Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3b - Water Pollution and Wastewater Treatment
Chapter 3b - Water Pollution and Wastewater Treatment
Uploaded by
Lionel Messi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views7 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views7 pagesChapter 3b - Water Pollution and Wastewater Treatment
Chapter 3b - Water Pollution and Wastewater Treatment
Uploaded by
Lionel MessiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
EP326/EE304
EP317/EG202
Environmental Engineering
Chapter 3b: Water Pollution &
Wastewater Treatment
‘roared by Dr Thang Weng,
a
Learning Outcome
Week 6
+ Outline the water quality management
+ Impact of pollutant to environment and human
+ Propose Wastewater treatment technologies
+ Pre-treatment
+ Primary Treatment
+ Secondary Treatment
+ Tertiary Treatment
Outline
Week 6
+ Sources And Classification Of Water Pollstants
+ Water Quality Parameter
+ Physical
+ Chemical
+ Biological
+ Water Quality Control Policy
+ Impact Of Pollutant To Environment And Human
+ Wastewater Trestment Technologies
+ Provtreatment
+ Primary Treatment
+ Seoondary Treatment
+ Tertiary Treatment
+ Water 4.0
Water Quality Management
‘The strategies and measures to be taken towards an effective
‘management of water resources, pollution control and
prevention of environmental degradation:
1. Legislation
2. Prevention
3. Water Pollution Sources and Control
4. Non-Point Pollution and its Control
5, Erosion and Sediment Control
6. River quality monitoring
1. Legislation
+ Restitions on plltion finland waters [Section 25, BQA 1974]
+ Prohibition of escharge of ol into Malysian waters [Section 27, BQA 1974]
Prohibition of aacharge of wate into Malaysian waters [Setin 29, EQA 1974]
+ CONTROL OF WATER POLLUTION FROM AGRO-BASED INDUSTRY
19 (Licensing) Reg.2977
129 (Preseribed Premises) (Crude Palos Ol) Reg. 1977
HQ ¢Preseribed Premises) (Raw Natural Rubber) Reg. 1978
+ CONTROL OF WATER POLLUTION FROM MUNICIPAL & INDUSTRIAL
WASTEWATER
+ EQ ladustrialEuent) Reg 2009
HQ (Sewage) Regulations 2009,
129 (Control of Pollution from Slid Waste Trancfer Station & Landi)
3. Water Pollution Sources and Control
+ Agreed industrler panic pala! ed to taletre WW cet ate
‘pens teipenee erate opine shade protacion watson
woteroultonin oder rece water lation tr he inde abo we eure
esp the pen elation and sie 80 4001 Creation
Sewage Dispos and Sewerage Works Sones mor plete Pe
compas on ahd maa serge es end sea spel int oat soe
Sullage(Gep-Water - WH fom exenadrine mea
each chon ik, aroma, wingman, stra we are and at
ig arr -1s big err Gorter nicer lag guts cf Winters
hats orice Dagrteigfrming rut arrests ene opr etal
fe WW acre fr eon
2. Prevention
+ thes974Hvirunmental Quality Ae Seton 944 Arepor on input onthe
‘environment rom prescribed actives (HLA requirement is mandatory
Preeribed actives that can case water potion inde airport, housing inst,
‘ining, petroleum, power generation, resol and recreational develope a wale
tweaunent nd lol faces,
Fornon-prescrite activi, ste stability evaluation to assess the capacity ofthe
area ecie elite] pollen oe ane reqirrco! for wet: Capea is
eed
+The vironmental Quality (Sewage and Industrial Een) Regulations 1979 ko
rosie that writen permission be obtained before the constriction of ny bling ot
| eaeying out any work that may es inne source of fuer or discharge
4. Non-Point Pollution and its Control
+ sinvlvesthe best management practice in conto te pain
+ Agricultura runoff-Good agieshurl parties to manag acti such peste
spsyng, eng.
Forestry ranoff- ood forestry peat to mine sol uso ad sation,
estbiation of team banks
rom plant ap, iting wept le lng cto and oan
‘wens wherever ese ond revegetation practic to npr verter quay
5. Erosion and Sediment Control
+ Brsinisthe detachment of prion of he sa src. This can gcur yc tbe
{pe ef coe ory the tarot Roving aren a Phe
Sent tat cape the it my vet ner en or weld and change the
Sarat cla terbed.
+ Erosion Conte
+ restive tbiaion (rs se)
raion conto Banta
+ elias
+ Seiment Contos
sateen,
+ ompost es sss
+ aa drain inet poeton
seine sein basins —
Water Quality Index
6. River Quality Monitoring
+ To detect changes in iver water quality on a continvous bass
+ Parameters monitored: DO, NH4, NH3, Conductivity, Turbidity, Salinity,
PH, Temperature, Time,
+ Water quality levels exceeding the ambient standard for specific
sd real-time to DOE
parameters willbe trans
+ Immediate inspection will be conducted at suspected sites.
Impacts of Water Pollution
+ ieases: In hutans, dking or consuming poled walerin ay ty sy
isso fects on oar hth teases typhoid chery, hepa and various ther
secs
+ Destrction of Feneystems: Econ are arene dynamic and rapt rea
‘alee uochecked
+ Butrophication: Chemis ina ater bry, ncournge the growth algae, Thee algae
form layer ontop ofthe pod or ake. acted on thie and this ceases tbe
aroun: of xpath waterbody, severely afoing the aquatic if thee
1 Effect the food chain: Disrpin‘n fat chins agpen whe in and polls ie
‘he waterae consume by agua nina, ella el which ar tbe conse by
mans. ——
Wastewater Treatment Process Selection
1 ep pi tote spe ei,
dreams mieeindsrerecrabete trie esr,
Bee etree
Satcher eer eet
‘lesiclameendomard (COD), hema oxygen dciand (BOD), al upended
‘ots CSS) lol itroger C1) and wl phosporeas
5 Inleat WW characteristic: Th caster ofthe fen ft the ype othe
Doors: tbe sed (Cem of ioe ad the reqeneat othe Pope,
4 limi constrains: Tempers fs ihr ofan th cen
Papen erecta pee create eee
‘Sts panda recy are Roe Soe ea i
i reer genet
Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies
4. Pre-treatment-Sereening and grit removal take out relatively large
floating and suspended debris andthe sand and grit that settles very
rapidly which may damage equipment.
2. Primary Treatment: Settling or claifcation removes the prtiles
that wil sett out by savy alone within afew hours
3. Secondary Treatment- Typically achieved by using biological
‘process to breakdown the degradable organie pollutants
4. Tertiary Treatment: Disinfection, Membrane filtration, Carbon
adsorption, Nutrient removal (* and N)
Wastewater Treatment Process Selection
6, Process Slang Restor singe ed om prow
‘Maestros
absent or pt pla is
cst Data for renton
rived aston expen of
Peerireereeeted Cnetreeee Ene eerestal tes ete reree pest nee
‘Specialy wher odors produced: Recving water ay hav speil ian,
‘egret ol moval oer ensues sath = mac
‘8, Flexibility in operation: The bly of he proceso wok nacre! ond it
oa Saag
‘9. Simple operation and maintenance: Spl opting or malnenare requirements
‘hola betonnenes
20, Reliab: What th ger elit of ert operation? Lethe racen ey
“an? Cu and pede foe dng? pb tt oe ge of eae?
1%, Bcgomi: Inurl on operon i nents nt he pont
9 Land availability: saute space to econumode the fae? Any ber sone
sya: e ay
Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies
etemntserning Pppsin pr)
inary Train pede lope)
lone
Flow Diagram of Typical Water Treatment Plant Flow Diagram of Typical Water Treatment Plant
Art iz
4. Sexeening and grt removalist tive ag ting nd spend Secondary setling sow be fow enough otha vy wen he Bc
SSSR ale gt sts wry rps uy aage Secondary eto hota ay 5
ccunment
een eer eee
Pinup detinsion eng or creon) erie ian, ilionsenor pee
Ee
gee ep name iaae
Disinfection contact provides sufiient time fr the added dsinfetant to
Primary Treatment
Comino
Sedimentation
Surface Loading rate (SLR)
A ‘A~ total surface area of tank?
SLR isthe minimum setting velocity that a particle ean have and still
{uarantood to be removed inseting tank.
‘Hydraulic Retention Time (RT)
2av te HRT, br
t=—— = Diy flowrate, m/e
@ V=tankvolume, m
‘The time it takes fora drop of water to travel from inet to outlet
Coagulation and Flocculation
cxaqaaton Fncuatan Sadnetason =
+ Themost common method usd to remove patles and a portion of dissolved
orgie imbinaon of oegulton and focation lowed by
+ Coagulation i change nestaization step that involves the condoning of
the suspended, colodal, and dissolved matter by adding coagulans(elumn
ALGO).
+The purpose of coagulant isto neutralize the surface charge, thus allowing the
particles to come together to form sight ager parties (micrftoe) hat ean be
ore cally removed
‘ai can disperse the coagulant propery and promote partie
ions, which are needed to achieve good coagulation,
In Class Practice : Sedimentation
‘The average flowrate ata small municipal wastewater treatment plant is
20000 m/d. The highest observed peak daly lowrate is 50000 m°/d.
Design a rectangular primary clarifier with a channel width of 2m, Use
surface loading rat of 4om’/m:d with side water depth of am. a) Compute
the hydraulic retention time, b) Determine the detention time and surface
loading rate at peak flow.
Coagulation and Flocculation
Nt
Seems
loceultion, a gentle mixing stage and aggregate the destabilized parties by
increasing the partis size rom submieroscoptemlcro-foc ovale lager
parties now a8 oc
"loc sie continues to ulld with addtional collsions and interaction with
‘edd inorganic polymers (coagulant) or organte polymers
‘Once flac ha eache it optimum size and strength, waters ready for
High mixing velocity may cause the flo tearing apart oF shearing. Once flocs
ar torn ape sic to get them to reformat ther optima sie and
Stent
Coagulation and Flocculation
oe
oc go.
What have we learned?
+ Outline the water quality management
+ Impact of pollutant to environment and human.
+ Propose Wastewater treatment technologies
Pretreasment-Srenng (Phil partie)
1 Barra Conn paris)
1 comminttr Rene of parle)
Rotary Drom Fine parses).
Primary Treatment (Supended als Onpnie mater)
4 Ghies eimetation)
ap ming Caglaton by drag of congas)
4 Recession
Lime-Soda Softening
‘The objective isto precipitate the cleum and the magnesium in the water
TInonde to preiptate clei, the pH ofthe water must be raised to about
103.
‘To precipitate magnesiom, the pH must be raised to about 1
Calcium Hydroxide, Ca(OH, lie) and Sodium carbonate, Na,SO, (soda) are
‘commonly used for softening the hard water,
0, Guo Cop 40
(Go Fane rex 2006 +210
spa; enom= #0 + 240
uf eo = DCR +)
“raeoye encoun
Sec sg
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Butterworths Journal of International Banking andDocument68 pagesButterworths Journal of International Banking andLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Fluid Properties of Natural Gas, Oil and WaterDocument20 pagesReservoir Fluid Properties of Natural Gas, Oil and WaterLionel Messi100% (1)
- Lecture 8 Sufrace Tenstion-Wettabilitty-Capillary Pressure-COMPLETEDDocument16 pagesLecture 8 Sufrace Tenstion-Wettabilitty-Capillary Pressure-COMPLETEDLionel MessiNo ratings yet
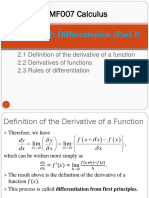
- Chapter 2: Differentiation (Part I) : MF007 CalculusDocument44 pagesChapter 2: Differentiation (Part I) : MF007 CalculusLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10-1 Basic Reservoir Fluid & Phase BehaviourDocument21 pagesLecture 10-1 Basic Reservoir Fluid & Phase BehaviourLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- MF007 Tutorial 5 DifferentiationDocument2 pagesMF007 Tutorial 5 DifferentiationLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- X y X X y y X y y X Y: Mf007 Calculus Tutorial 2Document1 pageX y X X y y X y y X Y: Mf007 Calculus Tutorial 2Lionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Fluid Saturation - COMPLETEDDocument10 pagesLecture 7 Fluid Saturation - COMPLETEDLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- MF007 Chapter 3 Integration Part I StudentsDocument58 pagesMF007 Chapter 3 Integration Part I StudentsLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Mb104 - Calculus and Analytical Geometry For Applied Sciences Chapter 2: Limits and Continuity Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesMb104 - Calculus and Analytical Geometry For Applied Sciences Chapter 2: Limits and Continuity Review QuestionsLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Limits & Continuity: MF007 CalculusDocument50 pagesChapter 1: Limits & Continuity: MF007 CalculusLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- MF007 Chapter 2 Differentiation Part IIDocument38 pagesMF007 Chapter 2 Differentiation Part IILionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 AlkanesDocument37 pagesChapter 2 AlkanesLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Eg208 Topic 2-Mineralogy P1 28052020Document29 pagesEg208 Topic 2-Mineralogy P1 28052020Lionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Software Installation Guide eBN2Document166 pagesSoftware Installation Guide eBN2Lionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Noise PollutionDocument39 pagesChapter 2 - Noise PollutionLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Casing Setting Depth SelectionDocument32 pagesLesson 7 Casing Setting Depth SelectionLionel Messi100% (1)
- The Annotated BibliographyDocument14 pagesThe Annotated BibliographyLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- C3 - 6 Uniform Acc MotionDocument34 pagesC3 - 6 Uniform Acc MotionLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- C1 - 4 Newton Laws and FrictionDocument38 pagesC1 - 4 Newton Laws and FrictionLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- C2 - 5 Torque and Simple MachinesDocument45 pagesC2 - 5 Torque and Simple MachinesLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Scalar Quantities: Chapter ObjectivesDocument56 pagesVectors and Scalar Quantities: Chapter ObjectivesLionel MessiNo ratings yet