Professional Documents
Culture Documents
π) + cos (60πt − 1) ?: X (2) = j3 and X (12) = −j3, respectively. a) What is the frequency in Hz of the component with
Uploaded by
Marabatalha McOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
π) + cos (60πt − 1) ?: X (2) = j3 and X (12) = −j3, respectively. a) What is the frequency in Hz of the component with
Uploaded by
Marabatalha McCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Prova de Processamento Digital de Sinais - 04/maio/2011 - UFPA/PPGEE
" #
1 5
1. Given a matrix A = design a unitary matrix B that is similar to A in the sense that
−1 3
its first basis (column) is a vector in the same direction as [1, −1]T .
2. What are the Fourier series coefficients for the signal x(t) = 10 + 4 sin(400πt + π/2) + 3 cos(20πt +
π) + cos(60πt − 1)?
3. A right-sided signal has Laplace transform X(s) = 5/(s2 + 3s + 2), with ROC σ > −1. Calculate:
a) X(s)|s=2+2j , b) if the corresponding Fourier transform X(Ω) exists, |X(Ω)| for Ω = π rad/s.
4. What is the Z transform X(z) of the signal x[n] = 2δ[n + 1] + 5δ[n − 4], including the ROC?
What are the values of X(z) for z = 0, −1 and z = 2ejπ/2 ? If the DTFT of x[n] exists, what are its
values for ω = 0 and π rad?
5. The bilateral Fourier series of a real signal x(t) with period T0 = 4 s has four non-zero coefficients.
Assume that c1 = 2e−j2 and c3 = 4ej3 . What is the expression for x(t)?
6. Prove the expression for the Z transform of x[n] = 0.7n u[n] − 0.8n u[−n − 1], indicating the ROC.
Does this signal have a DTFT?
7. Carefully draw the graph of the imaginary part of the DTFT of y[n] = 2 + 3ejπn for the range
−3π ≤ ω ≤ 3π.
8. What are the forward AH and inverse A matrices for a 4-points orthonormal DFT?
9. A signal x[n] has Z transform X(z) = (8z 2 + 3z + 1)/((z − 0.7)(z − 0.8)), with ROC |z| > 0.8.
Find x[n].
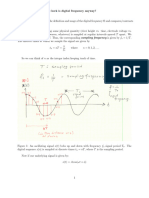
10. Consider that a periodic x(t) was sampled with Fs = 10 Hz, obeying the sampling theorem. A
12-points FFT was calculated using M atlab/Octave and the output X was normalized by N = 12.
The only non-zero coefficients were k = 0, 1 and 11, corresponding to the elements of X[1] = 2,
X[2] = j3 and X[12] = −j3, respectively. a) What is the frequency in Hz of the component with
largest power of x(t)? b) what is the average (DC) value of x(t)? c) what is the spacing in Hz between
neighboring elements of X? d) what is the maximum frequency found in x(t)?
11. There are four Fourier pairs for analyzing continuous and discrete-time signals: a) Fourier
transform, Fourier series, DTFT and DTFS (equivalent to the DFT). Provide the forward and inverse
equations for each pair and indicate the unit in frequency domain assuming that the unit in time is
Volts.
12. Using the orthogonality condition of the basis functions carefully prove the pair of Fourier series
equations. Indicate the assumptions in each step.
You might also like
- Mathematical Statistics and Data Analysis 3rd Edition - Chapter6 Solutions PDFDocument17 pagesMathematical Statistics and Data Analysis 3rd Edition - Chapter6 Solutions PDFnewpersia86% (7)
- ME 360, Fall 2021 Problem Set 5 Due at 3PM Monday, Oct 4Document2 pagesME 360, Fall 2021 Problem Set 5 Due at 3PM Monday, Oct 4Rounak ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Department of Electronic and Information EngineeringDocument4 pagesThe Hong Kong Polytechnic University Department of Electronic and Information EngineeringNiaz ManikNo ratings yet
- DtftproblemsDocument2 pagesDtftproblemsJeremiash ForondaNo ratings yet
- EC341 2018 MidDocument1 pageEC341 2018 MiddevNo ratings yet
- Analog Signal Processing Tutorial 2: Sampling and ReconstructionDocument12 pagesAnalog Signal Processing Tutorial 2: Sampling and ReconstructionDuy Ngô Phạm ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- 18EC504 Scheme of Evalueation Digital Signal Processing: FEB, 2021 Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument14 pages18EC504 Scheme of Evalueation Digital Signal Processing: FEB, 2021 Electronics & Communication EngineeringMaheshkumar McNo ratings yet
- Lab2-Spectral Analysis in MatlabDocument14 pagesLab2-Spectral Analysis in MatlabindameantimeNo ratings yet
- DigicomDocument2 pagesDigicomjohn alNo ratings yet
- Ss Model 2 2016 - SchemeDocument2 pagesSs Model 2 2016 - SchemeKaustubha ShahNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Ece, Eie)Document2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Ece, Eie)vinod chittemNo ratings yet
- Systems and Signals Laplace Transform PracticeDocument4 pagesSystems and Signals Laplace Transform PracticeDr. DriftNo ratings yet
- DSP AssignmentDocument10 pagesDSP AssignmentraviNo ratings yet
- AE06Document3 pagesAE06Sanjeev PanwarNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 DSP. Discrete Fourier TransformDocument16 pagesLab 3 DSP. Discrete Fourier TransformTrí TừNo ratings yet
- Component - UART V2.50Document11 pagesComponent - UART V2.50ANNAPUREDDY RAVINDER REDDYNo ratings yet
- Rr410201 Digital Signal ProcessingDocument1 pageRr410201 Digital Signal ProcessingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Lab I12Document8 pagesLab I12Lulzim LumiNo ratings yet
- EECS 250 Fall 2017 Homework 1: Due: Thu Oct 12 Before ClassDocument2 pagesEECS 250 Fall 2017 Homework 1: Due: Thu Oct 12 Before ClassTianxiang ZhengNo ratings yet
- InTech-Designing Antenna Arrays Using Signal Processing Image Processing and Optimization Toolboxes of MatlabDocument17 pagesInTech-Designing Antenna Arrays Using Signal Processing Image Processing and Optimization Toolboxes of MatlabAnonymous BbZceWkVnNo ratings yet
- Nr320402-Digital Signal ProcessingDocument8 pagesNr320402-Digital Signal ProcessingSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Lab 9Document9 pagesLab 9Ahtisham aliNo ratings yet
- 1 Unit 1: Ques No. UnitsDocument6 pages1 Unit 1: Ques No. Unitsrahulsaraswat_eceNo ratings yet
- DSP-1 (Intro) (S)Document77 pagesDSP-1 (Intro) (S)karthik0433No ratings yet
- TPO3: To Analyze and Implement Digital Signal Processing Systems in Time DomainDocument2 pagesTPO3: To Analyze and Implement Digital Signal Processing Systems in Time DomainKaushik SahaNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Inverse Filtering For High Accuracy Estimation of The Glottal SourceDocument8 pagesAdaptive Inverse Filtering For High Accuracy Estimation of The Glottal SourcePilar LirioNo ratings yet
- DSP Two MarksDocument33 pagesDSP Two MarksVijayendiran RhNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab ExptList 2020Document10 pagesDSP Lab ExptList 2020deepak raja.sekar.p.mNo ratings yet
- 9A04603 Digital Signal Processing16Document4 pages9A04603 Digital Signal Processing16Mahaboob SubahanNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks Questions & Answers: Cs-73 Digital Signal Processing Iv Year / Vii Semester CseDocument18 pages2 Marks Questions & Answers: Cs-73 Digital Signal Processing Iv Year / Vii Semester CseprawinpsgNo ratings yet
- Selective Problems For PracticeDocument5 pagesSelective Problems For PracticeBethlehem AbiyNo ratings yet
- DSP Question Bank IV CSE - Cs - 2403docDocument36 pagesDSP Question Bank IV CSE - Cs - 2403docSiva NandanNo ratings yet
- MT 2011 SolutionDocument6 pagesMT 2011 SolutionHashemAL-matariNo ratings yet
- Energy and Power Spectral DensitiesDocument11 pagesEnergy and Power Spectral DensitiesHurrem ArifNo ratings yet
- Spring/Summer 2016 Computer-Based Assignment # 4 Introduction To The Simulation of Signals and SystemsDocument5 pagesSpring/Summer 2016 Computer-Based Assignment # 4 Introduction To The Simulation of Signals and SystemsSelemon RetaNo ratings yet
- Final Syllabus Iiit Surat SecondyeareceDocument8 pagesFinal Syllabus Iiit Surat SecondyeareceKrishna MishraNo ratings yet
- Signal&Systems Review StudySetDocument3 pagesSignal&Systems Review StudySetIreth OronarNo ratings yet
- Rr320402-Digital Signal ProcessingDocument8 pagesRr320402-Digital Signal ProcessingSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Signals and System: Team: 1) Rohith S - 1DS20EC173 2) Phalgun M - 1DS20EC126 3) Rahul A K - 1DS20EC144Document13 pagesSignals and System: Team: 1) Rohith S - 1DS20EC173 2) Phalgun M - 1DS20EC126 3) Rahul A K - 1DS20EC144Amogh RNo ratings yet
- Matlab Exercises: IP Summer School at UW: 1 Basic Matrix ManipulationDocument6 pagesMatlab Exercises: IP Summer School at UW: 1 Basic Matrix ManipulationDierk LüdersNo ratings yet
- An FFT-based Spectral Analysis Method For Linear Discrete Dynamic Systems With Non-Proportional DampingDocument13 pagesAn FFT-based Spectral Analysis Method For Linear Discrete Dynamic Systems With Non-Proportional DampingBambang PiscesaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Practice SheetDocument2 pagesUnit 1 Practice SheetLingampalli AbhijithNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual For Digital Communications in PracticeDocument48 pagesSolutions Manual For Digital Communications in PracticecasdeaNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument101 pagesDigital Signal ProcessingDheekshith ShettigaraNo ratings yet
- The Multiscale Entropy Algorithm and Its Variantsentropy-17-03110Document14 pagesThe Multiscale Entropy Algorithm and Its Variantsentropy-17-03110Rodrigo VasconcelosNo ratings yet
- 3TR4 Exam 2015Document3 pages3TR4 Exam 2015RezaNo ratings yet
- Ece1004 Signals-And-systems Eth 2.0 39 Ece1004Document4 pagesEce1004 Signals-And-systems Eth 2.0 39 Ece1004Aryan VermaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1Sathwik MethariNo ratings yet
- Min Ex oDocument6 pagesMin Ex oamena ejazNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1Ashish KatochNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Communication Theory - 1 (EC5.203 - Spring 2021) January 16, 2021Document3 pagesAssignment 1: Communication Theory - 1 (EC5.203 - Spring 2021) January 16, 2021Jahnavi RameshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document153 pagesChapter 4zahra sakvandNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam2021 PartBDocument2 pagesComprehensive Exam2021 PartBAman GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 .... 1Document98 pagesChapter 4 .... 1FirewNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Spring 2011 Assignment # 3Document3 pagesDigital Signal Processing Spring 2011 Assignment # 3Haniya ElahiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2-1Document3 pagesAssignment 2-1opus2012No ratings yet
- Problem Sheets 1-9Document23 pagesProblem Sheets 1-9malishaheenNo ratings yet
- DSP 2020Document3 pagesDSP 2020nbg2006No ratings yet
- TDocument4 pagesTddsafdashfkjdsNo ratings yet
- DSP Ec1302 Parta & Part B Questions and Answers11Document33 pagesDSP Ec1302 Parta & Part B Questions and Answers11ohmshankar100% (2)
- CSE 383M / CS395T Midterm Exam Solution: 1 (20 Points)Document5 pagesCSE 383M / CS395T Midterm Exam Solution: 1 (20 Points)Marabatalha McNo ratings yet
- Sinais e Sistemas Oppenheim 2nd Edition Solutions - CompressDocument116 pagesSinais e Sistemas Oppenheim 2nd Edition Solutions - CompressMarabatalha McNo ratings yet
- Efficient Transformers: A SurveyDocument28 pagesEfficient Transformers: A SurveyMarabatalha McNo ratings yet
- Eece359 Midterm 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesEece359 Midterm 1 SolutionsMarabatalha McNo ratings yet
- Partial Parsing Via Finite-State Cascades: Steven AbneyDocument8 pagesPartial Parsing Via Finite-State Cascades: Steven AbneyMarabatalha McNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Introduction To Convolutional Neural Networks: A Case Study For Character RecognitionDocument10 pagesA Comprehensive Introduction To Convolutional Neural Networks: A Case Study For Character RecognitionMarabatalha McNo ratings yet
- LXMERT: Learning Cross-Modality Encoder Representations From TransformersDocument14 pagesLXMERT: Learning Cross-Modality Encoder Representations From TransformersMarabatalha McNo ratings yet
- Direct Power Control of DFIG Wind Turbine Systems Based On An Intelligent Proportional-Integral Sliding Mode ControlDocument16 pagesDirect Power Control of DFIG Wind Turbine Systems Based On An Intelligent Proportional-Integral Sliding Mode ControlMarabatalha McNo ratings yet
- DSP AssignmentDocument8 pagesDSP AssignmentSaruchi AttriNo ratings yet
- Matrices & Determinants WorksheetDocument13 pagesMatrices & Determinants Worksheetdiya jainNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 11 The Laplace Transform Dan TugasDocument18 pagesPertemuan 11 The Laplace Transform Dan TugasMaulana AzrielNo ratings yet
- Daubchies Filter PDFDocument10 pagesDaubchies Filter PDFThrisul KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Fracture Mechanics Prof. K. Ramesh Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocument27 pagesEngineering Fracture Mechanics Prof. K. Ramesh Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology, Madrasferi muhammadNo ratings yet
- Answers To My Algebra 1 HomeworkDocument6 pagesAnswers To My Algebra 1 Homeworkernttprv100% (1)
- GuideDocument117 pagesGuideChristian LapidNo ratings yet
- Airs-Lm Math-8 q2 Module-1Document28 pagesAirs-Lm Math-8 q2 Module-1Karissa Joyce Eslao DiazNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 5: Jay D. Bolano Math TeacherDocument15 pagesMathematics 5: Jay D. Bolano Math TeacherJey VlackNo ratings yet
- Week 8: Chapter 5 Matrix: DR Chan Shiau Wei Email: Phone No: 011-33798215Document26 pagesWeek 8: Chapter 5 Matrix: DR Chan Shiau Wei Email: Phone No: 011-33798215QayyumNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 6 - Quarter 3-KatDocument5 pagesMathematics 6 - Quarter 3-KatKatrena ObisNo ratings yet
- HW3Document9 pagesHW3FunmathNo ratings yet
- 2017 GR 9 MathsDocument1 page2017 GR 9 Mathsrowan chibiNo ratings yet
- RPT Add Maths Form 4 DLP 2021Document20 pagesRPT Add Maths Form 4 DLP 2021Lau Chiew Ing50% (2)
- 189641-Article Text-481518-1-10-20190911Document9 pages189641-Article Text-481518-1-10-20190911AnasthasiaNo ratings yet
- .Activity CombinedDocument30 pages.Activity CombinedTanishaNo ratings yet
- Solucion Sesion01Document13 pagesSolucion Sesion01Enrique Diaz Rubio100% (1)
- Multiple Regression AnalysisDocument41 pagesMultiple Regression AnalysisAmisha PandeyNo ratings yet
- Straight+Line Quick+Revision+in+one+shotDocument42 pagesStraight+Line Quick+Revision+in+one+shotCristiano RonaldoNo ratings yet
- CSEE W3827 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Homework Assignment 1Document11 pagesCSEE W3827 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Homework Assignment 1pauline ondisaNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Theorem of Markov ChainsDocument4 pagesThe Fundamental Theorem of Markov ChainsMichael PearsonNo ratings yet
- Computation of Multipliers: Specify The Survival Column, L (X), and The Cost of Care at Each AgeDocument7 pagesComputation of Multipliers: Specify The Survival Column, L (X), and The Cost of Care at Each AgeJay WhiteNo ratings yet
- Bloch TheoremDocument12 pagesBloch TheoremAhsan MoinNo ratings yet
- Adding and Subtracting PolynomialsDocument6 pagesAdding and Subtracting Polynomialsbowai741No ratings yet
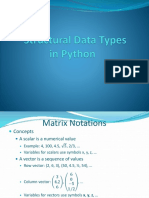
- Lec3 Structural Data Types in PythonDocument46 pagesLec3 Structural Data Types in PythonShanti GroverNo ratings yet
- Probability Distributions.Document47 pagesProbability Distributions.Sarose ThapaNo ratings yet
- PU II Matsh PASSING Questions & Answers 2022 ExamDocument34 pagesPU II Matsh PASSING Questions & Answers 2022 ExamBhai Mamu100% (1)
- 0-1 Knapsack ProblemDocument6 pages0-1 Knapsack ProblemShresthanshu SamantaNo ratings yet