Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pediatric Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Yes No
Uploaded by
Ratna TambaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pediatric Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Yes No
Uploaded by
Ratna TambaCopyright:
Available Formats
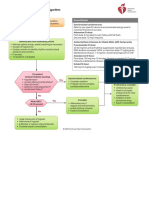
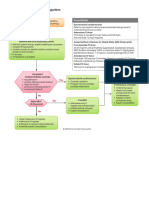
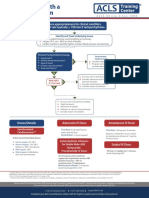
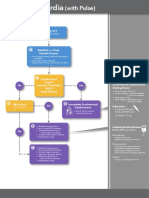
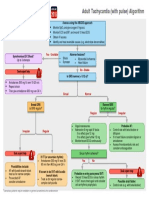
Pediatric Tachycardia With a Pulse Algorithm
Initial assessment and support Doses/Details
• Maintain patent airway; assist breathing as necessary Synchronized
• Administer oxygen cardioversion
• Cardiac monitor to identify rhythm; monitor pulse, Begin with 0.5-1 J/kg;
blood pressure, and oximetry if not effective, increase
• IV/IO access to 2 J/kg. Sedate if
• 12-Lead ECG if available needed, but don’t delay
cardioversion.
Drug Therapy
Probable sinus
tachycardia if Adenosine IV/IO dose
Evaluate rhythm
• P waves present/normal • First dose: 0.1 mg/kg
with 12-lead ECG
• Variable RR interval rapid bolus (maximum:
or monitor. 6 mg)
• Infant rate usually <220/min
• Child rate usually <180/min • Second dose:
0.2 mg/kg rapid bolus
(maximum second
dose: 12 mg)
Cardiopulmonary
Search for
compromise?
and treat cause. Yes No
• Acutely altered
mental status
• Signs of shock
• Hypotension
Narrow Wide Narrow Wide
(≤0.09 sec) (>0.09 sec) (≤0.09 sec) (>0.09 sec)
Evaluate Evaluate
QRS duration. QRS duration.
Probable supraventricular Possible ventricular Probable supraventricular Possible ventricular
tachycardia tachycardia tachycardia tachycardia
• P waves absent/abnormal • P waves absent/abnormal
• RR interval not variable • RR interval not variable
• Infant rate usually ≥220/min • Infant rate usually ≥220/min
• Child rate usually ≥180/min • Child rate usually ≥180/min
• History of abrupt rate change Synchronized • History of abrupt rate change If rhythm is regular and
cardioversion QRS monomorphic,
Expert consultation consider adenosine.
is advised before
additional drug
• If IV/IO access is present, therapies. Consider
give adenosine vagal maneuvers.
or Expert consultation
• If IV/IO access is not is recommended.
available, or if adenosine
is ineffective, perform
synchronized cardioversion If IV/IO access
is present, give
adenosine.
© 2020 American Heart Association
You might also like
- 10 Effective Ayurvedic Treatment For Hair LossDocument9 pages10 Effective Ayurvedic Treatment For Hair Lossrpav77No ratings yet
- Cardioversion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Types, Treatment of Arrhythmias And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCardioversion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Types, Treatment of Arrhythmias And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Doses/DetailsDocument1 pageAdult Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Doses/DetailsAlexis HospitalNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Tools: Doses, Routes, and Uses of Common DrugDocument1 pagePharmacological Tools: Doses, Routes, and Uses of Common DrugApuntesdemedicinaa blogNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide: Exploratory Course On Household ServicesDocument5 pagesCurriculum Guide: Exploratory Course On Household ServicesJovanni Mancao PodadorNo ratings yet
- 3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates CombinedDocument5 pages3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates Combinedamanrup randhawa100% (1)
- "Mode One" Author & Dating Coach Alan Roger Currie Releases Criticism of Alleged Harvey Weinstein BehaviorDocument3 pages"Mode One" Author & Dating Coach Alan Roger Currie Releases Criticism of Alleged Harvey Weinstein BehaviorPR.com100% (1)
- CHEQUERED PLATE - Engineer DiaryDocument9 pagesCHEQUERED PLATE - Engineer DiaryAnonymous imkwF8N7TeNo ratings yet
- PM PillarDocument56 pagesPM PillarNavneet Sharma75% (4)
- FPC Manual PreviewDocument5 pagesFPC Manual PreviewIbrahim Levent AkkoyunluNo ratings yet
- Construction Quality Control PlanDocument35 pagesConstruction Quality Control PlanMalik Riaz100% (4)
- Unit Weight of Materials Used at Construction Site - Online Civil PDFDocument2 pagesUnit Weight of Materials Used at Construction Site - Online Civil PDFKeshav VarpeNo ratings yet
- I. Leadership/ Potential and Accomplishments Criteria A. InnovationsDocument5 pagesI. Leadership/ Potential and Accomplishments Criteria A. InnovationsDEXTER LLOYD CATIAG100% (1)
- With A Pulse and Poor Perfusion: Pediatric TachycardiaDocument1 pageWith A Pulse and Poor Perfusion: Pediatric TachycardiaIin-Ignasia Diahayujulindah Mujiman0% (1)
- Pediatric Bradycardia With A Pulse AlgorithmDocument1 pagePediatric Bradycardia With A Pulse AlgorithmRatna TambaNo ratings yet
- Pals TachycardiaDocument1 pagePals TachycardiadarlingcarvajalduqueNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac ArrestDocument1 pageAdvanced Cardiac ArrestDebbie MeyerNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612Document1 pageAlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612must dietNo ratings yet
- Website Tachycardia Algorithm DiagramDocument1 pageWebsite Tachycardia Algorithm Diagramcolette zgheibNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Doses/DetailsDocument1 pageAdult Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Doses/DetailsZakiyahulfahdwNo ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument1 page2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmRyggie ComelonNo ratings yet
- Assess Appropriateness For Clinical Condition. Heart Rate Typically 150/min If TachyarrhythmiaDocument1 pageAssess Appropriateness For Clinical Condition. Heart Rate Typically 150/min If TachyarrhythmiaSiti Nur R Firda FauziyahNo ratings yet
- Managemen Disritmia: Dr. Rofika Hanifa, SPPDDocument20 pagesManagemen Disritmia: Dr. Rofika Hanifa, SPPDavivlabirdNo ratings yet
- Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument1 pageTachycardia AlgorithmGideon BahuleNo ratings yet
- Algo Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageAlgo Tachycardia PDFYudhistira AdiNo ratings yet
- 26) Approach To Pediatric ArrhythmiasDocument44 pages26) Approach To Pediatric ArrhythmiasJude AlyousefNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument37 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life SupportRoy Acosta GumbanNo ratings yet
- Algo Pals TachycardiaDocument1 pageAlgo Pals TachycardiaArdie FratamaNo ratings yet
- Tachycardia AlgorythmDocument1 pageTachycardia AlgorythmUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- 5.ALS Algorithms TachycardiaDocument1 page5.ALS Algorithms TachycardiaMassimo Di BenedettoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Bradycardia With A Pulse and Poor Perfusion AlgorithmDocument1 pagePediatric Bradycardia With A Pulse and Poor Perfusion AlgorithmRadhiatul MardhiahNo ratings yet
- Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Assess Appropriateness For Clinical ConditionDocument1 pageTachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Assess Appropriateness For Clinical ConditionDendy Frannuzul RamadhanNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmACLStachycardiawithapulse PDFDocument1 pageAlgorithmACLStachycardiawithapulse PDFDendy Frannuzul RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Algoritmos AHA ACLS AdultoDocument4 pagesAlgoritmos AHA ACLS AdultoChristianFelipePorrasCastroNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmsDocument16 pagesAlgorithmsirish laglevaNo ratings yet
- Onlinemeded Notes CardioDocument1 pageOnlinemeded Notes CardioCourtney HolbrookNo ratings yet
- ALS Algorithms LS Tachycardia 2.0Document1 pageALS Algorithms LS Tachycardia 2.0Lucian Alin DinuNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612Document1 pageAlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612YassarNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument7 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromePuskesmas Pinang JayaNo ratings yet
- Bradycardia AlgorithmDocument1 pageBradycardia AlgorithmGideon BahuleNo ratings yet
- Pals Pediatric BradycardiaDocument1 pagePals Pediatric BradycardiadarlingcarvajalduqueNo ratings yet
- Periarestne AritmijeDocument10 pagesPeriarestne AritmijeMustafa ŠabićNo ratings yet
- Algo Bradycardia DikonversiDocument5 pagesAlgo Bradycardia DikonversiDaniel SitungkirNo ratings yet
- Ecgs and Acute Cardiac Events: Yuniardi Alriyanto, MD Doris Sylvanus Hospital PalangkarayaDocument47 pagesEcgs and Acute Cardiac Events: Yuniardi Alriyanto, MD Doris Sylvanus Hospital PalangkarayaAuliaRusdiAllmuttaqienNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia Case PresentationDocument23 pagesPediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia Case Presentationapi-602288180No ratings yet
- AdultTachycardiaWithPulse AlgorithmDocument1 pageAdultTachycardiaWithPulse AlgorithmIsmail SlimNo ratings yet
- Algoritma Ambulance - PHCDocument11 pagesAlgoritma Ambulance - PHCYassarNo ratings yet
- .JPG 958×1,280 PixelsDocument1 page.JPG 958×1,280 Pixelsyordanos getachewNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityChris LeeNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityAlexis HospitalNo ratings yet
- Algorithms of AHA 2020Document23 pagesAlgorithms of AHA 2020Emirhan llkhanNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2565-05-03 at 10.34.19Document39 pagesScreenshot 2565-05-03 at 10.34.19Sugus PichayaNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia (With Pulse) AlgorithmDocument1 pageAdult Tachycardia (With Pulse) AlgorithmJames ChoiNo ratings yet
- PALS - Cardiac DistrDocument26 pagesPALS - Cardiac DistrRich AdamsNo ratings yet
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFibbs91No ratings yet
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFPlabber JuneNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Cardiac Medications 1231855169882073 2Document1 pageMicrosoft Word Cardiac Medications 1231855169882073 2api-19824701No ratings yet
- 12-Adult Post Resuscitation Care Algorithm 2021Document1 page12-Adult Post Resuscitation Care Algorithm 2021khaledNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Exam 2 - Lecture Notes: Treating Adult BradycardiaDocument5 pagesCardiology Exam 2 - Lecture Notes: Treating Adult BradycardiaAddieNo ratings yet
- ACLS Tachycardia Algorithm For Managing Stable TachycardiaDocument4 pagesACLS Tachycardia Algorithm For Managing Stable TachycardiaLady MuffinsNo ratings yet
- PALS - Rhythm Disturbance 02Document27 pagesPALS - Rhythm Disturbance 02Rich AdamsNo ratings yet
- Agent For Treating Heart FailureDocument26 pagesAgent For Treating Heart FailureClarisse SuanNo ratings yet
- Adult CardDocument1 pageAdult CardIvan MoralesNo ratings yet
- ACLS - Guidelines From 2005USADocument62 pagesACLS - Guidelines From 2005USAsbontchevNo ratings yet
- Acls Study Guide 2016Document2 pagesAcls Study Guide 2016Caridad RodasNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Algorithm: Yes NoDocument1 pagePediatric Cardiac Arrest Algorithm: Yes NoRatna TambaNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmNeonatal Resuscitation 200615Document1 pageAlgorithmNeonatal Resuscitation 200615Ratna TambaNo ratings yet
- Components of Post-Cardiac Arrest Care Check: Oxygenation and VentilationDocument1 pageComponents of Post-Cardiac Arrest Care Check: Oxygenation and VentilationRatna TambaNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmNeonatal Resuscitation 200615Document1 pageAlgorithmNeonatal Resuscitation 200615Ratna TambaNo ratings yet
- How To Stratify The Risk and When To Refer: NsteacsDocument28 pagesHow To Stratify The Risk and When To Refer: NsteacsRatna TambaNo ratings yet
- ABF Indonesia Bond Index Fund 1607481426838 827566Document1 pageABF Indonesia Bond Index Fund 1607481426838 827566Ratna TambaNo ratings yet
- How To Stratify The Risk and When To Refer: NsteacsDocument28 pagesHow To Stratify The Risk and When To Refer: NsteacsRatna TambaNo ratings yet
- LF1325LC 装机准备要求 LF1325LC installation requirementsDocument12 pagesLF1325LC 装机准备要求 LF1325LC installation requirementsEliasDraNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae (CV) - Design-AM-KAWSAR AHMEDDocument5 pagesCurriculum Vitae (CV) - Design-AM-KAWSAR AHMEDEngr.kawsar ahmedNo ratings yet
- Pin ContentDocument20 pagesPin ContentSwetha100% (2)
- Laboratory Report No.1Document6 pagesLaboratory Report No.1mary hemarNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 10 1 Grading Examination: E. Modern NationalismDocument3 pagesMapeh 10 1 Grading Examination: E. Modern NationalismMildred Abad SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Green Rating System - Ritik JainDocument6 pagesGreen Rating System - Ritik Jainmayuresh barbarwarNo ratings yet
- Brook Health Care Center Inc Has Three Clinics Servicing TheDocument1 pageBrook Health Care Center Inc Has Three Clinics Servicing Thetrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- PF700 Components Replacement (Frame 7)Document56 pagesPF700 Components Replacement (Frame 7)Jael molano avilaNo ratings yet
- PROD - Section 1 PDFDocument1 pagePROD - Section 1 PDFsupportLSMNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis Problem SetDocument6 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis Problem Setpalms thatshatterNo ratings yet
- EO MNC 10 June 2022Document4 pagesEO MNC 10 June 2022LeulaDianneCantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 - Bleeding Tendency DiseasesDocument64 pagesLecture 16 - Bleeding Tendency Diseasesapi-3703352100% (1)
- Mitra SejatiDocument2 pagesMitra Sejatiestu kurniaNo ratings yet
- Greetings: HVAC Design of Commercial Buildings With TESDocument49 pagesGreetings: HVAC Design of Commercial Buildings With TESchitradevipNo ratings yet
- Trump ReportDocument237 pagesTrump ReportAaron Nobel100% (1)
- DMD 2018 Stem and Non Stem Checklist Effective 2020-2021Document8 pagesDMD 2018 Stem and Non Stem Checklist Effective 2020-2021Elle DyNo ratings yet
- Geared Motor Device 100/130V E1/6-T8Document2 pagesGeared Motor Device 100/130V E1/6-T8seetharaman K SNo ratings yet
- Pulse Production in India: Major Constraints and Way ForwardDocument33 pagesPulse Production in India: Major Constraints and Way ForwardDeus EXNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001: 2015 Certified Semen Freezing LaboratoryDocument43 pagesISO 9001: 2015 Certified Semen Freezing LaboratoryShubhamNo ratings yet
- Itopride HCL Pynetic 50mg TabDocument2 pagesItopride HCL Pynetic 50mg TabAusaf AhmadNo ratings yet
- 1402AHS Prac Manual - 2023 - FINALDocument200 pages1402AHS Prac Manual - 2023 - FINALRuan BritsNo ratings yet