Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sector 2
Sector 2
Uploaded by
xilox67632Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sector 2
Sector 2
Uploaded by
xilox67632Copyright:
Available Formats
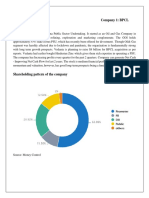
Sector Project 2: Oil & Gas
This analysis is from the perspective of an entrepreneur looking to setup a business in this industry.
Bargaining Power of Buyers: It can be measured based on number of buyers in the business, the
availability of alternatives, switch over costs and the impact of buyers in the cost and quality.
India’s energy need is projected to double to 1,516 Million Tonnes of Oil Equivalent by 2035
from 700.50 Million Tonnes of Oil Equivalent in 2015. Oil PSUs primarily dominate the segment
with almost 85% market share. The PSUs leverage their extensive network and operate on wafer
thin margin. For customer, energy is an essential commodity hence they have little power to
affect the price of fuels. However, India being the world’s fourth-largest energy consumer, the
oil companies have a higher ability to influence price and quality from their suppliers.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers: It can be evaluated based on the number of suppliers,
accessibility of substitutes for suppliers or vendors of manufacturers, influence of suppliers in
cost and quality and the industry in which supplier is operating. India is highly dependent on
non-renewable resources for energy demand. To meet these demands the companies import
vast quantities of fuel from a relatively small group of nations. Together, these groups of
countries like OPEC determine the prices and quantity of fuel to be produced. Since, we are
highly dependent on these nations, the suppliers have higher negotiation power.
Rivalry among Existing Competitors: Industry rivalry among existing competitors can be
assessed by the number of competitors, product differentiation, industry growth rate,
substitution costs involved and the strategic stakes of the producers· A relatively small number
of players control the Indian Oil & Gas segment. Since the margins are lower, these players are
highly competitive.
Threat of Substitutes Products: There is growing concern over the global warming and we are
one of the largest consumers of crude oil contribute significantly to it. Some Nordic countries
have shifted to complete EV setup. Similarly, India is trying to leverage renewable resources due
to its strategic location. Hence the threat of substitution is high.
Threat of New Entrants: The new entrants bring new capability and a yearning to gain market
share which adds pressure on current prices, costs, and the investment rate needed to compete
in an industry. The extent of present entry barriers determines the threat of entry. The entry
barriers comprise the factors like Economies of Scale, Brand uniqueness, Product Distinction,
customer Switch Over Costs, Capital requirement; access to technology, raw material and
distribution channels; and Government policies. Oil & Gas is highly capital and infrastructure
intensive business. The significant players today in India are PSUs who have developed
infrastructure over the years. Hence the threat of new entrant is low.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- ATPL Notes - ElectricsDocument23 pagesATPL Notes - ElectricsMoslem Grimaldi100% (3)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lab Manual-Manomety Lab Experiment PDFDocument12 pagesLab Manual-Manomety Lab Experiment PDFcheeball100% (1)
- Brain-A-Lytics 3.0 Case: A One-Stop Career CatalystDocument5 pagesBrain-A-Lytics 3.0 Case: A One-Stop Career Catalystxilox67632No ratings yet
- Crompton Greaves Consumer ElectricalDocument6 pagesCrompton Greaves Consumer Electricalxilox67632No ratings yet
- Crompton GreavesDocument6 pagesCrompton Greavesxilox67632No ratings yet
- Sector 2: Oil & Gas Company 1: BPCL General OverviewDocument5 pagesSector 2: Oil & Gas Company 1: BPCL General Overviewxilox67632No ratings yet
- Sector 2: Oil & Gas Company 2: Gujarat Gas LTD General OverviewDocument6 pagesSector 2: Oil & Gas Company 2: Gujarat Gas LTD General Overviewxilox67632No ratings yet
- Sector 1: Manufacturing Company 1: Vaibhav Global LTD General OverviewDocument6 pagesSector 1: Manufacturing Company 1: Vaibhav Global LTD General Overviewxilox67632No ratings yet
- 14 Prok - Dvs - Brouchure 2006Document2 pages14 Prok - Dvs - Brouchure 2006sceptersangramNo ratings yet
- Toshiba VFS9Document12 pagesToshiba VFS9PùbùdùPathirathnaNo ratings yet
- Curso Cat 950-962G Steering Syst STMGDocument24 pagesCurso Cat 950-962G Steering Syst STMGSilas F Pimenta100% (18)
- Electric ConversionDocument32 pagesElectric Conversionroger1papeshNo ratings yet
- MENG THESIS-BISMARK ANANE - Master File PDFDocument101 pagesMENG THESIS-BISMARK ANANE - Master File PDFPadala AmarnathNo ratings yet
- 9701 s16 QP 41Document20 pages9701 s16 QP 41ابرارفاروقNo ratings yet
- IEEE STD C57 - MaintenanceDocument5 pagesIEEE STD C57 - MaintenanceGILI RELIABILITYNo ratings yet
- Wiring: Handbook On LayoutDocument3 pagesWiring: Handbook On LayoutSathyakumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- UV and Its Effect On Plastics - An Overview - Knowledge Centre - Essentra Components UKDocument11 pagesUV and Its Effect On Plastics - An Overview - Knowledge Centre - Essentra Components UKMurari KumarNo ratings yet
- Chris Van Den Broeck - Alcubierre's Warp Drive: Problems and ProspectsDocument6 pagesChris Van Den Broeck - Alcubierre's Warp Drive: Problems and ProspectsHerftezNo ratings yet
- David L Ellis Resume 2007Document2 pagesDavid L Ellis Resume 2007dleoelNo ratings yet
- Trout TurbineDocument2 pagesTrout TurbinepdfscrNo ratings yet
- DieselNet Technology GuideDocument5 pagesDieselNet Technology Guidealoksemail2011No ratings yet
- EX Pro Repeater ManualDocument2 pagesEX Pro Repeater ManualmotaNo ratings yet
- Solar Tracking System: Abstract-The Solar Photovoltaic Panels Are Used To GenerateDocument4 pagesSolar Tracking System: Abstract-The Solar Photovoltaic Panels Are Used To GenerateAdrian Ebero NunezNo ratings yet
- NI PXI-4110 Specifications: Triple-Output Programmable DC Power SupplyDocument8 pagesNI PXI-4110 Specifications: Triple-Output Programmable DC Power SupplyDonnaNo ratings yet
- Catalogue VERS. 4.14Document172 pagesCatalogue VERS. 4.14smail blNo ratings yet
- Catalog 07 08Document172 pagesCatalog 07 08ikervaldesNo ratings yet
- EOR. Termal MethodsDocument2 pagesEOR. Termal MethodsMukhtarov Pg100% (1)
- Specify Gain and Phase Margins On All Your Loops: Venable Technical Paper # 2Document6 pagesSpecify Gain and Phase Margins On All Your Loops: Venable Technical Paper # 2vimaleviNo ratings yet
- Airframe 100 InspectionDocument7 pagesAirframe 100 InspectionAndres RosasNo ratings yet
- Pathfinder WBJEE 2014 Physics SolutionDocument12 pagesPathfinder WBJEE 2014 Physics SolutionafasdfasdNo ratings yet
- Fuji Lm2a Errors 1Document1 pageFuji Lm2a Errors 1Pim KoedijkNo ratings yet
- Transformer Protection - 1Document51 pagesTransformer Protection - 1Naveed Rabbani100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - ElectrochemistryDocument66 pagesChapter 4 - ElectrochemistryNa Ru ToNo ratings yet
- ABCB and SF6 CBDocument12 pagesABCB and SF6 CBNikunj AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Scheme of WorkDocument3 pagesScheme of WorkEiyra AmieyraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 30A UCLA Fall 2009 Midterm Exam II KEY: On My Honor, I Have Neither Given Nor Received Any Aid On This ExamDocument7 pagesChemistry 30A UCLA Fall 2009 Midterm Exam II KEY: On My Honor, I Have Neither Given Nor Received Any Aid On This ExamViceregalNo ratings yet