Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supraventricular Tachycardia: Birmingham Children's Hospital ED Handbook Version 1 (2011)
Uploaded by
madimadi11Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Supraventricular Tachycardia: Birmingham Children's Hospital ED Handbook Version 1 (2011)
Uploaded by
madimadi11Copyright:
Available Formats
Birmingham Children’s Hospital ED Handbook Version 1 (2011)
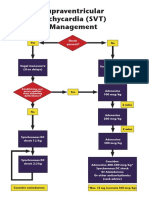
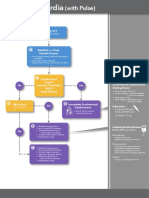
(1.6) SUPRAVENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA
Characteristics of SVT (as compared with sinus tachycardia) Vagal manoeuvres
220 bpm in infants (> 180 bpm in older children). Diving reflex (face immersed in
Negative P waves in II, III, aVF. iced water for 5 secs or ice in
glove applied to face)
No beat-to-beat variability.
1-sided carotid sinus manage
Abrupt termination.
Valsalva manoeuvre (e.g. blowing
Less likely to have a history consistent with shock. plunger out of a 50 ml syringe)
MANAGEMENT OF SUPRAVENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SVT)
YES Shock NO
present?
Vagal manoeuvre
Vagal manoeuvre
If no delays
Vascular YES Adenosine 100 mcg/kg
access quicker
than setting up with rapid saline flush
defibrillator?
2 mins
NO
Adenosine 200 mcg/kg
with rapid saline flush
Synchronous DC
shock 1 J/kg
2 mins
Adenosine 300 mcg/kg
with rapid saline flush
Synchronous DC
shock 2 J/kg
Consider:
Adenosine 400 – 500 mcg/kg
Max dose 12 mg
Consider
Neonates: max 300 mcg/kg
amiodarone
Synchronous DC shock
Amiodarone or other antiarrhythmic
(discuss with cardiology)
Reference
APLS The Practical Approach (5th Edition)
You might also like
- Algorithms - SVT PDFDocument1 pageAlgorithms - SVT PDFjhontarroNo ratings yet
- Bradycardia: Birmingham Children's Hospital ED Handbook Version 1 (2011)Document1 pageBradycardia: Birmingham Children's Hospital ED Handbook Version 1 (2011)madimadi11No ratings yet
- Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument1 pageTachycardia AlgorithmGideon BahuleNo ratings yet
- Adult CardDocument1 pageAdult CardIvan MoralesNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia (With Pulse) AlgorithmDocument1 pageAdult Tachycardia (With Pulse) AlgorithmJames ChoiNo ratings yet
- VT Ventricular TachyDocument1 pageVT Ventricular Tachymadimadi11No ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms Adult 2010Document12 pagesACLS Algorithms Adult 2010anon_336736395No ratings yet
- 26) Approach To Pediatric ArrhythmiasDocument44 pages26) Approach To Pediatric ArrhythmiasJude AlyousefNo ratings yet
- DC Shock: DR Buyung Span DR Ruddi SpanDocument12 pagesDC Shock: DR Buyung Span DR Ruddi SpantebehidayatullahNo ratings yet
- With A Pulse and Poor Perfusion: Pediatric TachycardiaDocument1 pageWith A Pulse and Poor Perfusion: Pediatric TachycardiaIin-Ignasia Diahayujulindah Mujiman0% (1)
- Acls Algorithms 2012Document12 pagesAcls Algorithms 2012kivuNo ratings yet
- Succunylcholine (Anectine) : University of San Carlos College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument1 pageSuccunylcholine (Anectine) : University of San Carlos College of Nursing Drug StudyFederico AndalesNo ratings yet
- Peri-Arrest ArrythmiaDocument14 pagesPeri-Arrest Arrythmiamohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Medication Administration PolicyDocument76 pagesMedication Administration PolicyJully GaciasNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Algorithm-2015 UpdateDocument2 pagesPediatric Cardiac Arrest Algorithm-2015 UpdateKholida UlfaNo ratings yet
- ER Clinical NotesDocument23 pagesER Clinical NotesmngaNo ratings yet
- VF & Pulseless VTDocument1 pageVF & Pulseless VTmadimadi11No ratings yet
- RCH - Peds Emergency Reference Card - Jan 2013Document2 pagesRCH - Peds Emergency Reference Card - Jan 2013Bob YongNo ratings yet
- AdultTachycardiaWithPulse AlgorithmDocument1 pageAdultTachycardiaWithPulse AlgorithmIsmail SlimNo ratings yet
- Ward 2005Document19 pagesWard 2005Emilio Emmanué Escobar CruzNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Supraventricular Tachycardia: in ChildrenDocument7 pagesManagement of Acute Supraventricular Tachycardia: in ChildrenRahmah LatifahNo ratings yet
- Most Common Medication - in Emergency RoomDocument24 pagesMost Common Medication - in Emergency RoomFerdos AdemNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ORDocument3 pagesDrug Study ORIvan Jules P. PALMARESNo ratings yet
- PICU Drug Boluses: Drug Dose /KG Range Administration NotesDocument5 pagesPICU Drug Boluses: Drug Dose /KG Range Administration NotesMaria BudnicNo ratings yet
- Common Goat Medications and "Easy To Understand" Dosages: WormersDocument2 pagesCommon Goat Medications and "Easy To Understand" Dosages: WormersCrosley NasmNo ratings yet
- AclsDocument1 pageAclsJoice DasNo ratings yet
- Pharma Drug StudyDocument56 pagesPharma Drug StudyGrace Pikit Bacsan100% (1)
- Acls Patient Algorithms: Greg Cook's Version of A Phoenix Fire DPT ClasicDocument4 pagesAcls Patient Algorithms: Greg Cook's Version of A Phoenix Fire DPT ClasicDouglas Greg CookNo ratings yet
- Farmacos Reanimacion PediatricaDocument1 pageFarmacos Reanimacion PediatricaMiriam C. F. TapiaNo ratings yet
- Tachycardia Algorithm 2021Document1 pageTachycardia Algorithm 2021Ravin DebieNo ratings yet
- 2019 Practice of Anesthesia For Infants and ChildrenDocument2 pages2019 Practice of Anesthesia For Infants and ChildrenJavier GlezqNo ratings yet
- ACLS Drug Therapy RevisedDocument4 pagesACLS Drug Therapy RevisedpaveethrahNo ratings yet
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFibbs91No ratings yet
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFPlabber JuneNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument28 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- DIGOXIN DRUG STUDYDocument2 pagesDIGOXIN DRUG STUDYVanessa EgaoNo ratings yet
- Acls Algorithms 2012Document12 pagesAcls Algorithms 2012Prashanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action Indication Adverse Effect Age and Administration Adrenaline (Epinephrine)Document7 pagesDrug Classification Action Indication Adverse Effect Age and Administration Adrenaline (Epinephrine)Danica LachicaNo ratings yet
- Muscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorDocument26 pagesMuscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorCess Lagera Ybanez88% (16)
- IM On Call (LANGE On Call) PDFDocument738 pagesIM On Call (LANGE On Call) PDFindia2puppy100% (8)
- Drug AnalysisDocument9 pagesDrug AnalysisKyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- Drug DictonaryDocument3 pagesDrug DictonaryDattatreyaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal symptoms guideDocument1 pageGastrointestinal symptoms guideCHIEF DOCTOR MUTHUNo ratings yet
- ICE DrugsDocument2 pagesICE DrugsRichelle FrondaNo ratings yet
- 3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates CombinedDocument5 pages3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates Combinedamanrup randhawa100% (1)
- Drug Study OverviewDocument26 pagesDrug Study Overviewrn msnNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest Circular AlgorhythmDocument4 pagesCardiac Arrest Circular AlgorhythmAisyah Nur KarimahNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithm GuideDocument1 pageACLS Algorithm GuideAhmed AlkhaqaniNo ratings yet
- Atropine, Glycopyrrolate and Hyoscine comparison for anticholinergic effectsDocument2 pagesAtropine, Glycopyrrolate and Hyoscine comparison for anticholinergic effectsDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- PSMMC IV GUIDE LINES - Copy6Document18 pagesPSMMC IV GUIDE LINES - Copy6NhcpsNo ratings yet
- DKA Guideline: Diagnosis and ManagementDocument4 pagesDKA Guideline: Diagnosis and ManagementHassen Kavi IsseNo ratings yet
- EMD-MNH Clinical Protocal-12 March 2014Document14 pagesEMD-MNH Clinical Protocal-12 March 2014tgrrwccj98No ratings yet
- I. Definitions: Management of Hyperkalemia in AdultsDocument2 pagesI. Definitions: Management of Hyperkalemia in AdultsUpitFlowNo ratings yet
- Resus Edited 140921Document15 pagesResus Edited 140921adilah fazliNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Bradycardia With A Pulse and Poor Perfusion AlgorithmDocument1 pagePediatric Bradycardia With A Pulse and Poor Perfusion AlgorithmRadhiatul MardhiahNo ratings yet
- Inotropes and vasoactive drugs in the PICUDocument2 pagesInotropes and vasoactive drugs in the PICULynda TsaiNo ratings yet
- Fellow in Dermatology JD - No Out of HoursDocument8 pagesFellow in Dermatology JD - No Out of Hoursmadimadi11No ratings yet
- Preventing Neonatal InfectionsDocument27 pagesPreventing Neonatal Infectionsmadimadi11No ratings yet
- Use of Oral Sucrose 08Document16 pagesUse of Oral Sucrose 08madimadi11No ratings yet
- Aseptic Technique Checklist CompDocument2 pagesAseptic Technique Checklist Compmadimadi11100% (1)
- Pae PutiDocument3 pagesPae Putimadimadi11No ratings yet
- Loc PostDocument1 pageLoc PostByank ScinteieNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection PIAG 84Document3 pagesUrinary Tract Infection PIAG 84madimadi11No ratings yet
- Candidati Ex SpecialistDocument42 pagesCandidati Ex Specialistmadimadi11No ratings yet
- Prescribing On The Neonatal Unit Feb2010Document54 pagesPrescribing On The Neonatal Unit Feb2010madimadi11No ratings yet
- Cranial Ultrasound Scan Competency PackageDocument2 pagesCranial Ultrasound Scan Competency Packagemadimadi11No ratings yet
- SelfDirectedLearning CUSScan On NICUDocument43 pagesSelfDirectedLearning CUSScan On NICUmadimadi11No ratings yet
- Infant Feeding Learning PackageDocument70 pagesInfant Feeding Learning Packagemadimadi11No ratings yet
- PN SelfDirected Learning Package July 2011Document34 pagesPN SelfDirected Learning Package July 2011madimadi11No ratings yet
- CFM Learning Package 2009Document33 pagesCFM Learning Package 2009madimadi11No ratings yet
- CFAM Competency Doc Feb 2010Document1 pageCFAM Competency Doc Feb 2010madimadi11No ratings yet
- Brief Guide To Developmental CareDocument5 pagesBrief Guide To Developmental Caremadimadi11No ratings yet
- Nitric Oxide Competency Document Feb 2010Document2 pagesNitric Oxide Competency Document Feb 2010madimadi11No ratings yet
- Competency Statement NEO PUFFDocument2 pagesCompetency Statement NEO PUFFmadimadi11No ratings yet
- Stephanie Competency Document Feb 2010Document1 pageStephanie Competency Document Feb 2010madimadi11No ratings yet
- Index To Self Directed Learning PackagesDocument2 pagesIndex To Self Directed Learning Packagesmadimadi11No ratings yet
- Reluctant Feeder GuidelineDocument5 pagesReluctant Feeder Guidelinemadimadi11No ratings yet
- Competency Statement NEO PUFF - ANSWERS-1Document2 pagesCompetency Statement NEO PUFF - ANSWERS-1madimadi11No ratings yet
- Infant Feeding CompetencyDocument2 pagesInfant Feeding Competencymadimadi11No ratings yet
- CFAM Competency Doc Feb 2010Document1 pageCFAM Competency Doc Feb 2010madimadi11No ratings yet
- BCG Vaccination Aug 08Document25 pagesBCG Vaccination Aug 08madimadi11No ratings yet
- Aseptic Technique Checklist CompDocument2 pagesAseptic Technique Checklist Compmadimadi11100% (1)
- Cranial Ultrasound Scan Competency PackageDocument2 pagesCranial Ultrasound Scan Competency Packagemadimadi11No ratings yet
- Infant Flow Si-PAP Competency Document Feb 2010Document1 pageInfant Flow Si-PAP Competency Document Feb 2010madimadi11No ratings yet
- QMC Notes Teaching Package Aug08Document22 pagesQMC Notes Teaching Package Aug08madimadi11No ratings yet
- TB Rates by Rate and by CountryDocument10 pagesTB Rates by Rate and by Countrymadimadi11No ratings yet
- SIP Debugging Commands Overview - Cisco CommunityDocument5 pagesSIP Debugging Commands Overview - Cisco CommunitysenthilNo ratings yet
- A 268 - A 268M - 01 Qti2oc0wmq - PDFDocument6 pagesA 268 - A 268M - 01 Qti2oc0wmq - PDFMan98No ratings yet
- NS2-DVN-2540.Rev4 - Profomal Packing List BLR Piping Hanger Support Beam-Unit 2 - 20200710Document27 pagesNS2-DVN-2540.Rev4 - Profomal Packing List BLR Piping Hanger Support Beam-Unit 2 - 20200710PHAM PHI HUNGNo ratings yet
- Children Literature Evaluation Form I Aint Gonna Paint No MoreDocument4 pagesChildren Literature Evaluation Form I Aint Gonna Paint No Moreapi-548506674No ratings yet
- Dunhill The Old WindmillDocument2 pagesDunhill The Old WindmillMaría Hernández MiraveteNo ratings yet
- Alien Bestiary PDFDocument450 pagesAlien Bestiary PDFDũng Lê100% (13)
- The Macquarie Australian Slang DictionarDocument7 pagesThe Macquarie Australian Slang DictionarnetshidoNo ratings yet
- Syeda Qirtas Zehra 14948 ObcDocument20 pagesSyeda Qirtas Zehra 14948 ObcSyeda ZehraNo ratings yet
- Fire Master Mirine PlusDocument3 pagesFire Master Mirine PlusCarlos BarriosNo ratings yet
- ECON 211: Principles of Macroeconomics-901: Smhussain@vcu - EduDocument6 pagesECON 211: Principles of Macroeconomics-901: Smhussain@vcu - EdusshinnNo ratings yet
- Department of Labor: BC Bond ListDocument67 pagesDepartment of Labor: BC Bond ListUSA_DepartmentOfLabor100% (1)
- Polyethylene PolyamineDocument6 pagesPolyethylene PolyamineAV kayanNo ratings yet
- UNDERGROUND MINE DESIGN & PLANNING PROCESSDocument59 pagesUNDERGROUND MINE DESIGN & PLANNING PROCESSRahat fahimNo ratings yet
- HLTARO001 HLTAROO05 Student Assessment Booklet 1 1Document68 pagesHLTARO001 HLTAROO05 Student Assessment Booklet 1 1Amber PreetNo ratings yet
- Math 2 MakilingDocument28 pagesMath 2 MakilingAnnabelle Poniente HertezNo ratings yet
- Service Manual for OPT 70 EC 02 Operating TableDocument36 pagesService Manual for OPT 70 EC 02 Operating TableTEYLER BARBOZANo ratings yet
- Dharmakirti On Pratyaksa PDFDocument14 pagesDharmakirti On Pratyaksa PDFonlineyyk100% (1)
- Review Problems Chapter 6Document8 pagesReview Problems Chapter 6Yue FeiNo ratings yet
- Airport Lounges Industry-Report-Frost-SullivanDocument112 pagesAirport Lounges Industry-Report-Frost-SullivansandeepNo ratings yet
- Patchu Time Management and Its Relation To The Working StudentsDocument17 pagesPatchu Time Management and Its Relation To The Working StudentsGui De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Extracurricular Activities On The Academic Performance of Student AthletesDocument3 pagesImpacts of Extracurricular Activities On The Academic Performance of Student AthletesKarlo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Data Science BooksDocument11 pagesData Science BooksAnalytics Insight100% (1)
- Henry's Bench: Keyes Ky-040 Arduino Rotary Encoder User ManualDocument4 pagesHenry's Bench: Keyes Ky-040 Arduino Rotary Encoder User ManualIsrael ZavalaNo ratings yet
- Management From RamayanaDocument14 pagesManagement From Ramayanasaaket batchuNo ratings yet
- How To Plant Thoughts in Her Mind Ross Jeffries: TranscriptDocument12 pagesHow To Plant Thoughts in Her Mind Ross Jeffries: TranscriptAlcajNo ratings yet
- 1250kva DG SetDocument61 pages1250kva DG SetAnagha Deb100% (1)
- Retail ImageDocument76 pagesRetail ImageayushiNo ratings yet
- Major06 QP DLP NEET2019 (Pmtcorner - In) PDFDocument40 pagesMajor06 QP DLP NEET2019 (Pmtcorner - In) PDFMegha HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Manner, Matter, and MethodDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Manner, Matter, and MethodRIVALDO MALAWATNo ratings yet
- PPSDM GEOMINERBA Geotechnical Investigation ReportDocument35 pagesPPSDM GEOMINERBA Geotechnical Investigation ReportMiftahul JannaNo ratings yet