Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Botleafreviewer
Botleafreviewer
Uploaded by
Christine SimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Botleafreviewer
Botleafreviewer
Uploaded by
Christine SimCopyright:
Available Formats
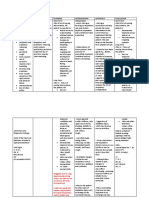
Tissue Location Characteristics Function Monocot Dicot
1. Epidermis upper and lower
surfaces of the
leaf
a single layer of cells (ordinary EPIDERMAL
CELLS and crescent-shaped GUARD CELLS)
from the protoderm
protection from water loss, abrasions, and
entry of fungi and bacteria that cause
diseases
usually non-photosynthetic regulates the exchange of gases- CO2,
H2O, and water vapor that are
outer layer of leaf cells needed/produced by leaves
Upper a single layer of cells containing few or no reponsible for preventing water loss by with upper no
epidermis chloroplasts. evaporation (through cutin) bulliform cells bulliform
cells
The cells stomata
quite transparent (dumbell
shaped) without
permit most of the light that strikes stomata
them to pass through to the
underlying cells.
cutin is present in the upper epidermis
cutin the upper
surface of a leaf
a waxy, waterproof cuticle serves to reduce water loss from the leaf.
Lower Reason: most of the stomata (thousands per square allow gases to enter and leave the leaf as a stomata with
epidermis stomata- centimeter) are located in the lower result of photosynthesis and respiration; (dumbell stomata
protected from epidermis, surrounded by two guard transpiration shaped) (kidney
the highest cells/stomata shaped)
temp. Function of stomata: allows CO2 to enter
accumulate less the leaf --> photosynthesis-->
dust and fewer carbohydrates--> water vapor and O2
fungal spores *O2 may exit/enter the leaf depending on
the time of day
Inversely proportional to the opening of
stomata:
high temp and winds
High concentration of CO2 (signal
the plant that sufficient CO2 is
available)
Mechanics of Guard cells and stomata:
A. water--> guard cells--> guard cells swell
& curve due to cellulose on cell wall--->
stomata opens
B. guard cells lose water--> stomata closes
2.
Collenchyma
mesophyll of the
leaf section;
occur in
occur in aggregates
possess thicker primary cell walls than
The main function:
to provide additional support to the
plant, especially in areas of
aggregates just parenchyma cells.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- ECG For InternsDocument31 pagesECG For InternsAgus SyaifudinNo ratings yet
- CPRDocument13 pagesCPRMeenu Dogra100% (1)
- Ib Biology Topic 9 - Plant Biology HL Revision Sheet: © David Faure, InthinkingDocument1 pageIb Biology Topic 9 - Plant Biology HL Revision Sheet: © David Faure, InthinkingMarwan PharaonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Applications of Induced Hypothermia: Mark Luscombe John C AndrzejowskiDocument5 pagesClinical Applications of Induced Hypothermia: Mark Luscombe John C AndrzejowskiSajid NadafNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Independent: Short TermDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Independent: Short TermMarlo Dañez NorbeNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Lily ModifiedDocument57 pagesHeart Failure Lily ModifiedSabila FatimahNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Kerja Obat Anestesi Lokal: Ratno Samodro, Doso Sutiyono, Hari Hendriarto SatotoDocument14 pagesMekanisme Kerja Obat Anestesi Lokal: Ratno Samodro, Doso Sutiyono, Hari Hendriarto Satotoumar sahidNo ratings yet
- 100 Slides McqsDocument102 pages100 Slides McqsUmair tahir khanNo ratings yet
- Breathing During PregnancyDocument2 pagesBreathing During PregnancyHandita RatriNo ratings yet
- SynapseDocument7 pagesSynapseNadzierah RazakNo ratings yet
- S9LT Ig J 31 Activity Sheets 1Document8 pagesS9LT Ig J 31 Activity Sheets 1Benedict BacaniNo ratings yet
- Hyperbil ABO IncompDocument9 pagesHyperbil ABO IncompAyen FornollesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Critical Care Nursing 6th Edition Sole Test BankDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Critical Care Nursing 6th Edition Sole Test Bankgabrielnt3me100% (15)
- Endo & Exogenous Pacemakersin Biological RhythmsDocument2 pagesEndo & Exogenous Pacemakersin Biological RhythmsMiss_M90No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Questions - LippincotDocument3 pagesCardiovascular Questions - LippincotRammy KhanNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Saraf OtonomDocument32 pagesFisiologi Saraf OtonomNiaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ResonanceDocument72 pagesNervous System ResonanceEkta ManglaniNo ratings yet
- Types of Hypertrophy ProgramsDocument2 pagesTypes of Hypertrophy Programsok okNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 3, Cardiovascular Sys.Document3 pagesActivity No. 3, Cardiovascular Sys.Mariel CaylanNo ratings yet
- The Language of MedicineDocument9 pagesThe Language of MedicineErnesto SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Assessing General Status Vital Signs 1Document20 pagesAssessing General Status Vital Signs 1Geylla FaeldoniaNo ratings yet
- 7-Moto Renal - MCQsDocument62 pages7-Moto Renal - MCQspvs5155No ratings yet
- Biruh T Workeneh Hyponatremia Demystified IntegratingDocument17 pagesBiruh T Workeneh Hyponatremia Demystified IntegratingsaqqarazoserNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular JunctionDocument6 pagesNeuromuscular Junctiondrahmed1028No ratings yet
- Physiological Changes in Pregnancy 1209300529108168 8Document36 pagesPhysiological Changes in Pregnancy 1209300529108168 8fariz_maulana88_9890No ratings yet
- STEMi Reading MaterialDocument14 pagesSTEMi Reading MaterialJerry GohNo ratings yet
- WameedMUCLecture 2021 9260965Document5 pagesWameedMUCLecture 2021 9260965Mubarak Abubakar yaroNo ratings yet
- How To Interpret BGADocument24 pagesHow To Interpret BGASondang Herikson PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- 12D G3 Research-ProjectDocument125 pages12D G3 Research-ProjectGERONES, Christian Mark B.No ratings yet
- b9 Respiration Mark SchemeDocument15 pagesb9 Respiration Mark SchemeAreebah9No ratings yet