0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views6 pagesMotion Graphs KEY
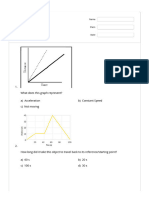
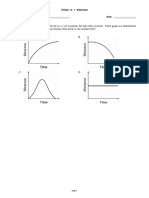
The document provides information about using graphs to represent motion, including distance-time graphs and speed-time graphs. It discusses how to interpret various graph shapes, such as horizontal lines representing constant speed or no motion, upward curving lines representing acceleration, and downward sloping lines representing deceleration. Examples of graphs are presented and matched to descriptions of motion. Practice problems at the end ask students to interpret graphs of runners in a race and changes in a bus's speed over time.
Uploaded by
spenyebeyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views6 pagesMotion Graphs KEY
The document provides information about using graphs to represent motion, including distance-time graphs and speed-time graphs. It discusses how to interpret various graph shapes, such as horizontal lines representing constant speed or no motion, upward curving lines representing acceleration, and downward sloping lines representing deceleration. Examples of graphs are presented and matched to descriptions of motion. Practice problems at the end ask students to interpret graphs of runners in a race and changes in a bus's speed over time.
Uploaded by
spenyebeyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Motion Graphs: Introduces the concept of motion graphs, explaining the basics and how to interpret axes.
- Distance-Time Graphs: Explains the interpretation and analysis of distance-time graphs with examples and graphical illustrations.
- Speed-Time Graphs: Examines speed-time graphs, showing how to read and interpret changes in speed graphically.