Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cost/effort in Collecting The Data: Frequency
Uploaded by
Sudarshan Gopal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageOriginal Title
7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageCost/effort in Collecting The Data: Frequency
Uploaded by
Sudarshan GopalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
weak position.
If the largest competitor had a share of only 5%, the ratio would be
4:1, implying that the brand owned was in a relatively strong position, which might
be reflected in profits and cash flows. If this technique is used in practice, this scale
is logarithmic, not linear.
Frequency
Usually measured annually but perhaps more frequently in fast-moving markets.
Source of the data
The figures required to calculate the relative market share of a company can usually
be sourced from annual reports or market research that has been carried out.
Cost/effort in collecting the data
Costs and effort for collecting market share can be very high, especially in those
cases where no good-quality data are available and market research has to estab-
lish baseline data. Benchmark data are available in many industries but this can
also be expensive. The lowest costs for collecting data are incurred when the data
are readily available.
Target setting/benchmarks
Targets can be gleaned from existing market research. Benchmarks can be gleaned
from articles etc. that explain how other organisations secured high relative market
share positions.
Example Consider the following example concerning small urban cars. As a
starting point for making the relative market share calculation, we describe the
performance of the key players:
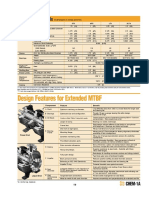
Units sold Revenue (thousands Market
(thousands) of US dollars) share
Zipper 25 375,000 40%
Twister 10 200,00 21.3%
A-One 7.5 187,500 20%
Bowlz 5 125,000 13.3%
L
2 8 R EL AT I V E M A R K ET S H A R E 135
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- All Dimensions in Inches and (MM)Document1 pageAll Dimensions in Inches and (MM)Sudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- Optimized Conversions Using RSMDocument3 pagesOptimized Conversions Using RSMSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- E.I. Dupont Reg. Trademark LTX Power End Features Duplex Angular ContactDocument1 pageE.I. Dupont Reg. Trademark LTX Power End Features Duplex Angular ContactSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- How Do I Measure It?: Data Collection MethodDocument1 pageHow Do I Measure It?: Data Collection MethodSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- SulfidationDocument5 pagesSulfidationSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- General Map OVHDDocument1 pageGeneral Map OVHDSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- HW+ 6'dpdjh%olvwhulqj+,&62+,&66&Document6 pagesHW+ 6'dpdjh%olvwhulqj+,&62+,&66&Sudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- Alloy % Notes: TandardDocument1 pageAlloy % Notes: TandardSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- Brine CorrosionDocument3 pagesBrine CorrosionSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- 5Document1 page5Sudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- Section 5-Design: 5.1 GeneralDocument1 pageSection 5-Design: 5.1 GeneralSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- 4-10 Api S 620: Group IDocument1 page4-10 Api S 620: Group ISudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- Table 4-1-Minimum Requirements For Plate Specifications To Be Used For Design Metal TemperaturesDocument1 pageTable 4-1-Minimum Requirements For Plate Specifications To Be Used For Design Metal TemperaturesSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- SSN College of Engineering - Association of Chemical Engineers (ACE) Annual Academic Report - 2018-2019Document1 pageSSN College of Engineering - Association of Chemical Engineers (ACE) Annual Academic Report - 2018-2019Sudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- Vani Institute Gate/Ies: Chemical - Ii Duration: 3Hrs Maximum Marks: 100Document9 pagesVani Institute Gate/Ies: Chemical - Ii Duration: 3Hrs Maximum Marks: 100Sudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- Remarks 2019-2020 Term IIDocument8 pagesRemarks 2019-2020 Term IISudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- Speciality and EconomicsDocument3 pagesSpeciality and EconomicsSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet