Document8 pagesMezze Dim I 2016Marcos ChuquiagoNo ratings yet
- Common Voice DisordersDocument33 pagesCommon Voice DisordersMedic PresentNo ratings yet
- Does Voice Therapy Cure All Vocal Fold Nodules?: Ijopl IjoplDocument5 pagesDoes Voice Therapy Cure All Vocal Fold Nodules?: Ijopl IjoplDesi Ratnasari EndangNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Voice - Disorders2Document20 pages2.3 Voice - Disorders2Fernanda MerichesNo ratings yet
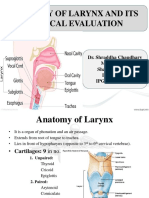
- Anatomy of Larynx and Its Clinical EvaluationDocument43 pagesAnatomy of Larynx and Its Clinical Evaluationshraddha chaudhary100% (2)
- Voice Disorders: by Dr. Baseem N. AbdulhadiDocument23 pagesVoice Disorders: by Dr. Baseem N. AbdulhadiAli Abd AlrezaqNo ratings yet
- Hoarseness: What Is The Voice Trying To Tell You?Document5 pagesHoarseness: What Is The Voice Trying To Tell You?lancealiuNo ratings yet
- Ent Clinical ExaminationDocument7 pagesEnt Clinical ExaminationKhalid MahidaNo ratings yet
- Presbycusis: J. R. Kearns, MDDocument5 pagesPresbycusis: J. R. Kearns, MDnick_mdNo ratings yet
- Hoarseness-Causes and TreatmentsDocument33 pagesHoarseness-Causes and TreatmentsbestaNo ratings yet
- Current Concepts: Review ArticleDocument7 pagesCurrent Concepts: Review ArticleMia Mia MiaNo ratings yet
- T1 Classification Manual For Voice Disorders IDocument14 pagesT1 Classification Manual For Voice Disorders IJacqueline muñozNo ratings yet
- Review For ENT (2008 Batch)Document9 pagesReview For ENT (2008 Batch)HaslinNo ratings yet
- Multi-Site Diagnosis and Management of 260 Patients With Auditory Neuropathy - Dys-Synchrony (Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder)Document15 pagesMulti-Site Diagnosis and Management of 260 Patients With Auditory Neuropathy - Dys-Synchrony (Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder)Ailin TosiNo ratings yet
- Speech-In-Noise Perception in High-Functioning Individuals With Autism or Asperger's SyndromeDocument8 pagesSpeech-In-Noise Perception in High-Functioning Individuals With Autism or Asperger's SyndromeYahoska TijerinoNo ratings yet
- Stuttering With SoundDocument12 pagesStuttering With SoundTeresa CarrascosaNo ratings yet
- Vocal Fold Self-Disruption After Phonotrauma On A Lead Actor: A Case PresentationDocument7 pagesVocal Fold Self-Disruption After Phonotrauma On A Lead Actor: A Case PresentationJean Carlo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Collaboration and Conquest MTD As Viewed by Voice Teacher (Singing Voice Specialist) and Speech-Language PathologisDocument6 pagesCollaboration and Conquest MTD As Viewed by Voice Teacher (Singing Voice Specialist) and Speech-Language PathologisClaudia TorresNo ratings yet
- Dysarthria - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument10 pagesDysarthria - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfdaohailongNo ratings yet
- Loge Mann 1978Document11 pagesLoge Mann 1978bencicovakikaNo ratings yet
- Final 641 NodayDocument9 pagesFinal 641 Nodaynatalie nodayNo ratings yet
- Meniers DsDocument59 pagesMeniers DsAnurag SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Communication and Swallowing Disorders (Speech)Document27 pagesCommunication and Swallowing Disorders (Speech)Asma JamaliNo ratings yet
- Ventricular PhonationDocument2 pagesVentricular PhonationKevin CrossNo ratings yet
- Speech Disorders: Presented byDocument32 pagesSpeech Disorders: Presented byHafsa SajjadNo ratings yet
- Accent Method of Voice Therapy For Treatment of Severe Muscle Tension DysphoniaDocument4 pagesAccent Method of Voice Therapy For Treatment of Severe Muscle Tension DysphoniaChrisNo ratings yet
- Clinical Characteristics and Voice Analysis of Patients With Mutational Dysphonia: Clinical Significance of Diplophonia and Closed QuotientsDocument8 pagesClinical Characteristics and Voice Analysis of Patients With Mutational Dysphonia: Clinical Significance of Diplophonia and Closed Quotientsmariola_joplinNo ratings yet
- J Jfludis 2010 05 001 PDFDocument11 pagesJ Jfludis 2010 05 001 PDFAdriana GarciaNo ratings yet
- Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology: College of Health Sciences School of Medical SciencesDocument25 pagesKwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology: College of Health Sciences School of Medical SciencesEmmanuel DanquahNo ratings yet
- Northwestern Medicine Benign Vocal Lesions PDFDocument5 pagesNorthwestern Medicine Benign Vocal Lesions PDFHata MujadzicNo ratings yet
- JOURNAL CLINICAL ManggalaDocument24 pagesJOURNAL CLINICAL ManggalaEndika CahyoNo ratings yet
- Allucination DeafDocument3 pagesAllucination Deaftamora86No ratings yet
- Taste Disorders: DR - Abdullah Alhayani, MBBSDocument33 pagesTaste Disorders: DR - Abdullah Alhayani, MBBSalhayaniNo ratings yet
- Nikolaus Ronald Indra 4Document137 pagesNikolaus Ronald Indra 4Florence StellaNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument2 pagesSpeechJuliana Valentina Tellez SuarezNo ratings yet
- Vocal Improvement After Voice Therapy in Unilateral Vocal Fold ParalysisDocument6 pagesVocal Improvement After Voice Therapy in Unilateral Vocal Fold ParalysisAngela Lleuful ToledoNo ratings yet
- DEAFNESS, TINNITUS, VERTIGO AND NEURALGIA. Archives of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, 46Document35 pagesDEAFNESS, TINNITUS, VERTIGO AND NEURALGIA. Archives of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, 46dcipledudeNo ratings yet
- V PhysiologyDocument0 pagesV PhysiologyWaqar Ahmed AwanNo ratings yet
- Benign Vocal Fold Mucosal DisordersDocument3 pagesBenign Vocal Fold Mucosal DisordersAnish RajNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduciton To PhonaitrcsDocument21 pages1 - Introduciton To Phonaitrcsibn.emaraNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Otolaryngolo GY: DR Surya Prakash D R Associate Professor of Ent Ramaiah Medical CollegeDocument85 pagesGeriatric Otolaryngolo GY: DR Surya Prakash D R Associate Professor of Ent Ramaiah Medical CollegeSurya Prakash D RNo ratings yet
- 1514 Treatment of Functional Voice Disorders Historical Perspective and Clinical ApproachesDocument40 pages1514 Treatment of Functional Voice Disorders Historical Perspective and Clinical ApproachesJuan CarlosNo ratings yet
- Rhinologic and Sleep Apnea Surgical Techniques 1st Ed 2007 SDocument427 pagesRhinologic and Sleep Apnea Surgical Techniques 1st Ed 2007 SKarolina RamirezNo ratings yet
- Ent Recommended Reading ListDocument1 pageEnt Recommended Reading Listpredrag_maksimovichNo ratings yet
- Marques 2021Document5 pagesMarques 2021LORENZO GABRIEL BANAYONo ratings yet
- Hearing.: NameDocument3 pagesHearing.: NameDuyBùiNo ratings yet
- Acoustical and Perceptual Characteristics of Alaryngeal SpeechDocument59 pagesAcoustical and Perceptual Characteristics of Alaryngeal SpeechKUNNAMPALLIL GEJO JOHN100% (1)
- Bài Ktra NG Âm 1 k5 LýDocument8 pagesBài Ktra NG Âm 1 k5 LýpmquyetNo ratings yet
- Absensi Daring Kelompok G Stase THTDocument7 pagesAbsensi Daring Kelompok G Stase THTAlifia PutriNo ratings yet
- Cu 10 (Ncma111)Document2 pagesCu 10 (Ncma111)Arjay VerdejoNo ratings yet
- Nervous Co-Ordination: Life SciencesDocument10 pagesNervous Co-Ordination: Life SciencesLeboNo ratings yet
- Paediatric OtorhinolaryngologyDocument37 pagesPaediatric OtorhinolaryngologySana BushraNo ratings yet
- Resp System KoleyaDocument96 pagesResp System KoleyaAlberto MeroNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH Presentation Speech MechanismDocument22 pagesENGLISH Presentation Speech MechanismGaurav Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- ENT Prelims TransDocument45 pagesENT Prelims TransRaven CocjinNo ratings yet
- Otoacoustic EmissionsDocument3 pagesOtoacoustic EmissionsAnish RajNo ratings yet
- 2019 - Hearing Loss in The CommunityDocument50 pages2019 - Hearing Loss in The CommunityVaenusha MuruganNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology: Maam Mehak Munawer HOD Language and Literature Hajvery University (HU)Document26 pagesPhonetics and Phonology: Maam Mehak Munawer HOD Language and Literature Hajvery University (HU)Zainab Ajmal ZiaNo ratings yet
- W6 Ome - THTDocument4 pagesW6 Ome - THTStevanie SesiliaNo ratings yet
- Chranjivi HospitalsDocument12 pagesChranjivi HospitalsRATI RAMNo ratings yet
- Hearing Impairment: HistoryDocument3 pagesHearing Impairment: HistoryNorence BuenoNo ratings yet