0% found this document useful (0 votes)
182 views1 pageBradycardia Management Algorithm
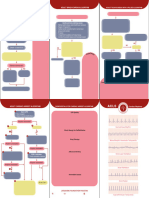
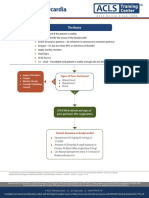
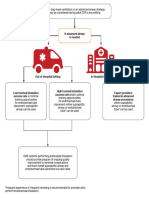
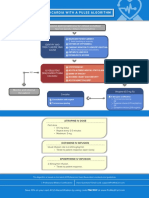
This document provides an algorithm for managing bradycardia in adults and pediatrics. It outlines steps for airway, breathing, circulation, establishing IV access, performing ECG and identifying causes of instability. For unstable adult bradycardia it recommends atropine or adrenaline. For unstable pediatric bradycardia it recommends starting CPR and administering adrenaline or atropine. It also lists alternative treatments and notes when specialist advice should be sought.
Uploaded by
Gideon BahuleCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
182 views1 pageBradycardia Management Algorithm
This document provides an algorithm for managing bradycardia in adults and pediatrics. It outlines steps for airway, breathing, circulation, establishing IV access, performing ECG and identifying causes of instability. For unstable adult bradycardia it recommends atropine or adrenaline. For unstable pediatric bradycardia it recommends starting CPR and administering adrenaline or atropine. It also lists alternative treatments and notes when specialist advice should be sought.
Uploaded by
Gideon BahuleCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd